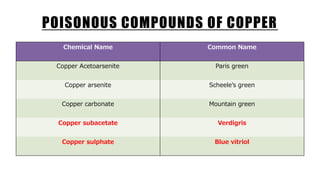
Copper poisoning occurs due to toxic copper salts, leading to symptoms like metallic taste, nausea, vomiting, and severe complications such as renal failure and death. Treatment includes stomach washing and chelation therapy, with postmortem changes showing greenish-blue stains and affected organs. Chronic exposure can result in conditions like Wilson's disease and is often accidental, as copper salts are rarely used for intentional harm.