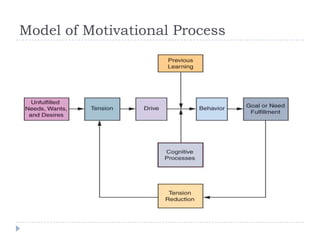
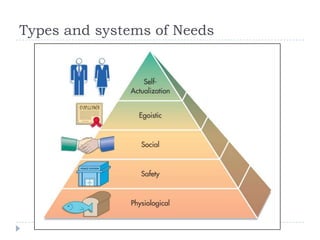
The document discusses consumer motivation and the motivational process. It defines motivation as the driving force that impels individuals to action. The motivational process involves needs, both innate and acquired, that give rise to motives. These motives then lead to the selection of goals, both positive and negative. Needs are never fully satisfied and new needs emerge as old needs are met. Motivation is influenced by success, failure, and defense mechanisms. Motives can be aroused physiologically, emotionally, and cognitively. The document also discusses measuring motivation through qualitative research methods.