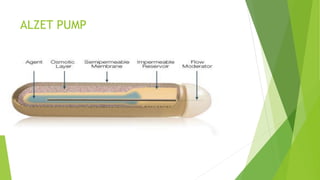
This document discusses osmotic drug delivery systems, specifically ALZET pumps. It begins by defining osmosis and osmotic pressure, and explaining how these principles are used in osmotic drug delivery. The basic components of osmotic drug delivery systems are then outlined, including the drug, semipermeable membrane, osmogens, and coatings. ALZET pumps are introduced as implantable osmotic pumps used in laboratory animals. Factors that affect drug release from these systems include drug solubility, osmotic pressure, delivery orifice size, and membrane properties. Evaluation methods and advantages like zero-order release and long duration of action are also summarized.