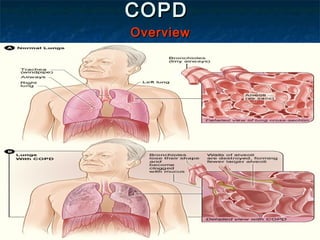
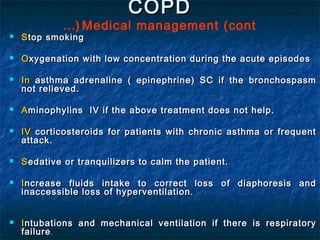
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease characterized by difficulty breathing. It is caused by long-term exposure to irritating gases and particulate matter, primarily from cigarette smoking. Symptoms include a productive cough, breathlessness, and chest infections. The disease is diagnosed through pulmonary function tests and imaging. Treatment focuses on reducing symptoms through bronchodilators and antibiotics for infections. Nursing care involves assessing symptoms, monitoring diagnostic tests, and teaching patients about prevention, treatment, and managing exacerbations.