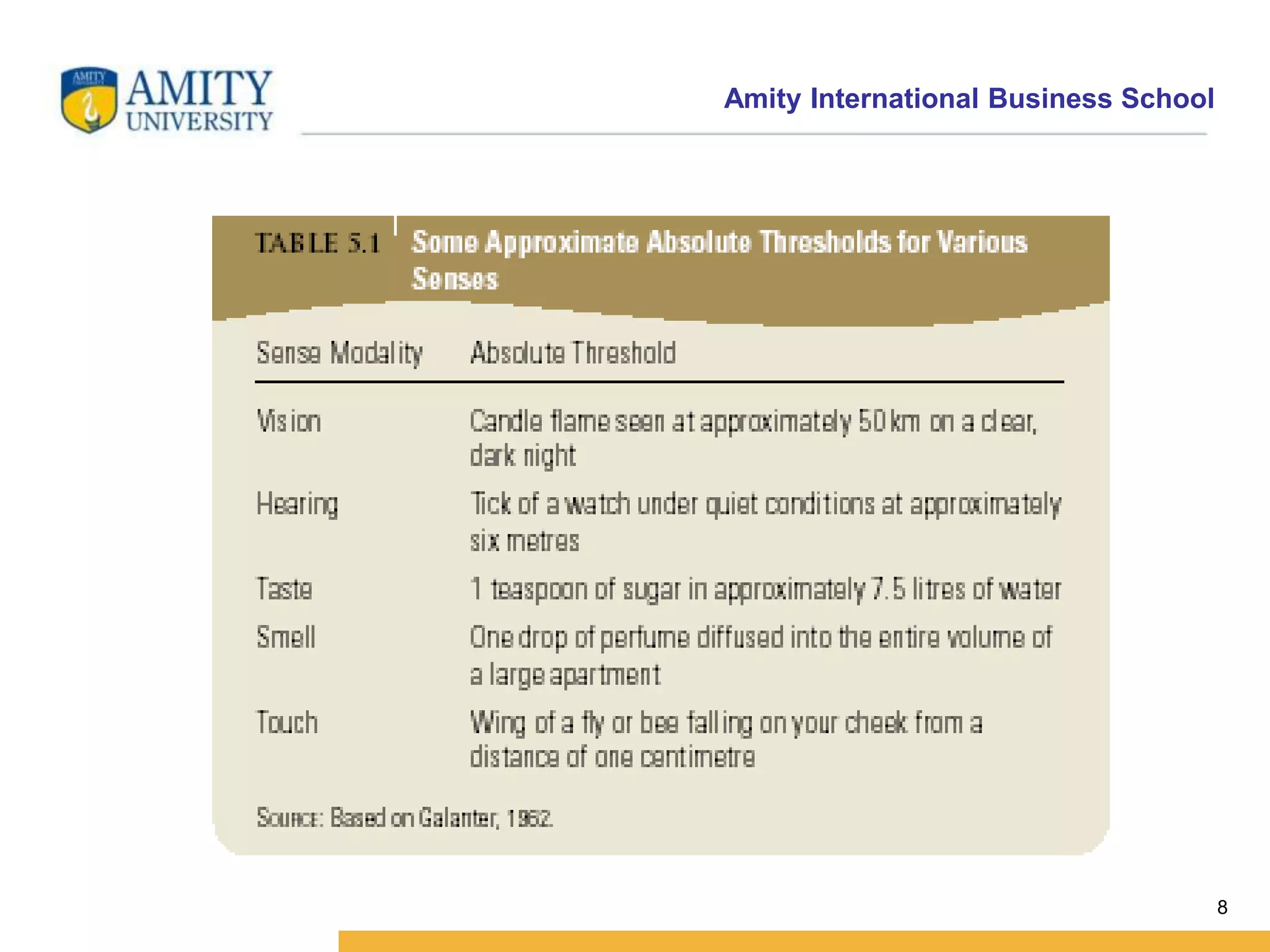
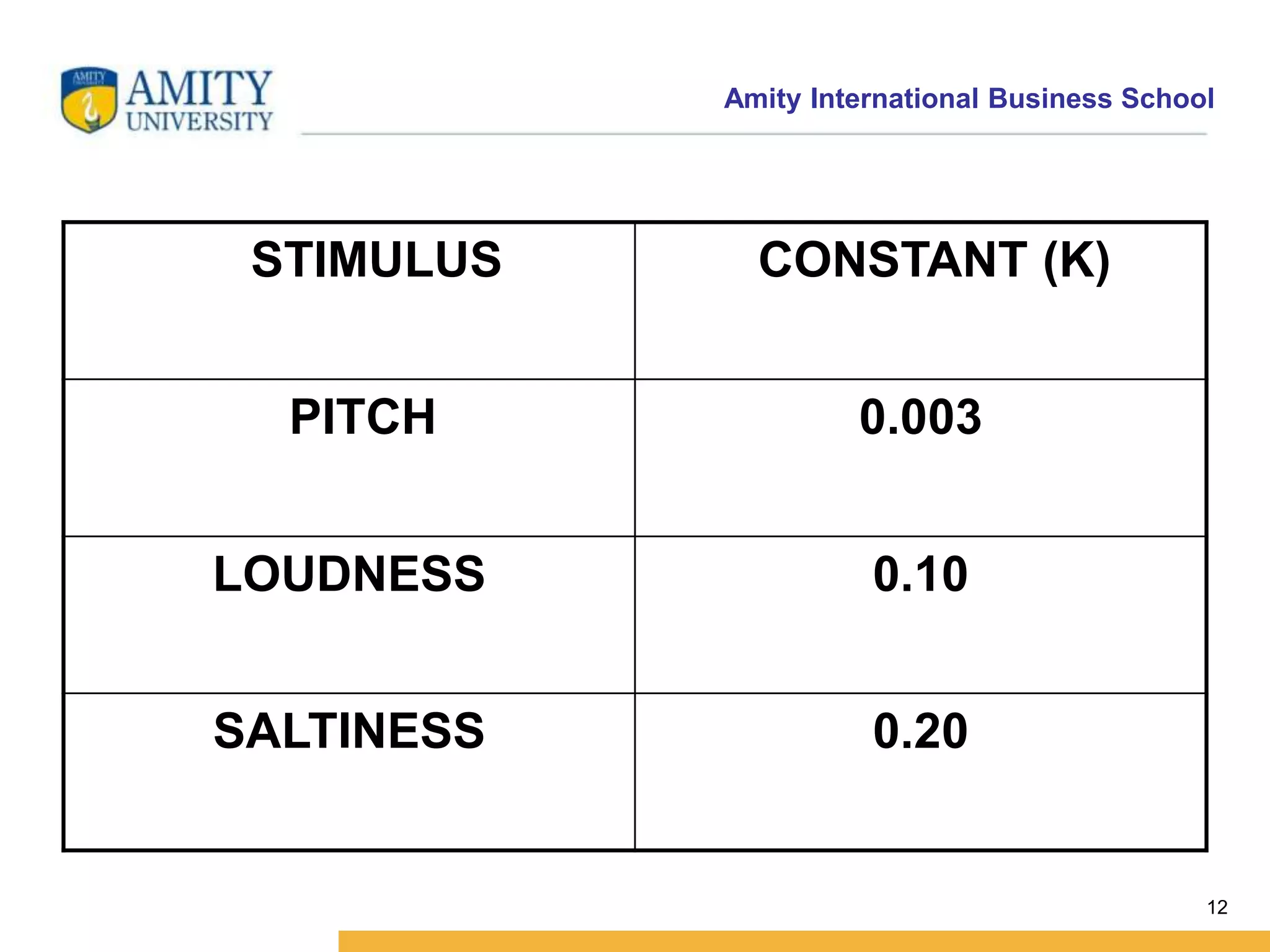
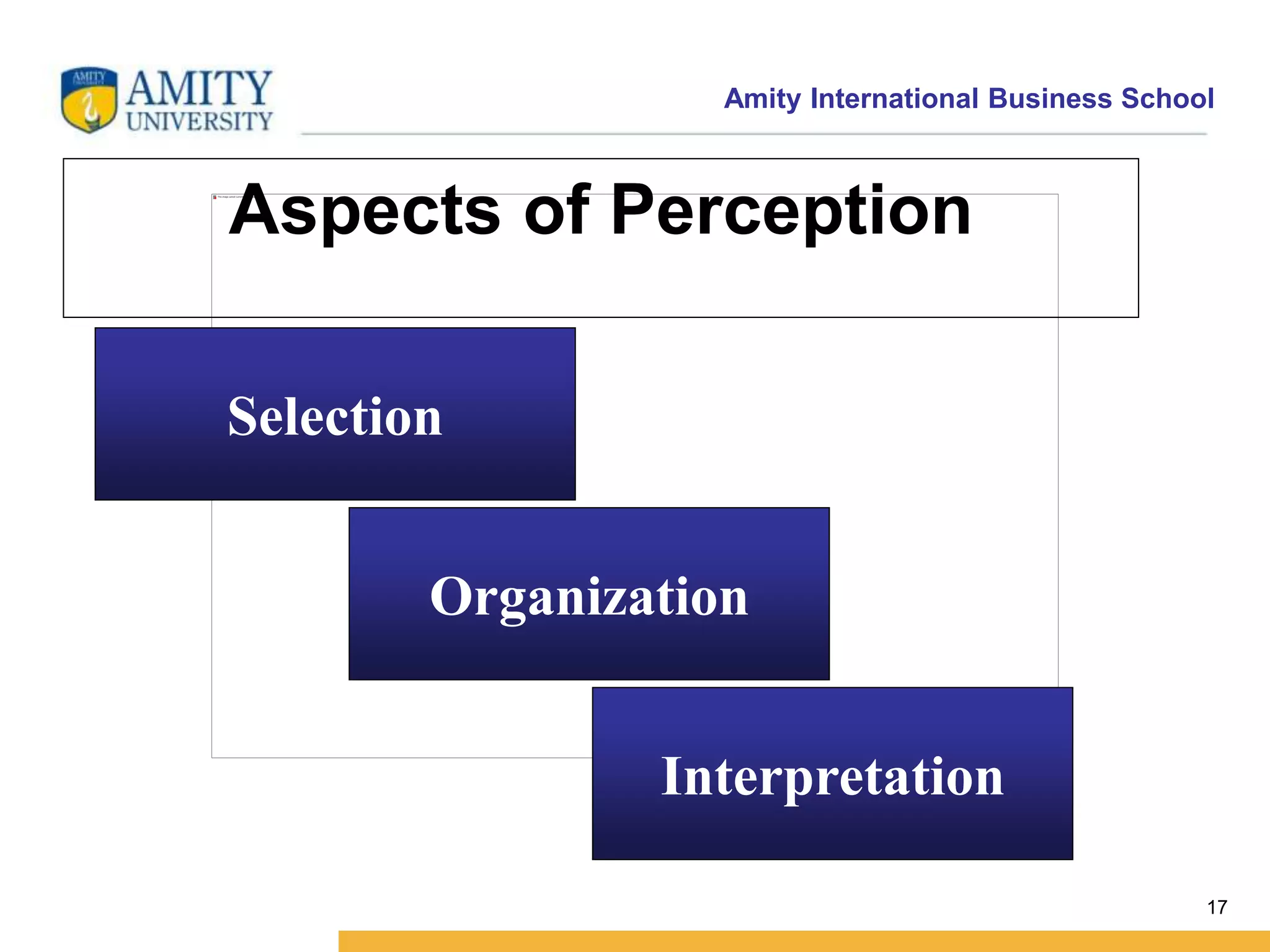
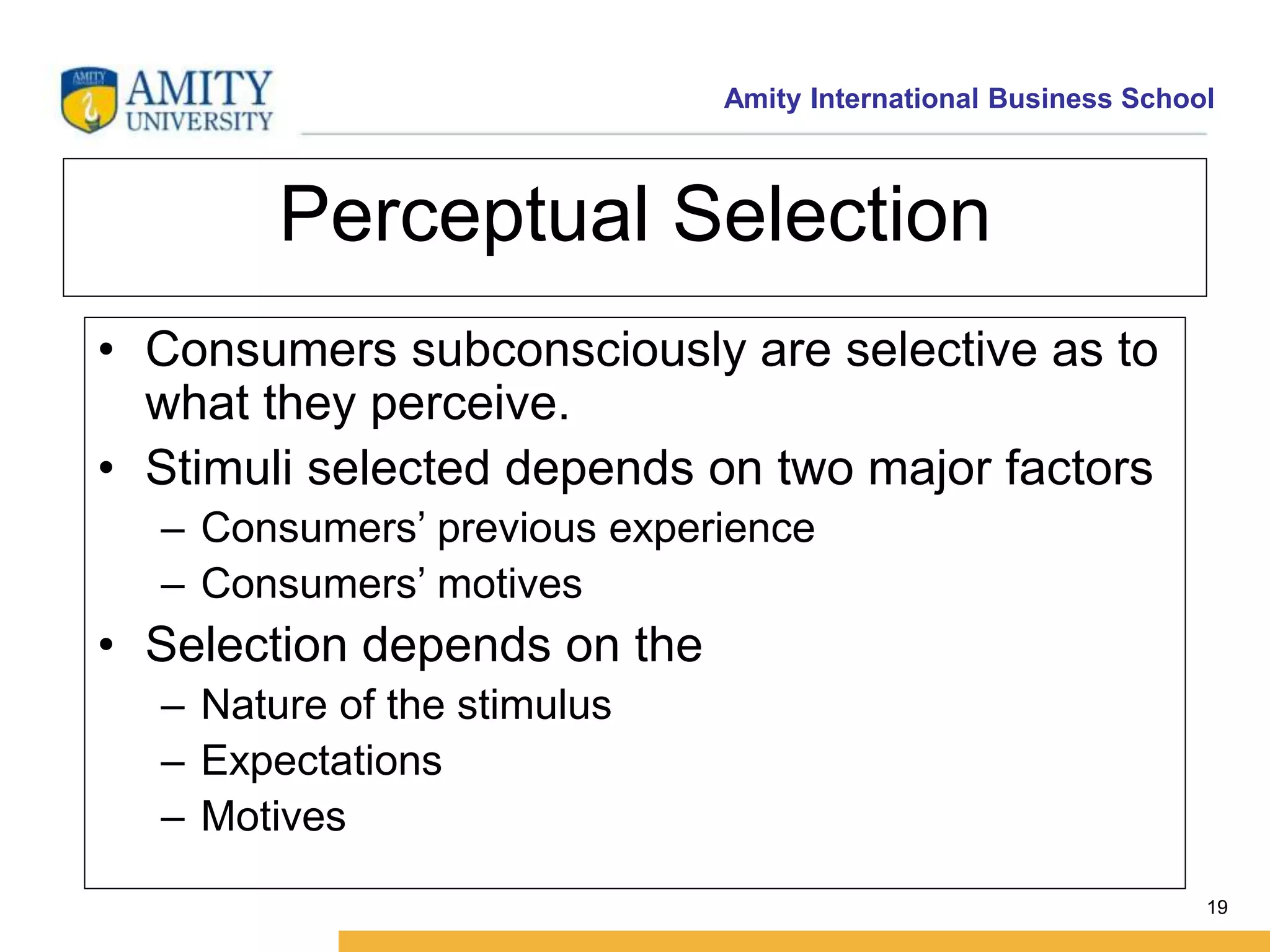
