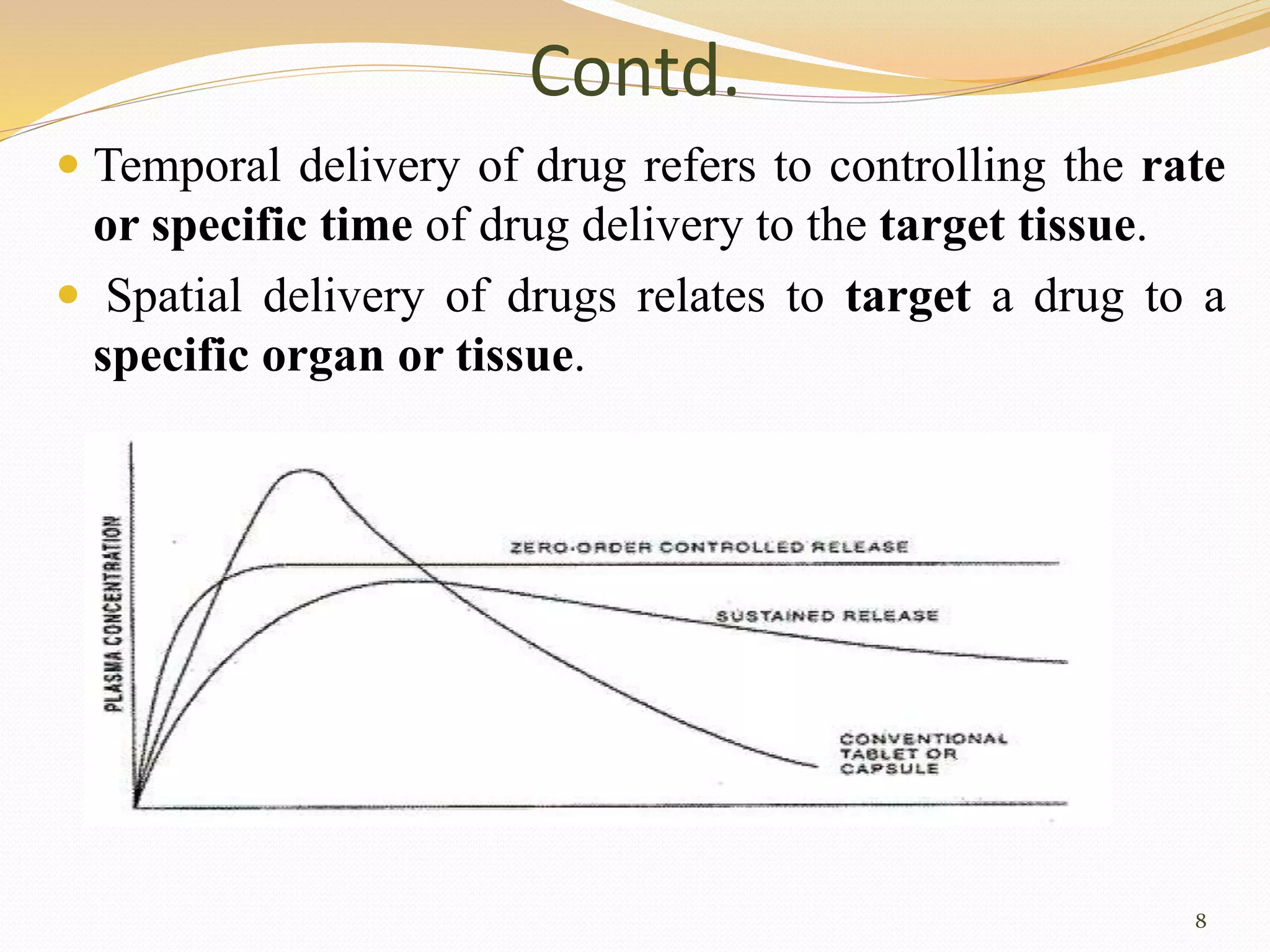
This document discusses modified release drug delivery systems (MRDDS), including extended release, delayed release, and targeted release dosage forms. It defines MRDDS as systems that control the time and location of drug release to accomplish therapeutic objectives. The document outlines the rationale for controlled drug delivery systems (CDDS), their advantages and disadvantages, criteria for selecting drug candidates, and important physiological and biological properties to consider for CDDS.