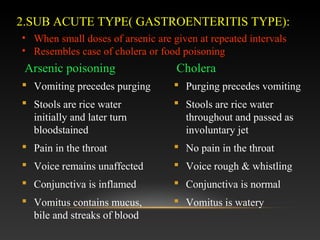
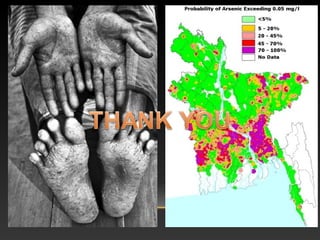
This document discusses arsenic poisoning. It describes arsenic as a heavy metallic inorganic irritant poison, with inorganic arsenic compounds being poisonous. Arsenic acts by binding to sulfhydryl groups in enzymes and replacing phosphorus in bones. Signs and symptoms of arsenic poisoning include acute fulminating poisoning with shock and death, subacute gastroenteritis-like poisoning, and chronic poisoning causing skin pigmentation, nail changes, and neuritis. Treatment involves gastric lavage, chelating agents like BAL, DMSA, and penicillamine. Arsenic poisoning was historically used for homicide due to its low cost and difficulty detecting symptoms.