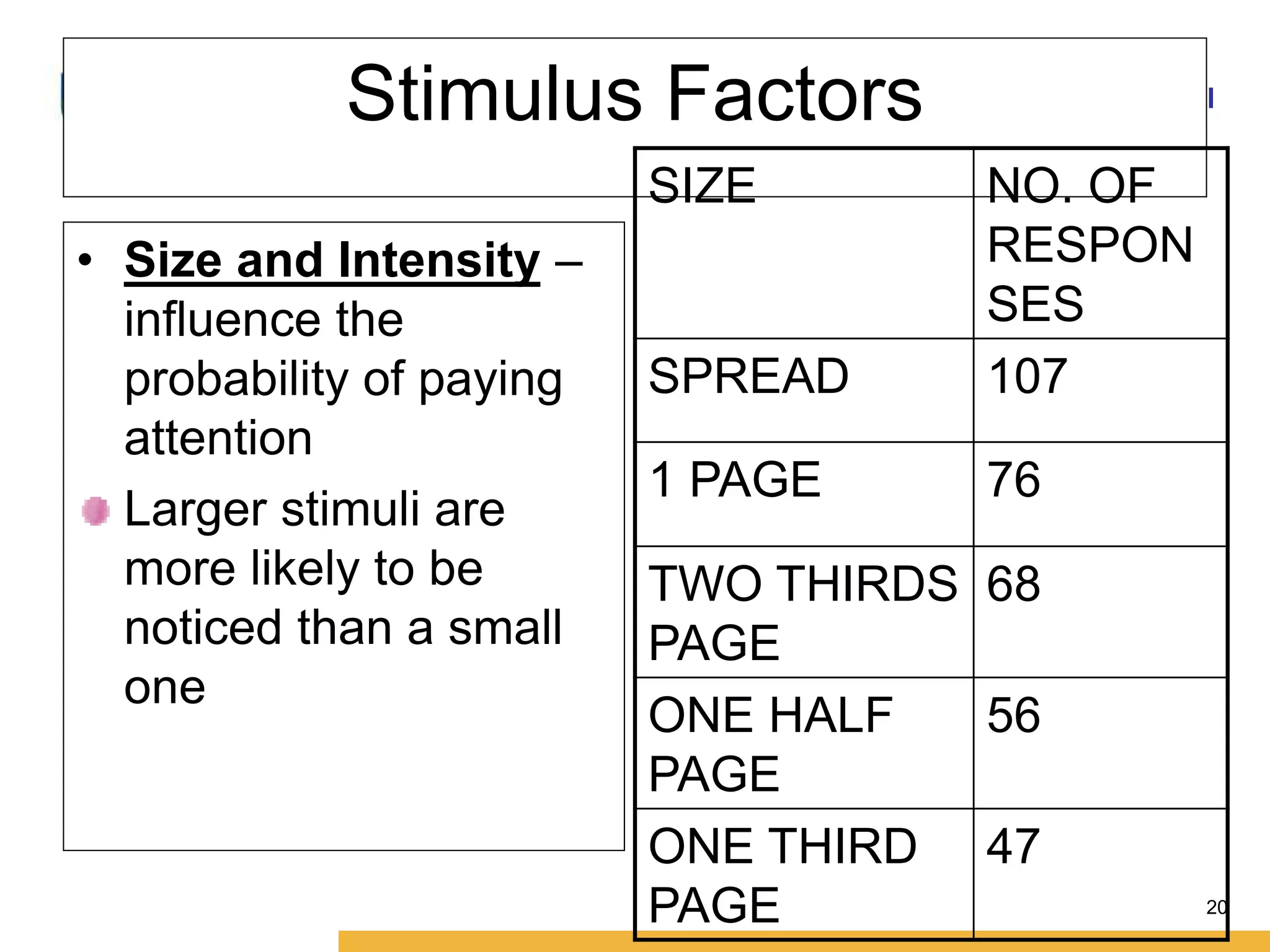
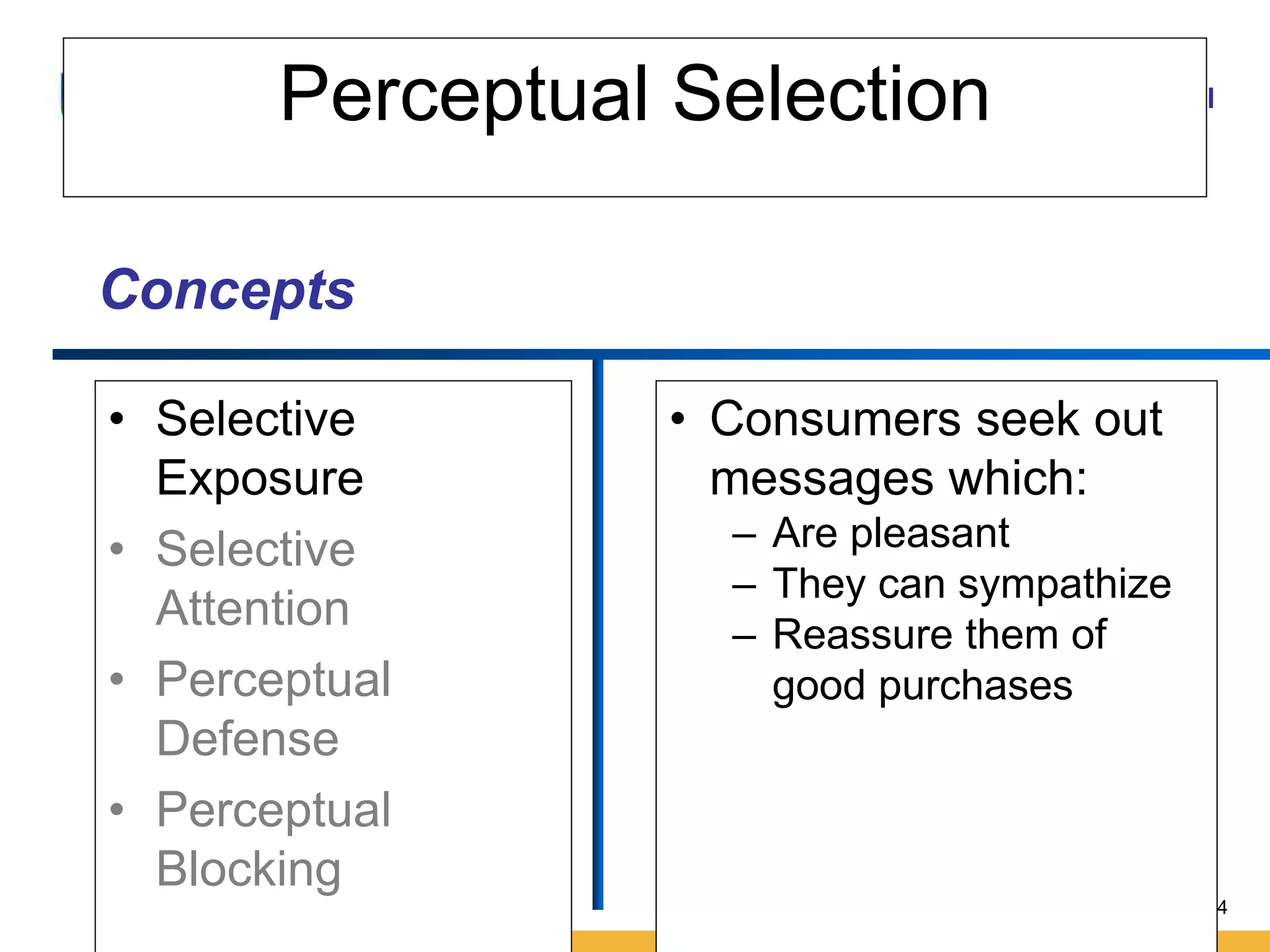
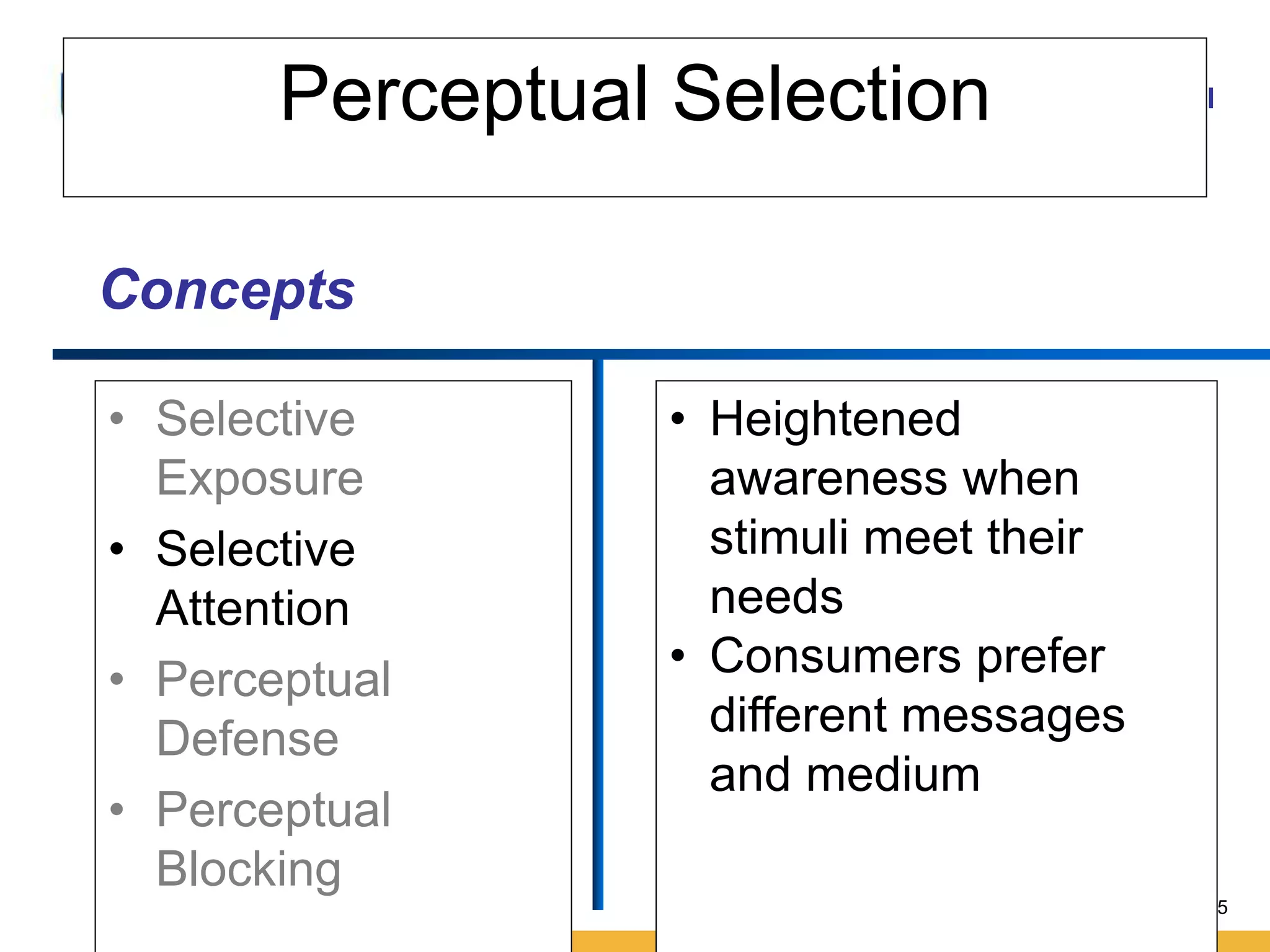
