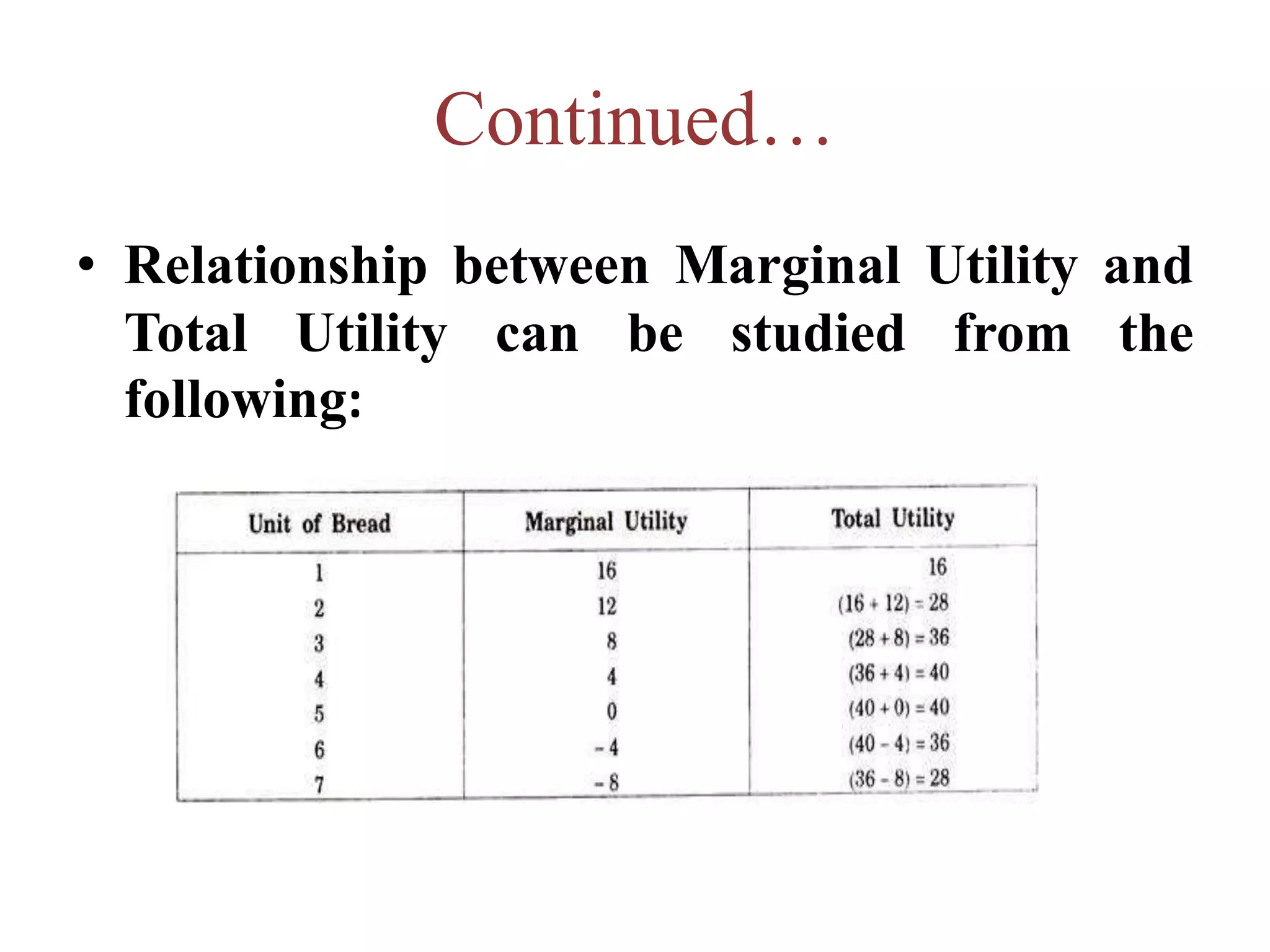
This document discusses the concept of utility in economics. It defines utility as the capacity of a good or service to satisfy human wants. The document outlines several key characteristics of utility, including that it is psychological, individual, relative, and cannot be objectively measured. It also discusses different types of utility related to production and consumption, including form utility, place utility, time utility, service utility, marginal utility, total utility, and average utility. The relationship between marginal utility and total utility is explored, noting that total utility is maximized when marginal utility reaches zero.