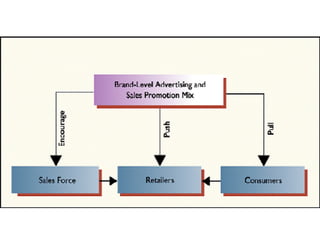
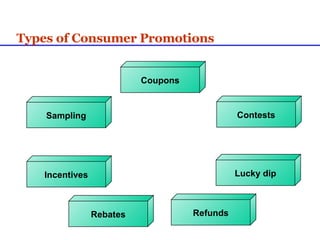
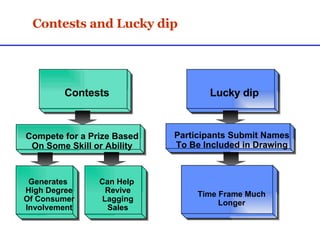
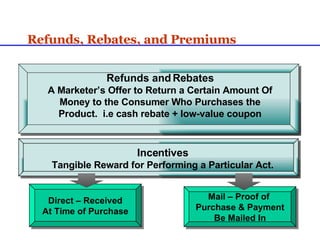
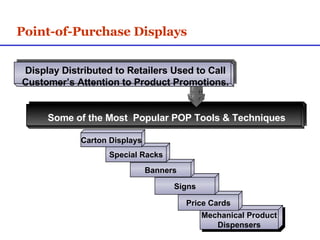
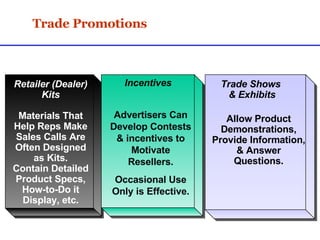
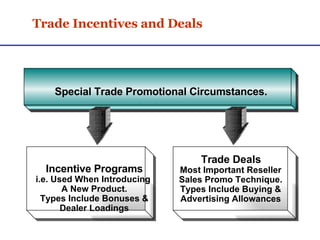
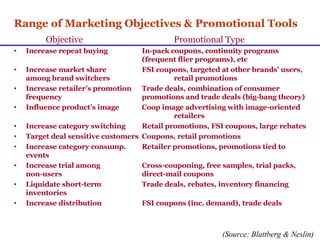
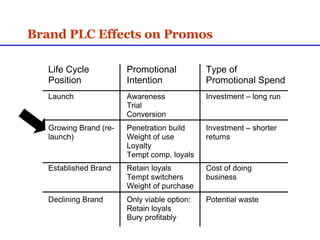
Sales promotions aim to increase immediate sales, gain trade support, and support the sales force. They are widely used due to pressure to quickly boost sales and because they can easily target consumers, trade partners, and salespeople. Common consumer promotions include coupons, rebates, samples, and contests which are flexible and can be combined to meet objectives. Trade promotions target wholesalers and retailers through point-of-purchase displays, trade shows, retailer kits, and incentives to gain merchandising support and distribution. Loyalty programs aim to increase retention through rewards while sponsorship and events associate brands with lifestyles.