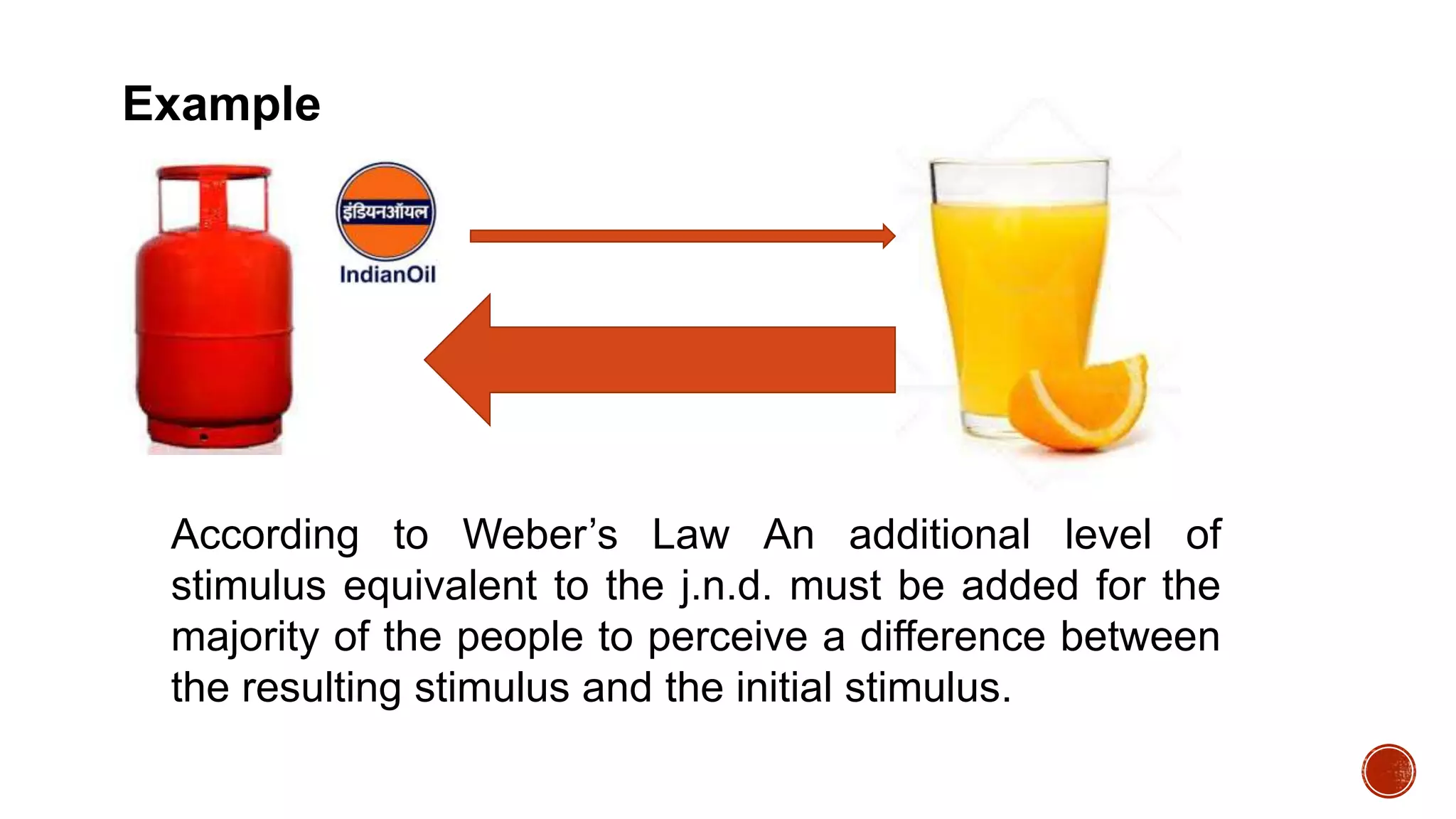
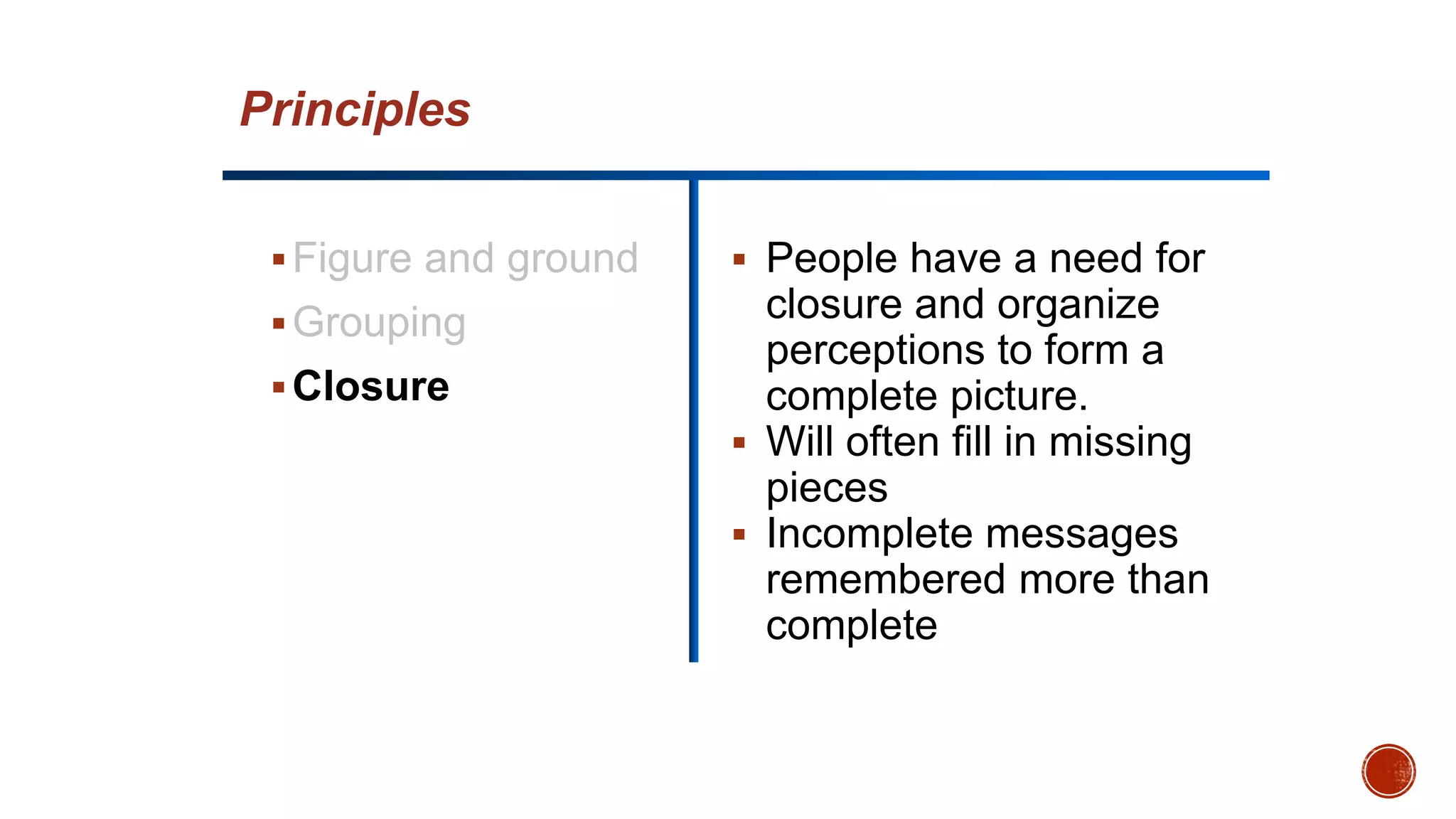
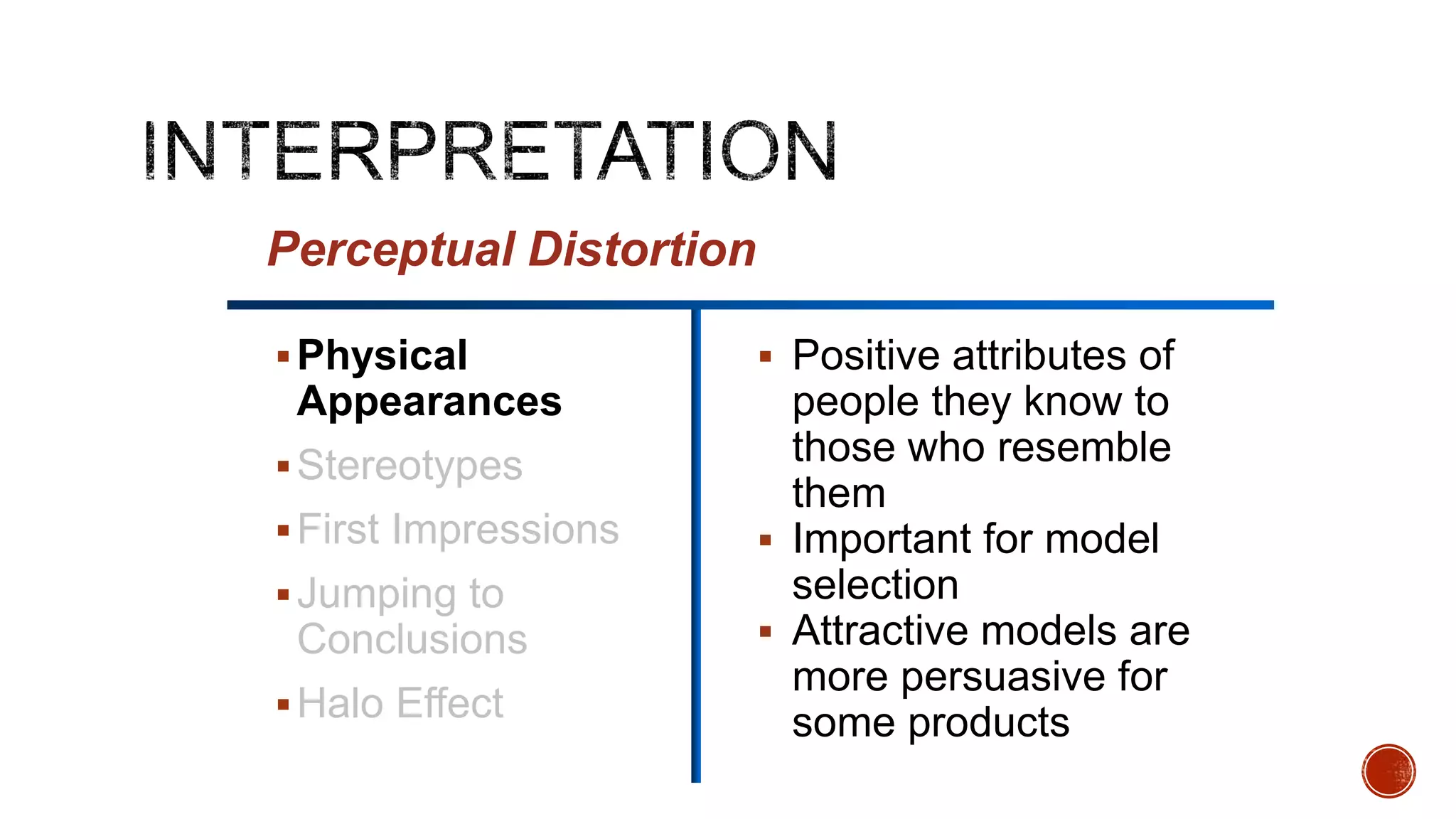
