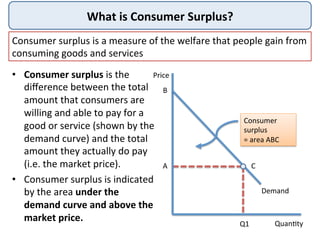
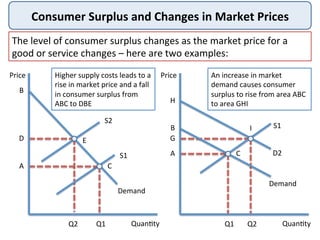
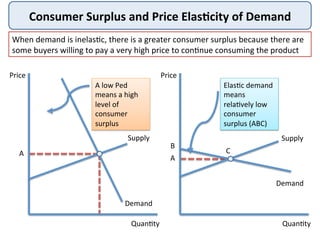
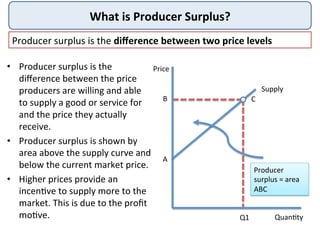
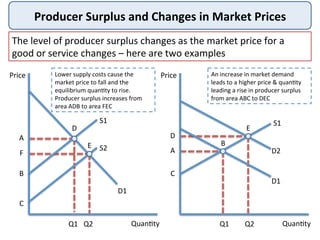
This document defines and provides examples of consumer surplus and producer surplus. Consumer surplus is the difference between what consumers are willing to pay for a good and what they actually pay, represented by the area under the demand curve. Producer surplus is the difference between the price producers are willing to supply a good for and the actual market price, shown as the area above the supply curve. The levels of consumer and producer surplus change with market price fluctuations. At equilibrium, consumer surplus is the area under the demand curve above the market price, while producer surplus is the area above the supply curve below the market price.