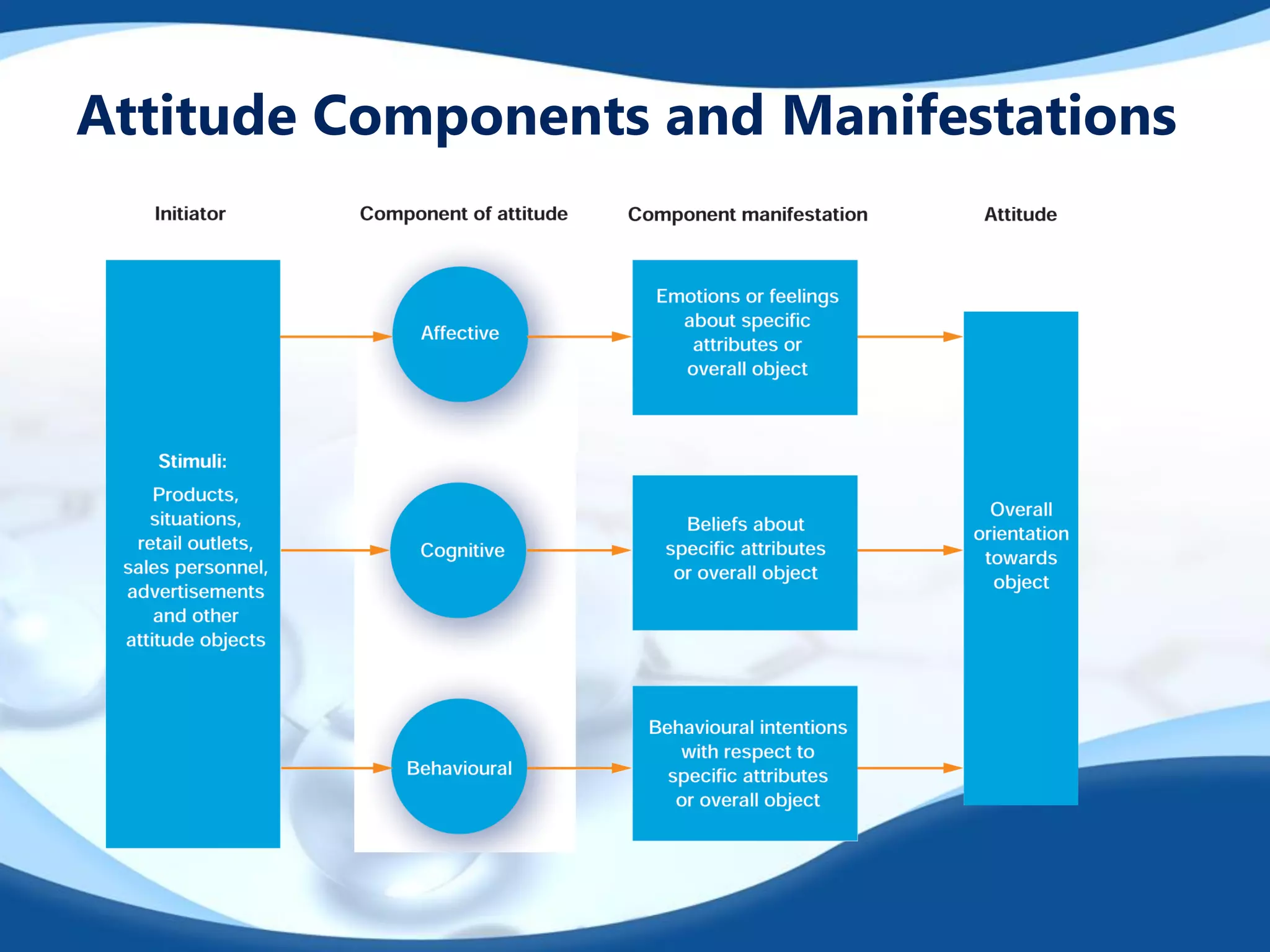
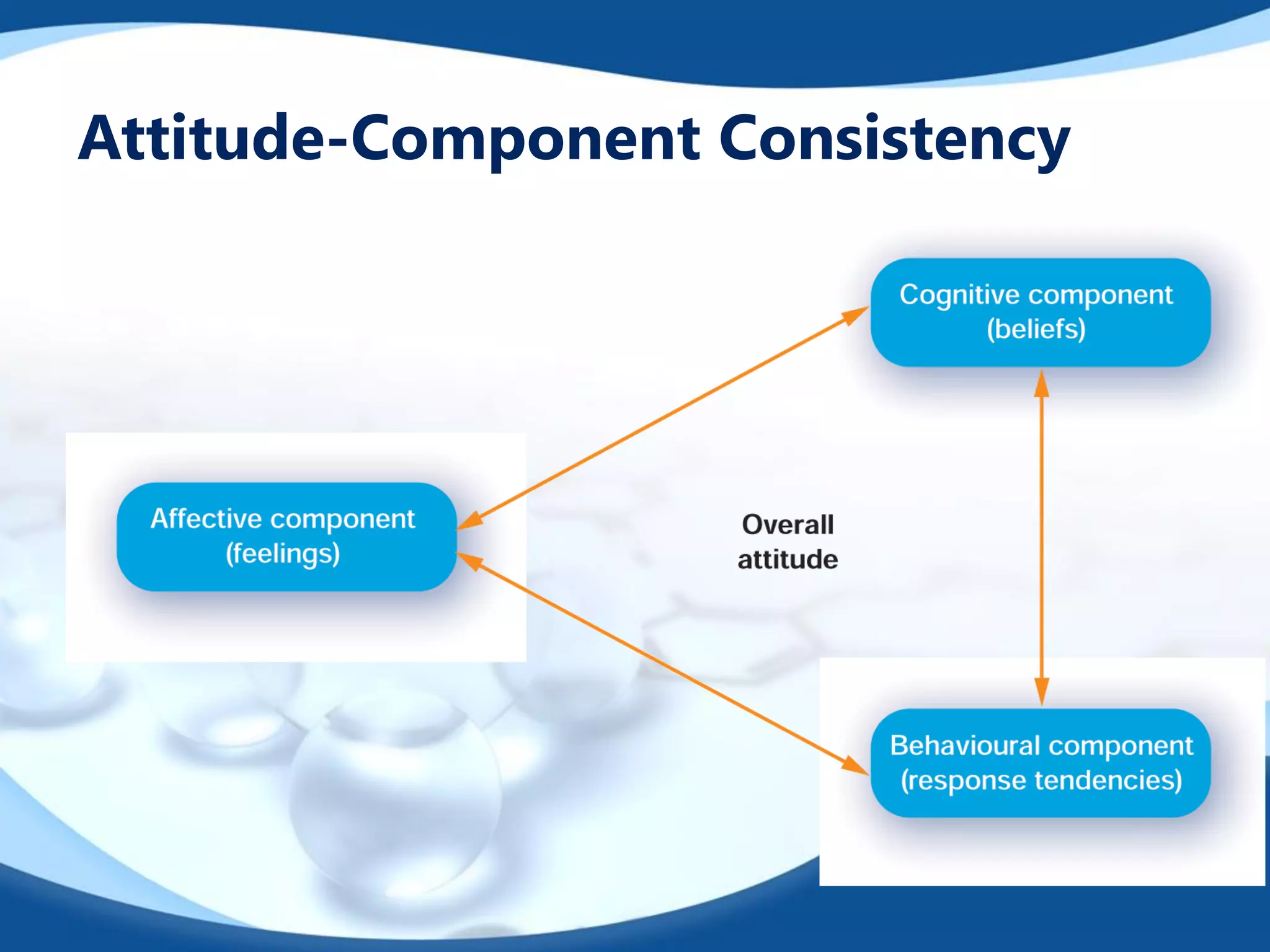
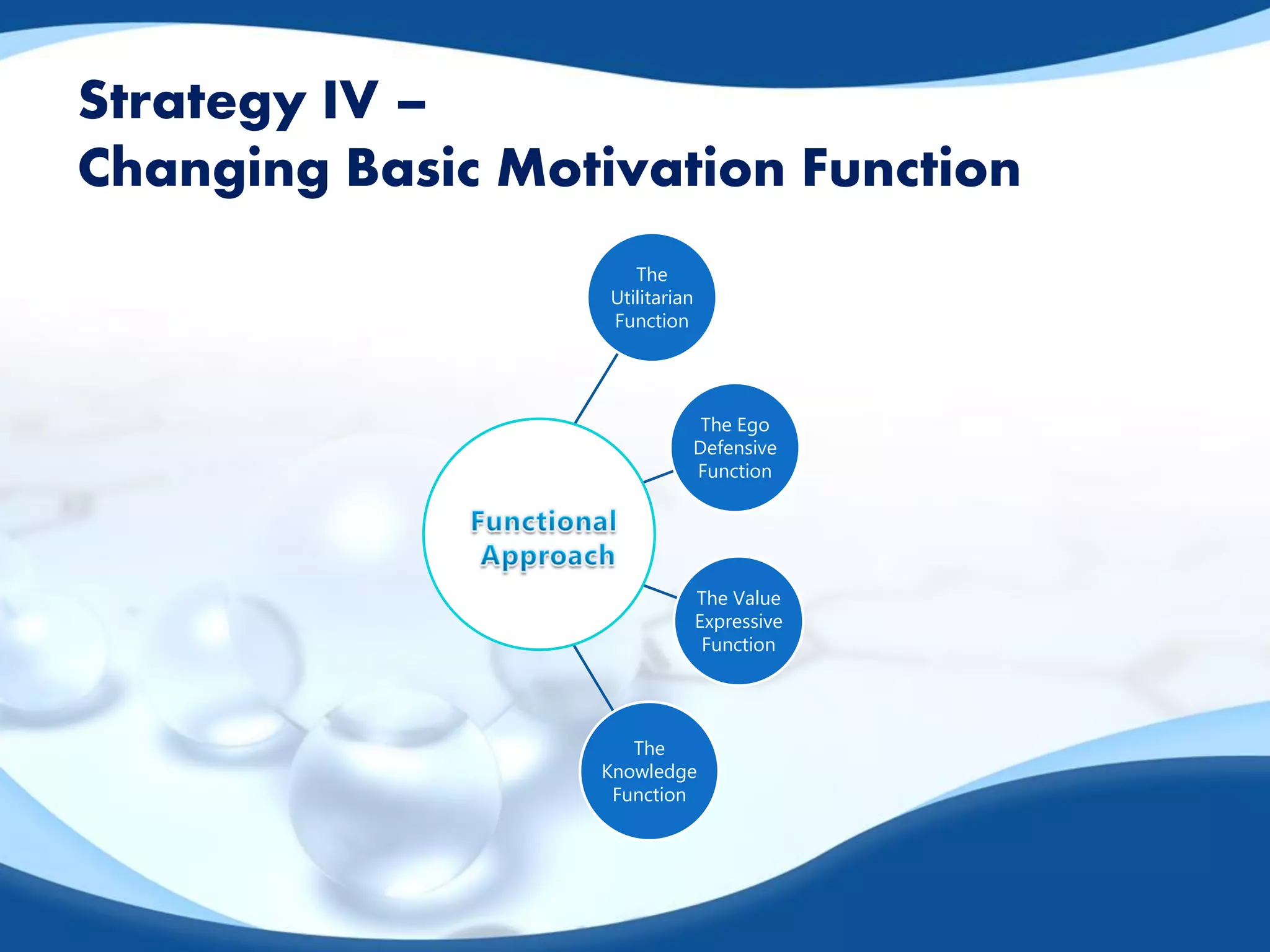
This document outlines strategies for changing consumer attitudes. It defines attitudes and discusses their components and formation. Four main strategies for attitude change are described: 1) Changing beliefs about competitor brands, 2) Associating products with admired groups/causes, 3) Altering components of multi-attribute models like attributes or brand ratings, and 4) Changing basic motivation functions like the utilitarian, ego-defensive, value-expressive, or knowledge functions. The document also addresses resolving conflicts between positive and negative attitudes.