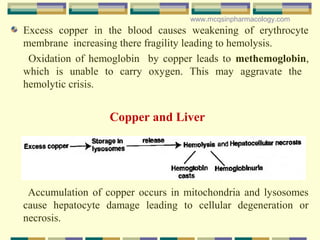
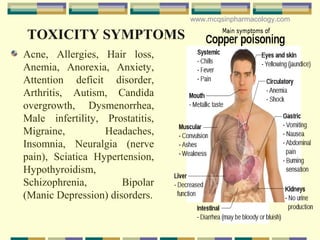
Copper is an essential metal that has been used by humans for thousands of years. It plays important roles in the body as a component of enzymes and as a conductor of electricity. However, excess copper can be toxic and is absorbed through various sources like industrial work, supplements, and cookware. Symptoms of copper toxicity include acne, headaches, and neurological or psychological issues. Diagnosis involves tests of copper levels in blood, liver, or hair. Chelation therapies can help remove excess copper from the body. Genetic disorders also exist that impact copper metabolism.