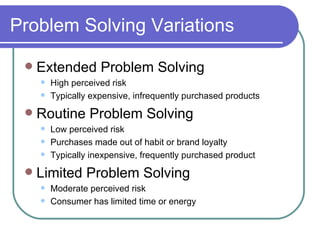
This document outlines the consumer decision making process, which includes problem recognition, information search, alternative evaluation, decision, and post-decision evaluation. It discusses three types of problem solving variations - extended, routine, and limited problem solving. It also covers internal and external information search, evaluative criteria, decision rules, and factors that influence the decision making process like situational influences and low effort heuristics.