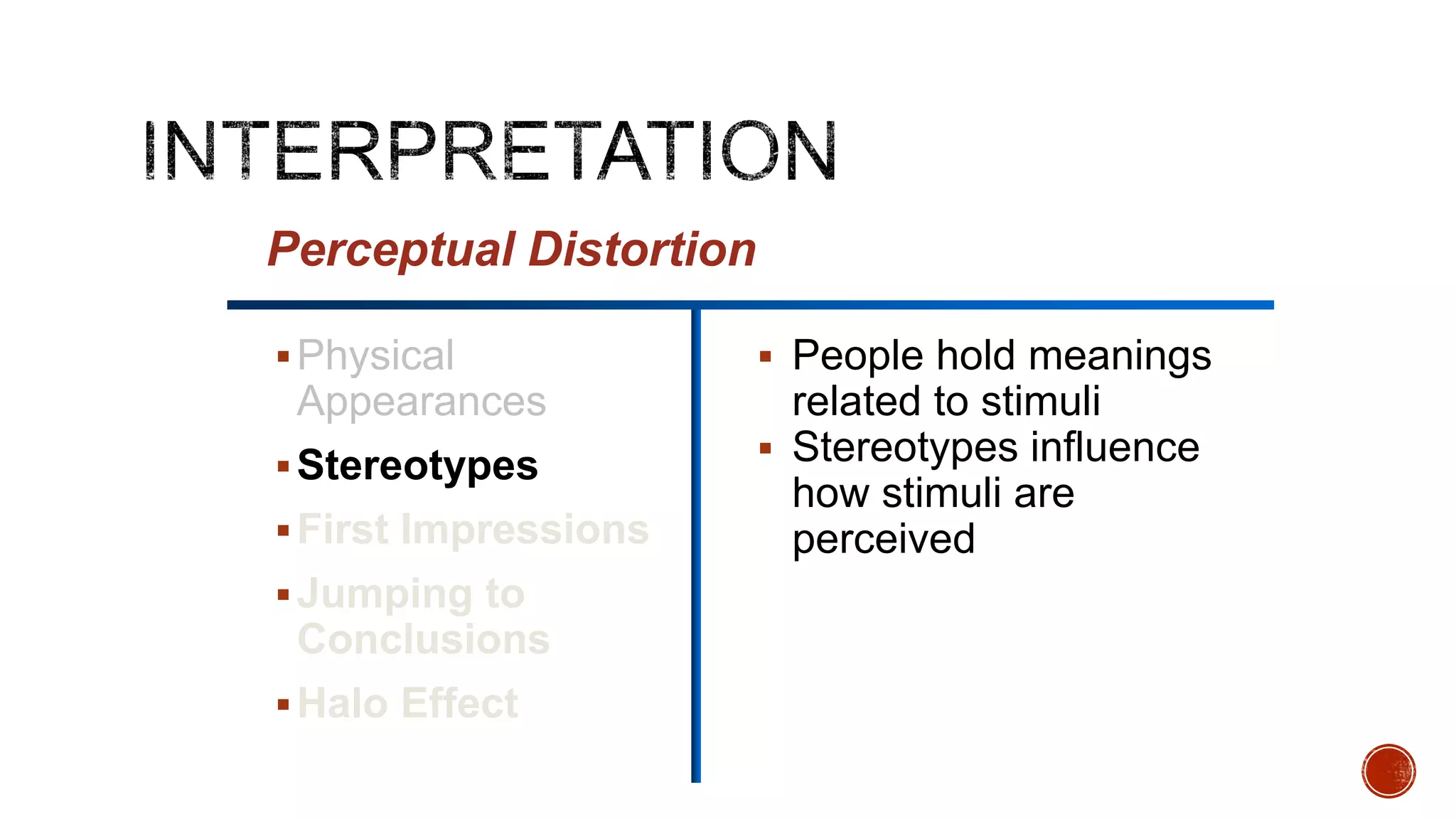
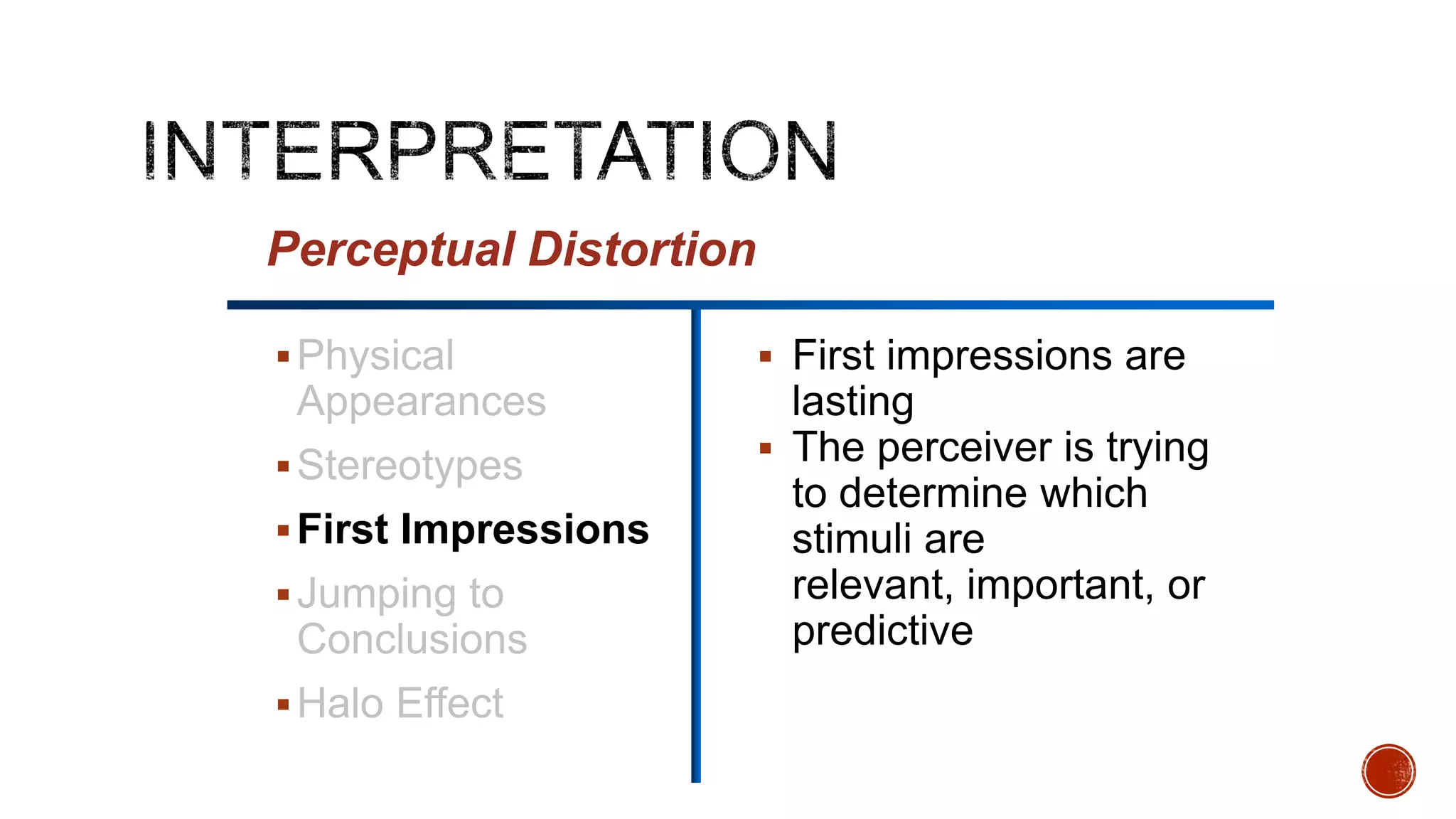
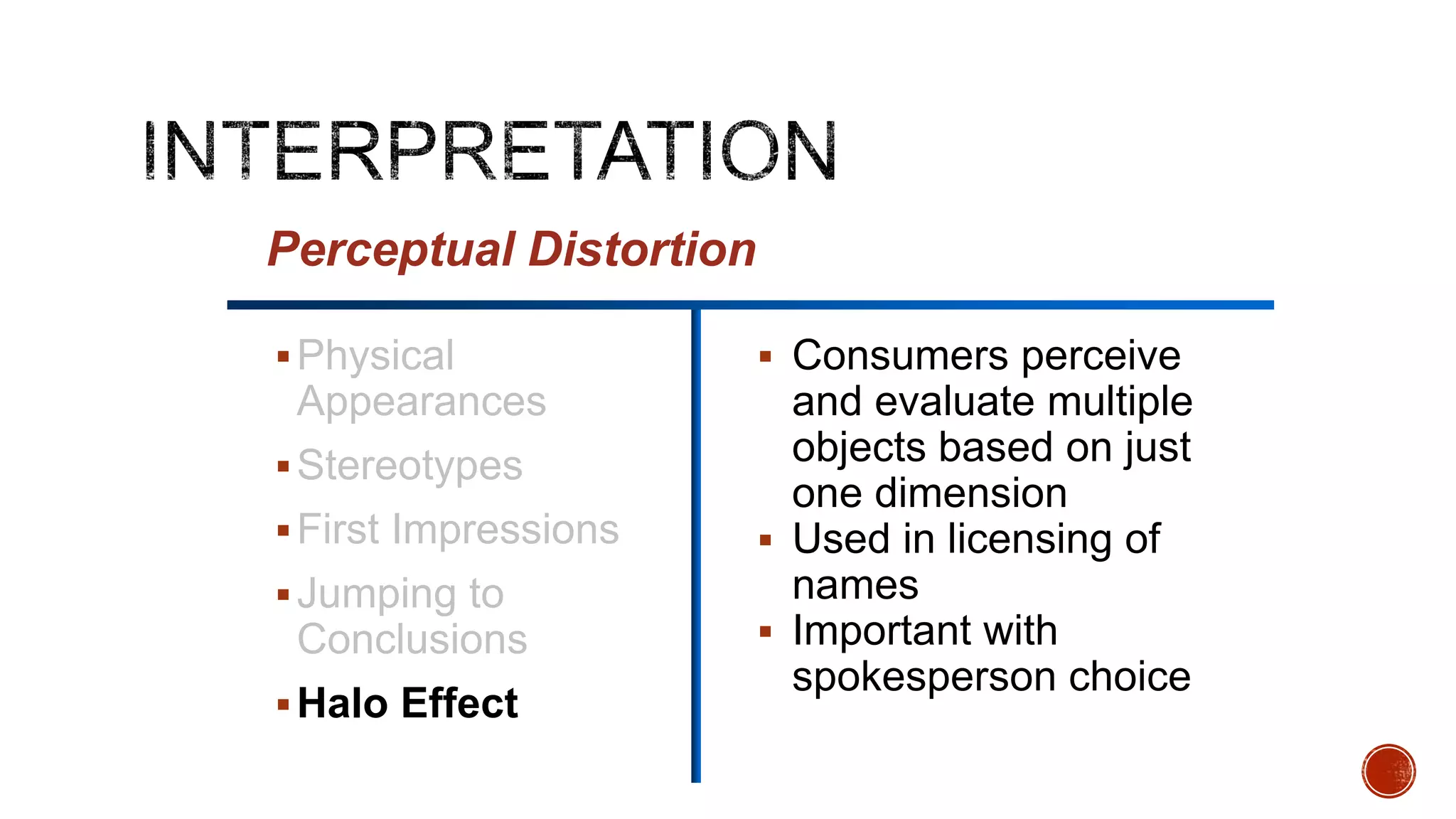
This document discusses perception and its elements. Perception is described as how people interpret sensory impressions to form a view of the world. It is based on incomplete information but guides behavior. Perception in marketing refers to how consumers identify, organize, and interpret information to create meaning. The elements of perception discussed include sensation, absolute and differential thresholds, and subliminal perception.