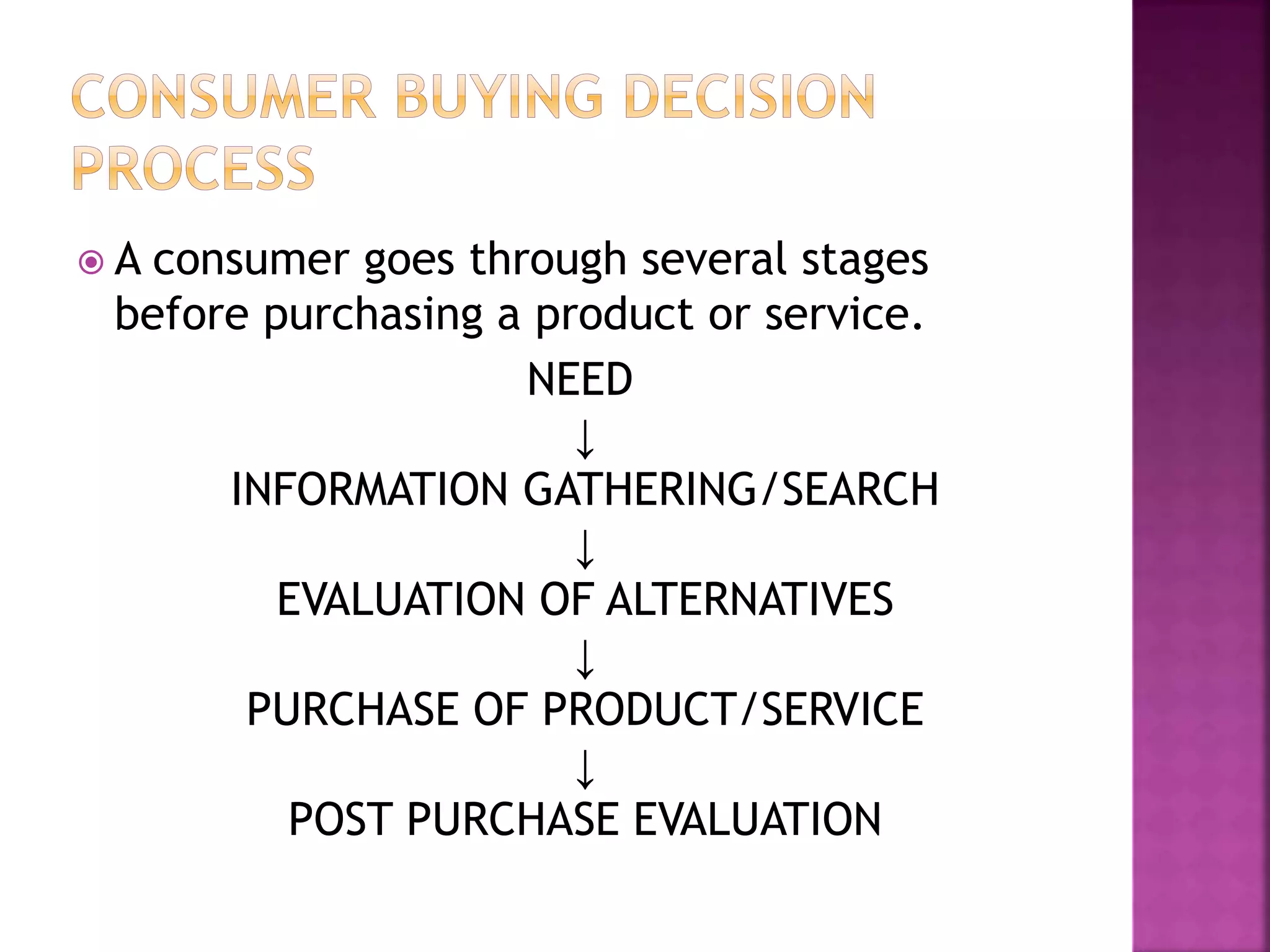
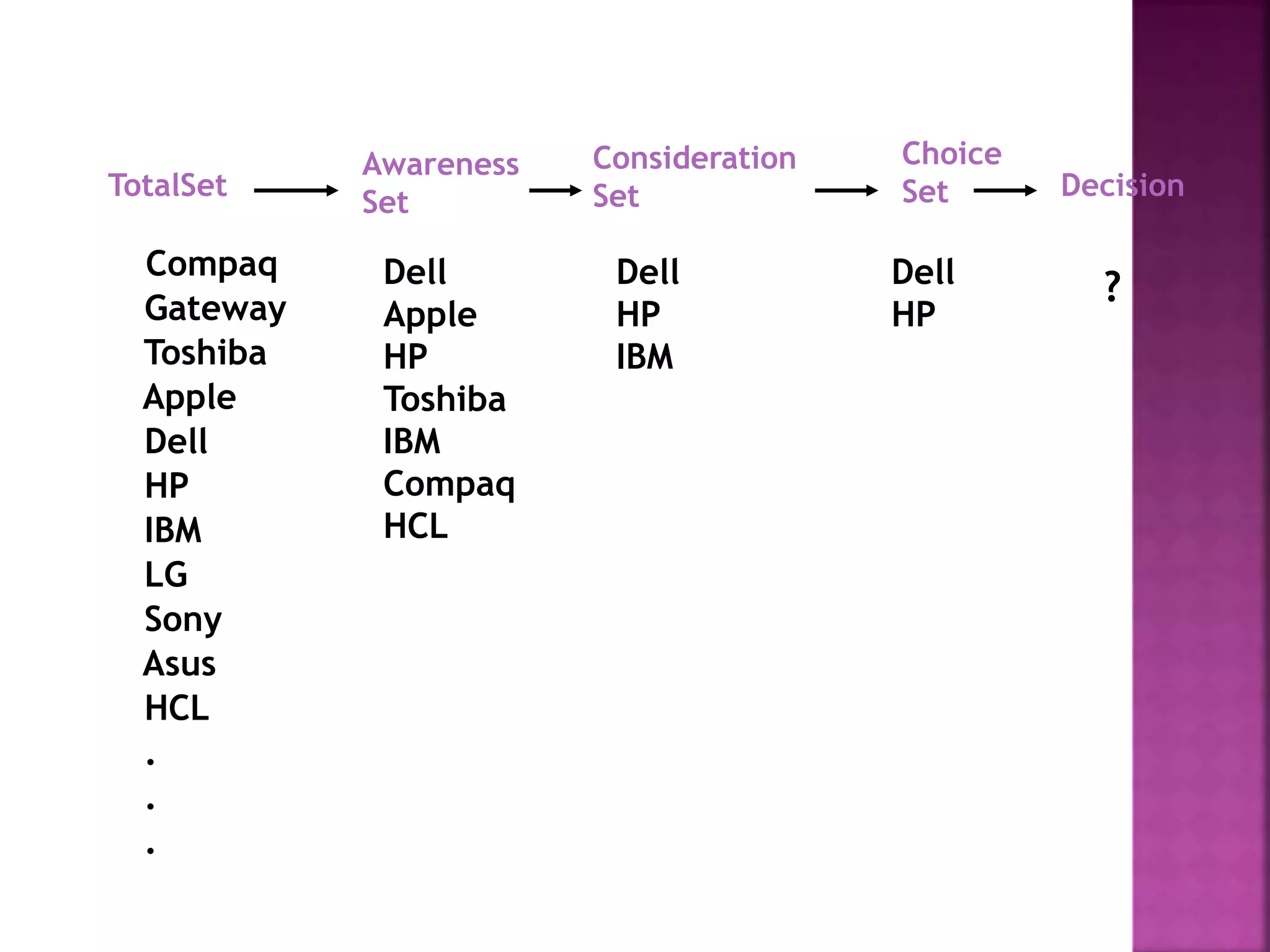
Consumer behavior is the study of the diverse needs, wants, and purchasing patterns of individuals and groups, emphasizing the buying process from pre-purchase to post-purchase evaluation. It encompasses various factors influencing behavior, including cultural, social, personal, and psychological aspects. Understanding these elements is essential for marketers to effectively satisfy consumer needs and gain a competitive edge.