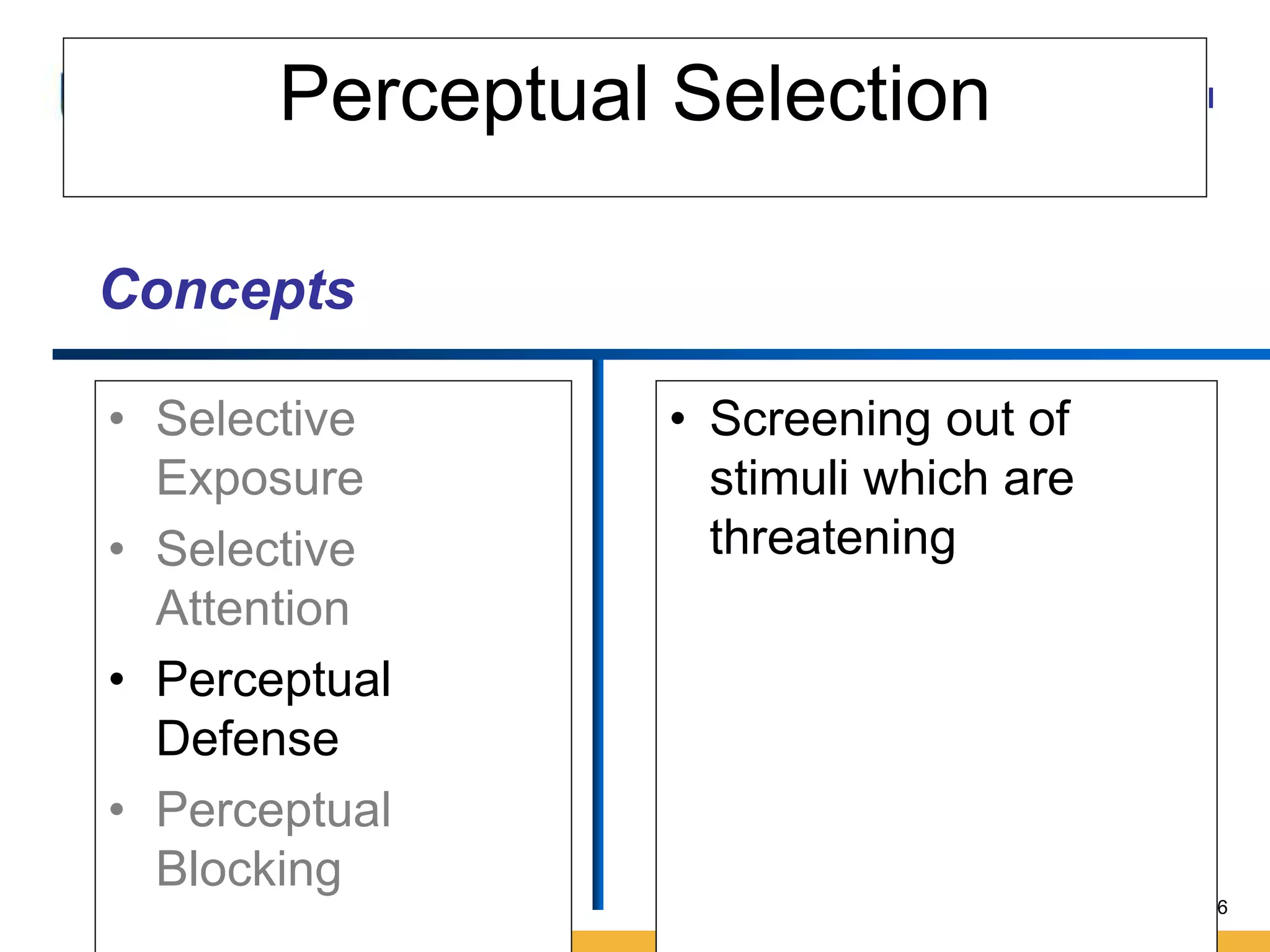
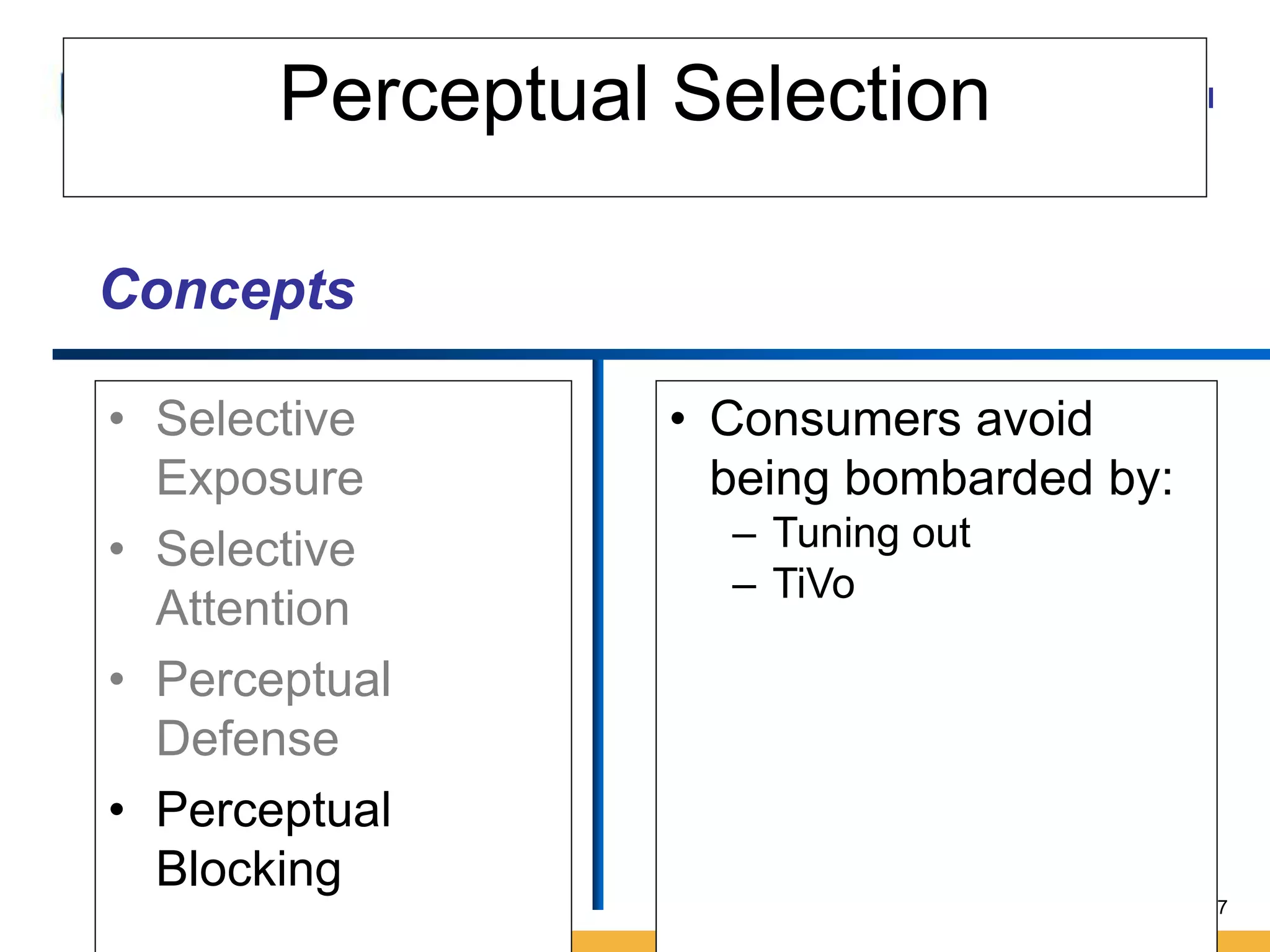
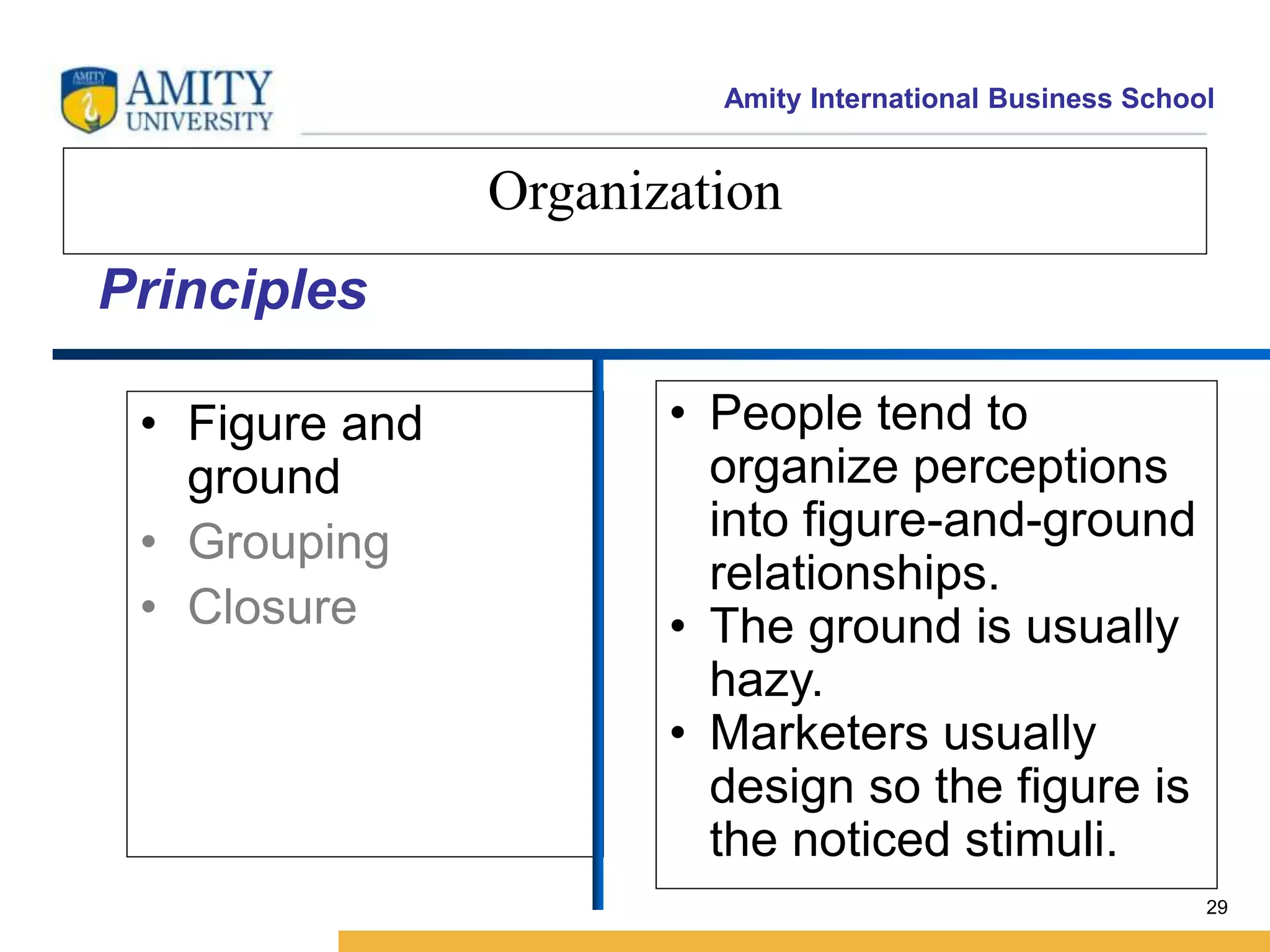
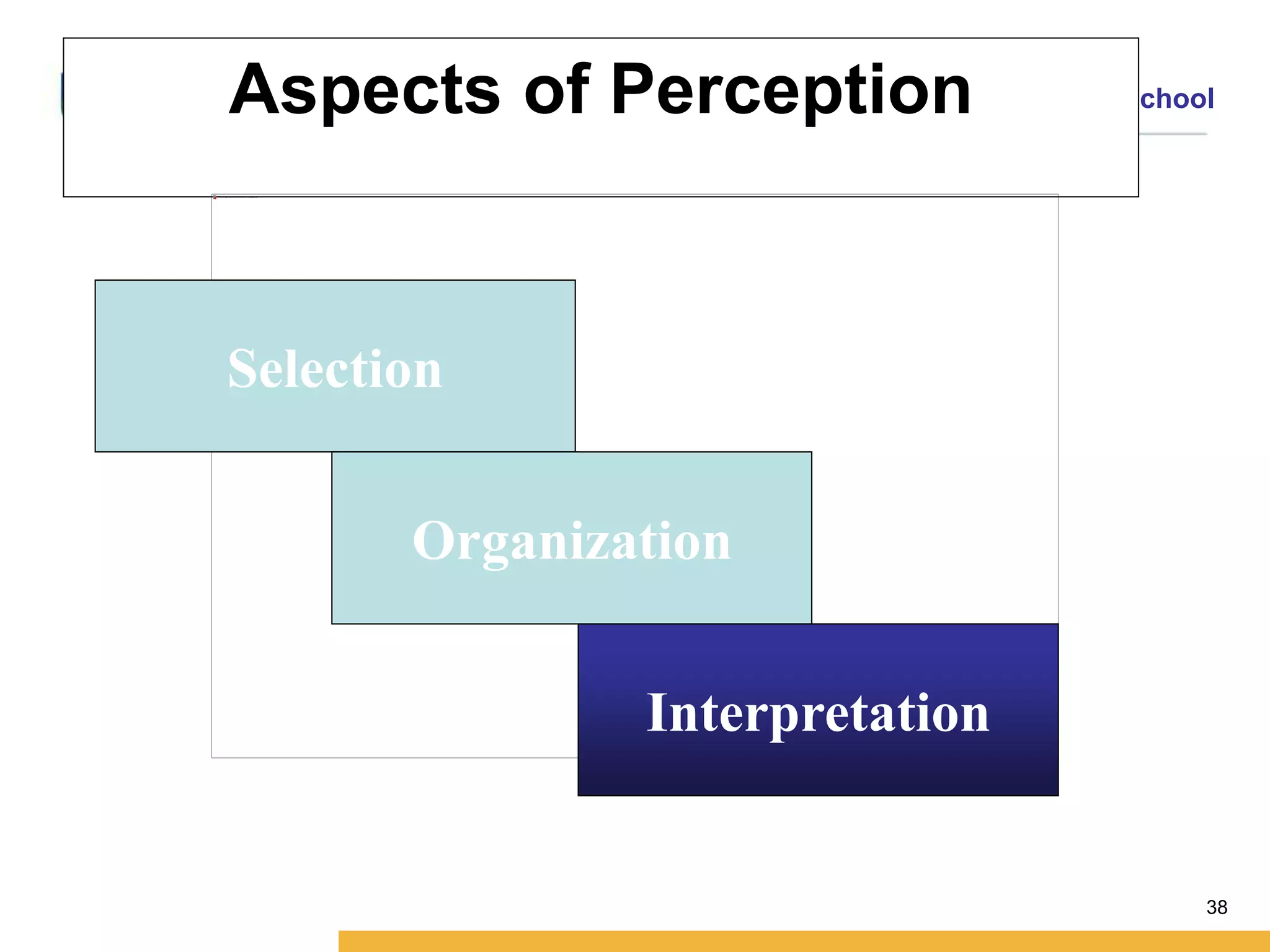
