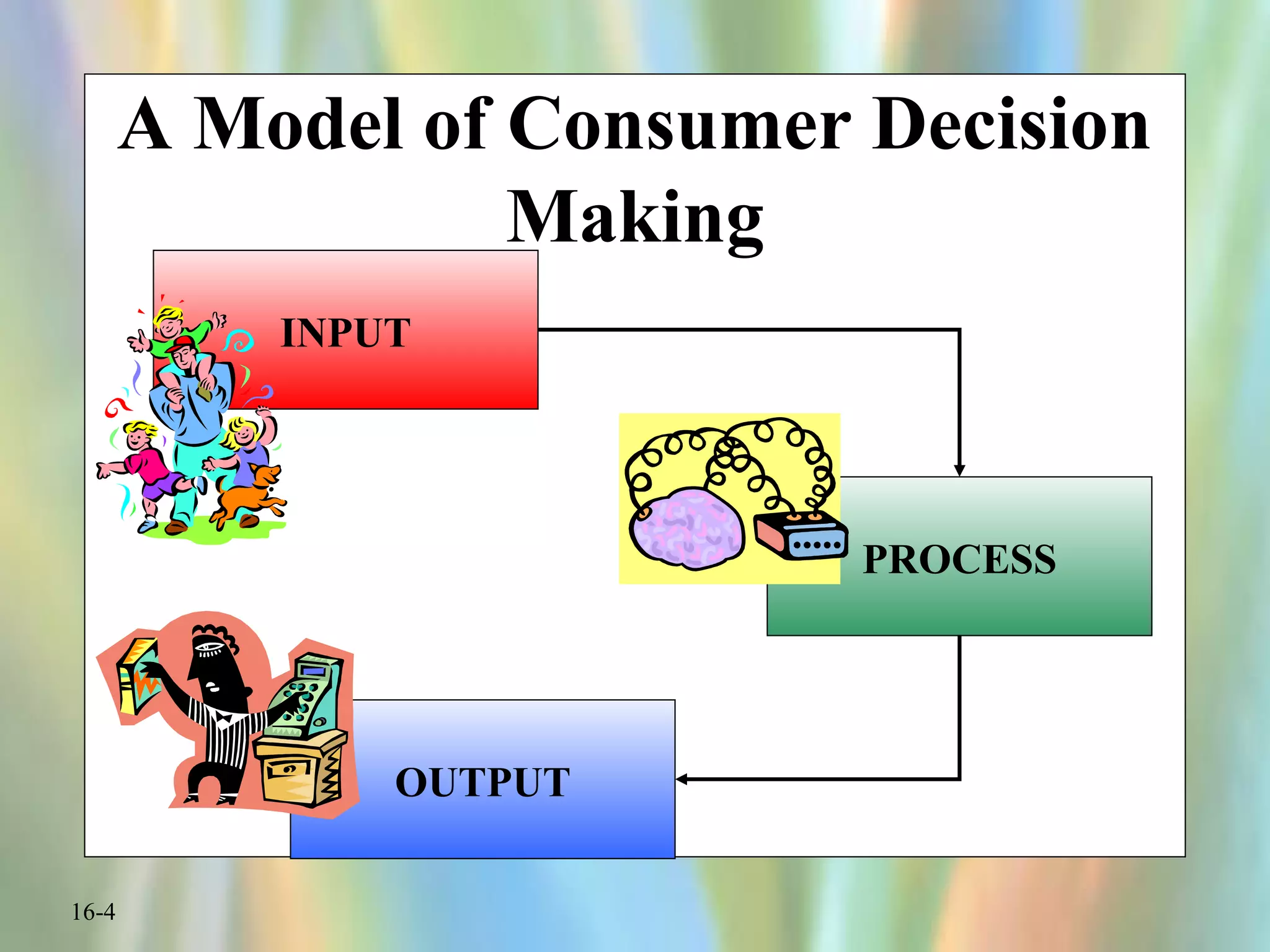
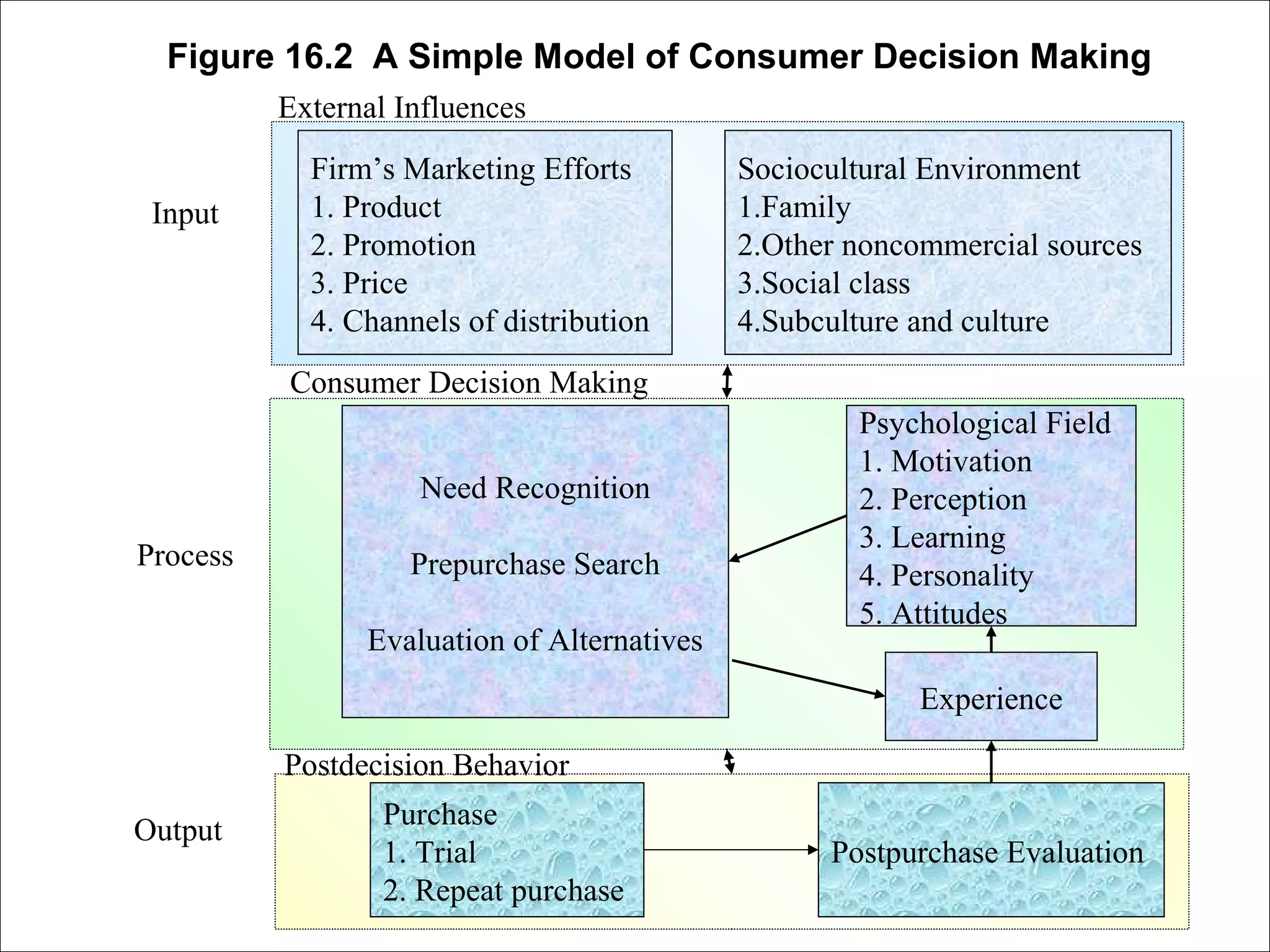
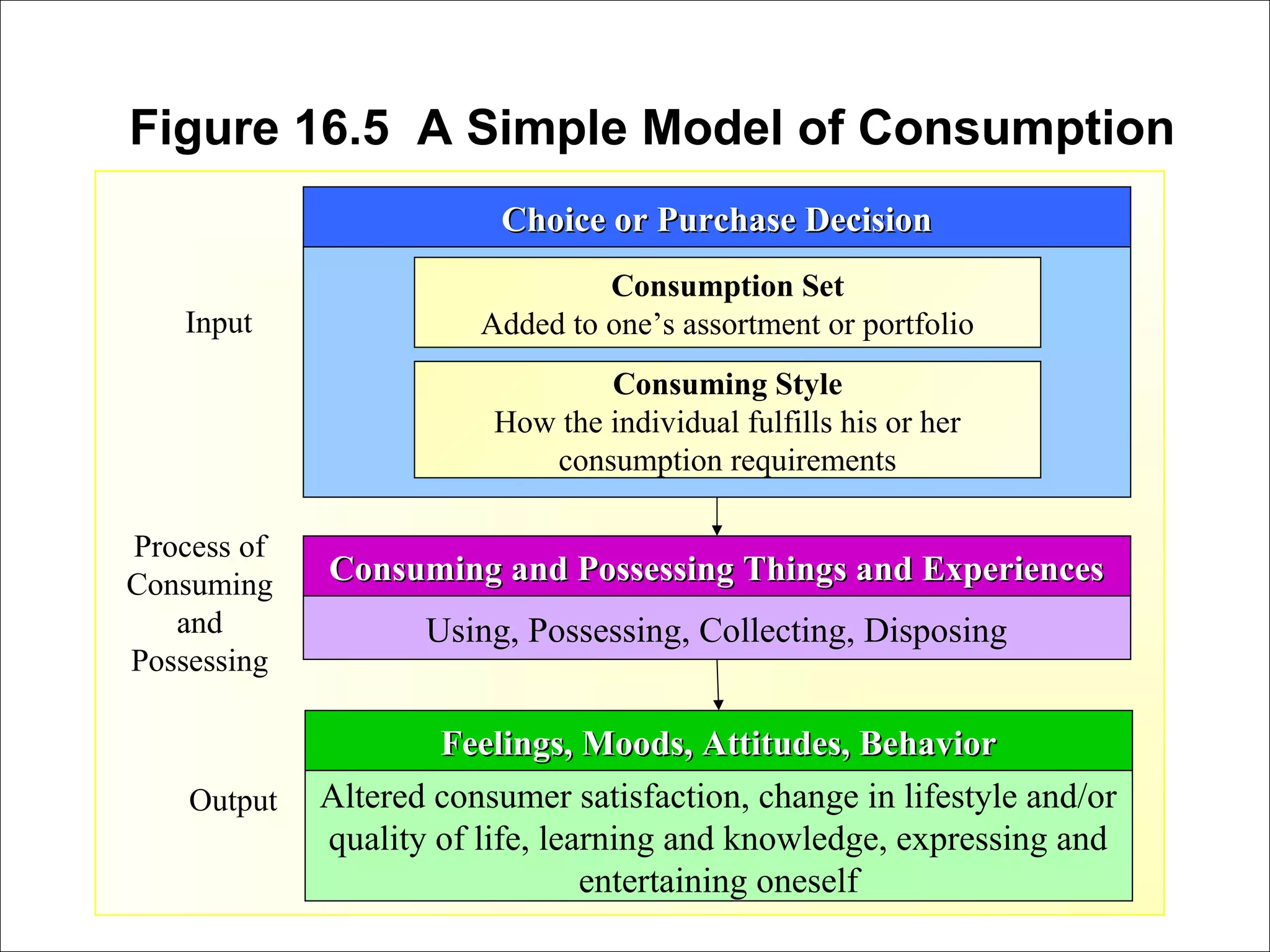
This document discusses consumer decision making processes and models. It describes four views of how consumers make decisions: economic, passive, cognitive, and emotional. It then presents a simple model of consumer decision making that shows external and psychological influences affecting the need recognition, information search, evaluation, purchase, and post-purchase evaluation stages. Graphs and tables further explain the evaluation of alternatives and outcomes. The document also differentiates between trial, repeat, and long-term commitment purchases in consumer decision making.