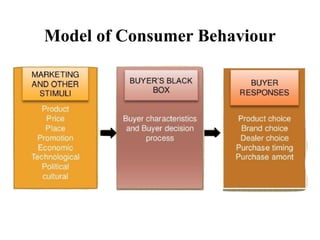
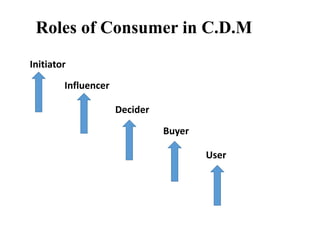
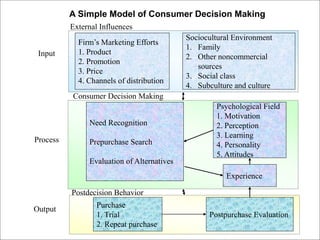
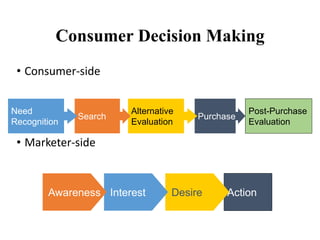
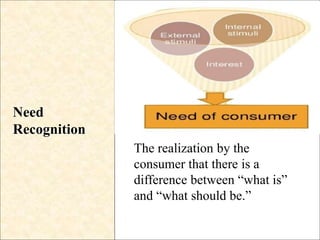
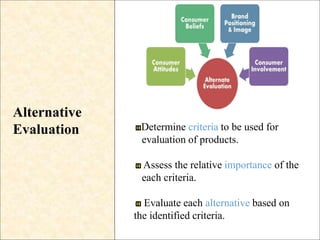
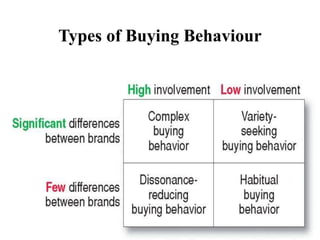
Consumer behavior is the study of how, why, when, and where people buy products. It draws from psychology, sociology, anthropology, and economics to understand individual and group decision making. Factors like culture, social class, motivation, learning, and attitudes influence the consumer decision process of need recognition, information search, alternative evaluation, purchase, and post-purchase evaluation. Understanding consumer behavior helps firms improve marketing efforts to better satisfy consumer needs.