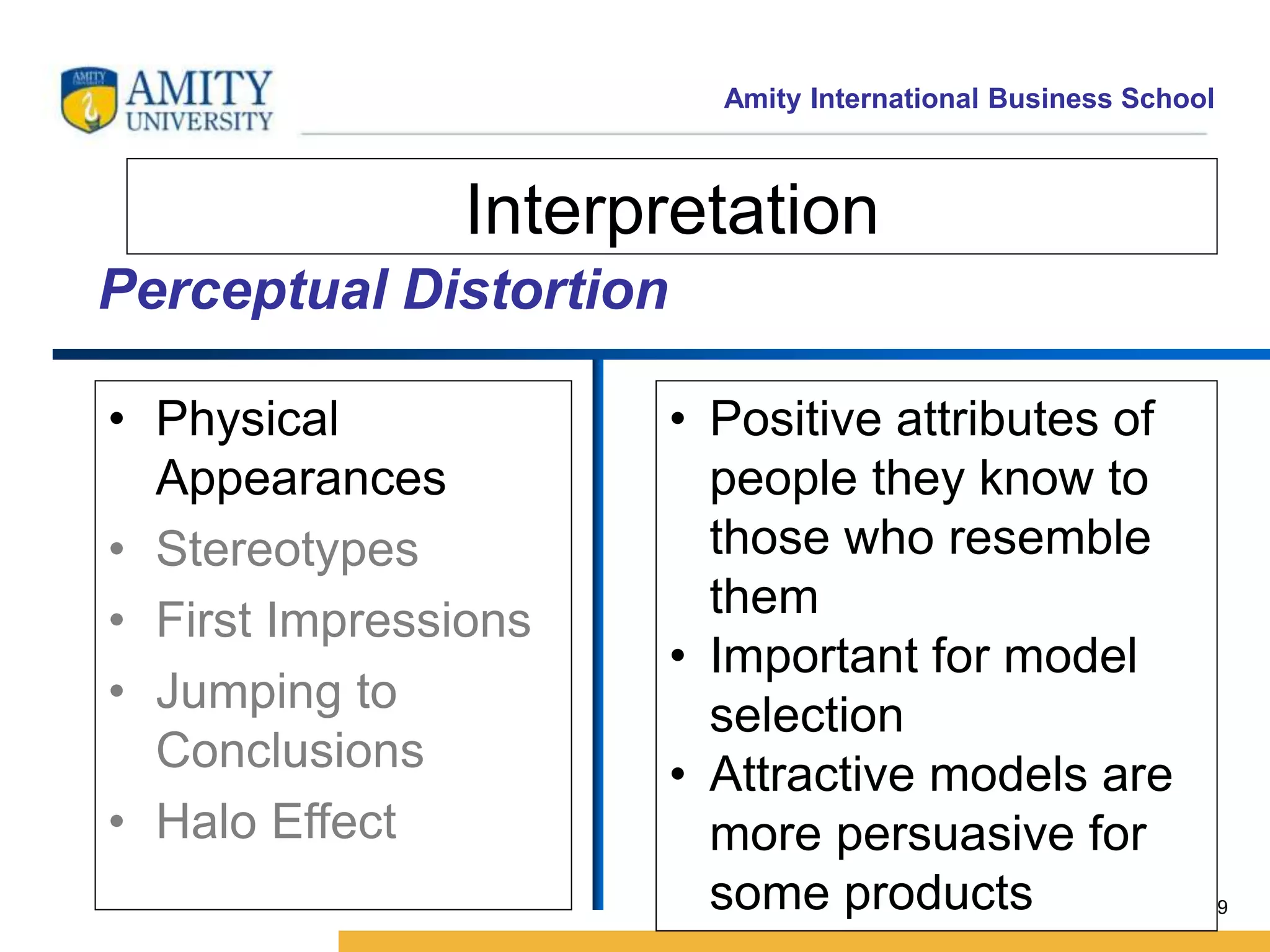
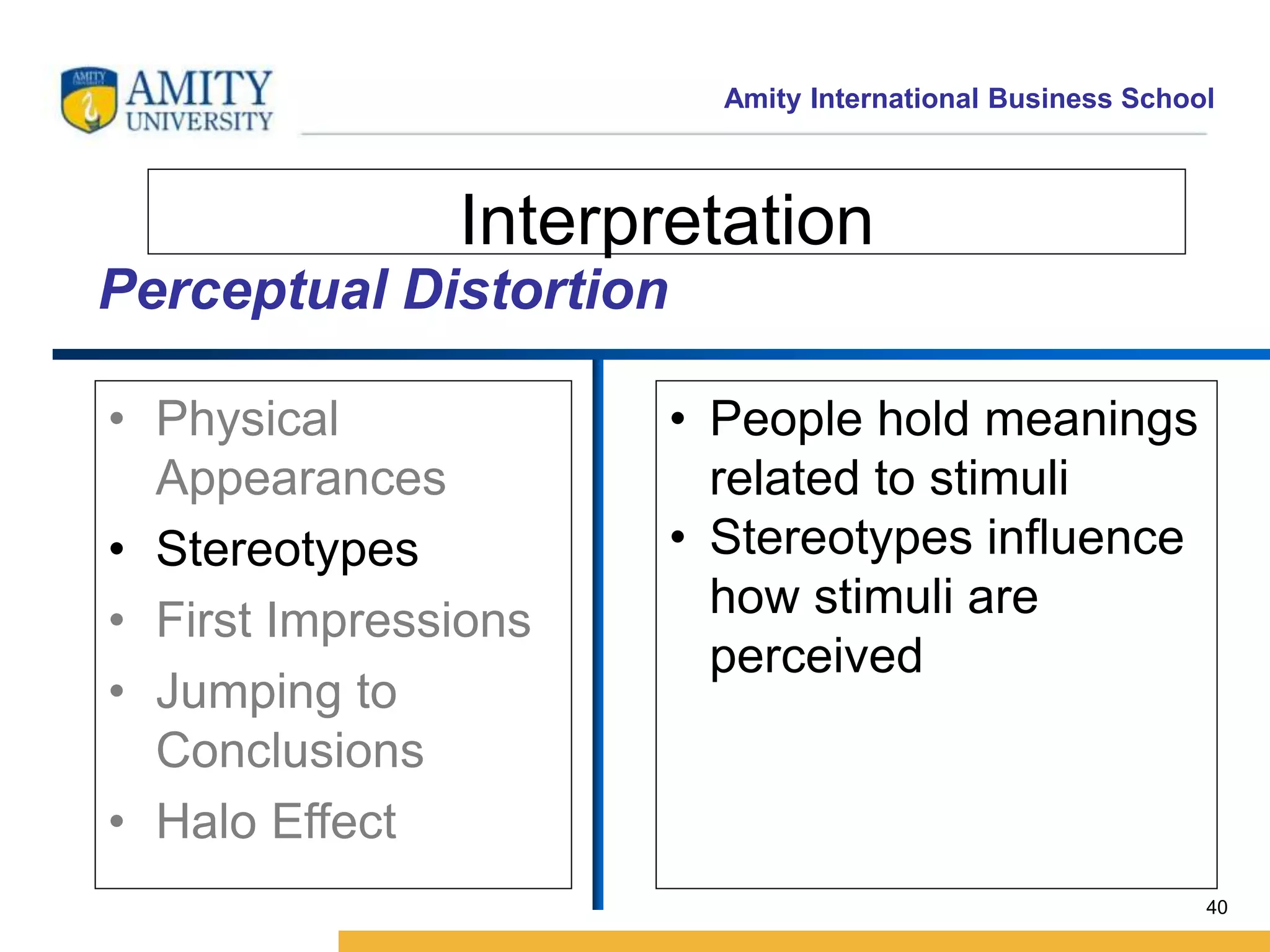
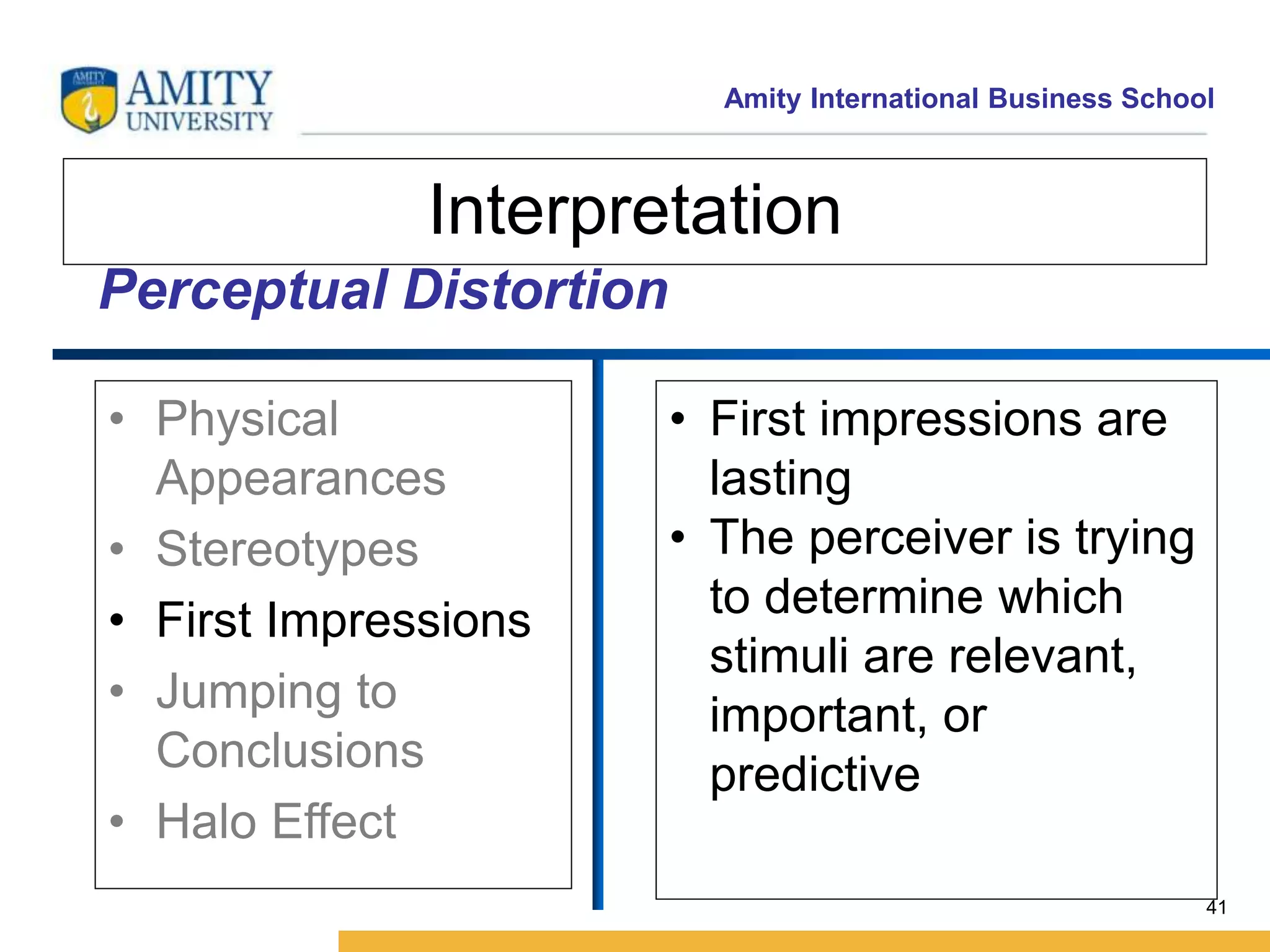
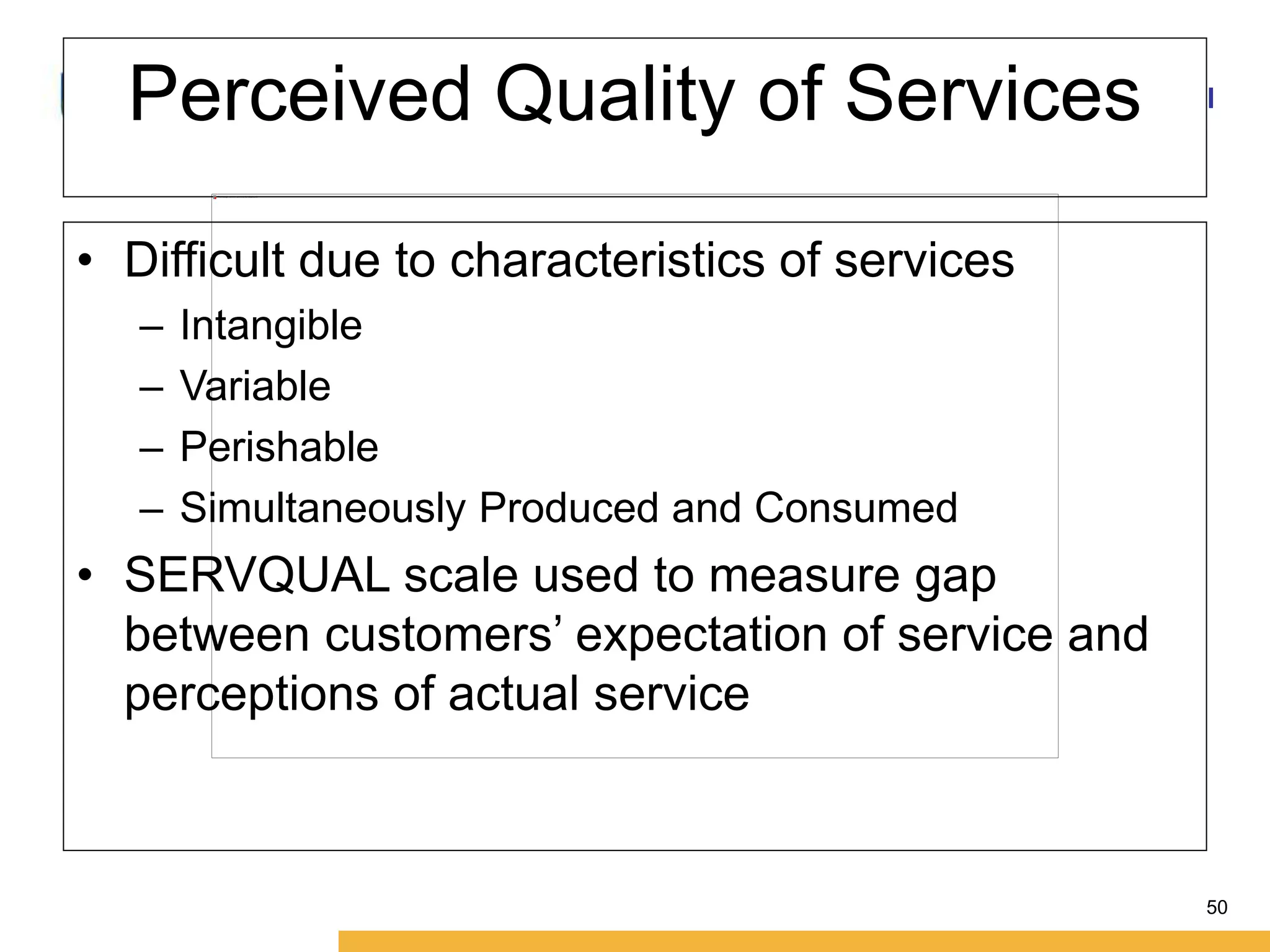
This document discusses consumer perception and related concepts from a marketing perspective. It is from Amity International Business School and covers topics like the definition of perception, the nature and elements of perception including sensation, thresholds, and subliminal perception. It also discusses the aspects of perception including selection, organization, and interpretation. Specifically, it describes principles of organization, perceptual distortions in interpretation, issues in consumer imagery like positioning and perceived quality, and techniques for positioning products.