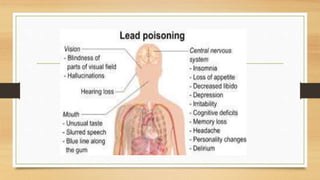
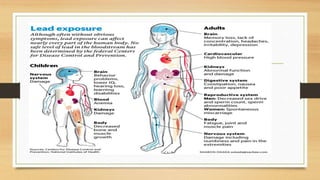
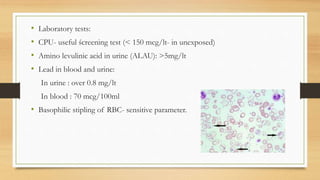
Lead poisoning is a serious medical condition caused by elevated levels of lead in the body, primarily due to industrial exposure, contaminated soil, and lead-containing products. It affects various organs and can cause a range of symptoms from abdominal pain to neurological issues, with children under six being particularly vulnerable. Preventive measures include substitution of lead products, proper ventilation, and health education, while treatment involves removing lead sources and using chelation therapy for severe cases.