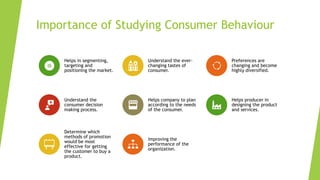
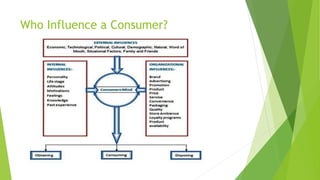
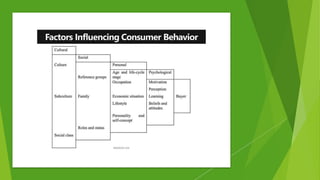
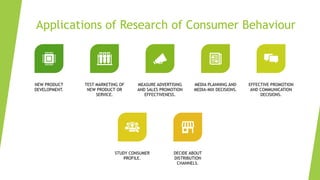
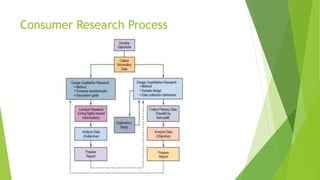
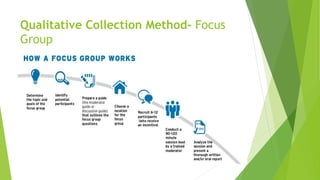
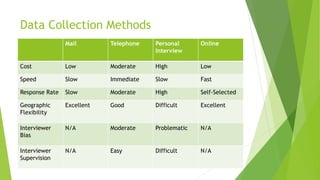
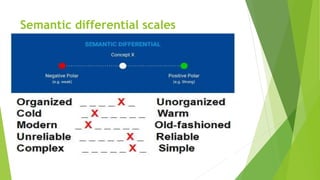
The document is an overview of consumer behavior, focusing on its importance in understanding buying decisions and market dynamics. It explains the need for studying consumer behavior due to factors like changing preferences and evolving market conditions, while also detailing research methods, data collection techniques, and the interdisciplinary nature of the field. Additionally, it covers the roles of consumer research in marketing strategies and the significance of understanding consumer insights for successful business operations.