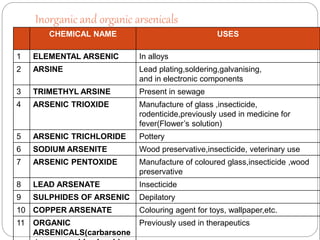
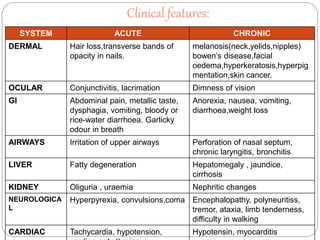
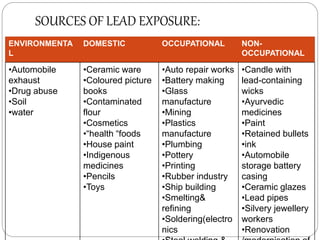
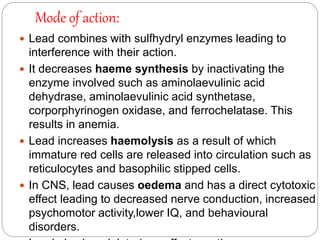
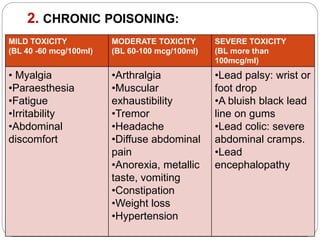
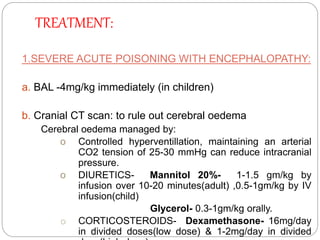
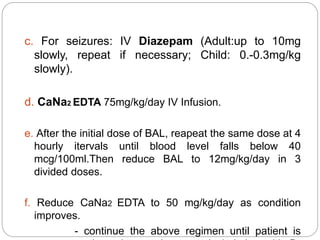
This document summarizes information on arsenic and lead poisoning. It discusses the sources, physical properties, uses, and toxic effects of arsenic and lead. For both poisons, it describes the absorption, distribution, and mechanisms of toxicity. The clinical manifestations of acute and chronic poisoning are outlined for each element. Diagnosis involves measuring levels in blood and urine. Treatment of arsenic poisoning involves chelation therapy with BAL, penicillamine or DMSA. For severe lead poisoning, chelation with CaNa2EDTA or BAL is recommended along with supportive care. Mild to moderate lead poisoning is treated with oral chelation agents like D-penicillamine.