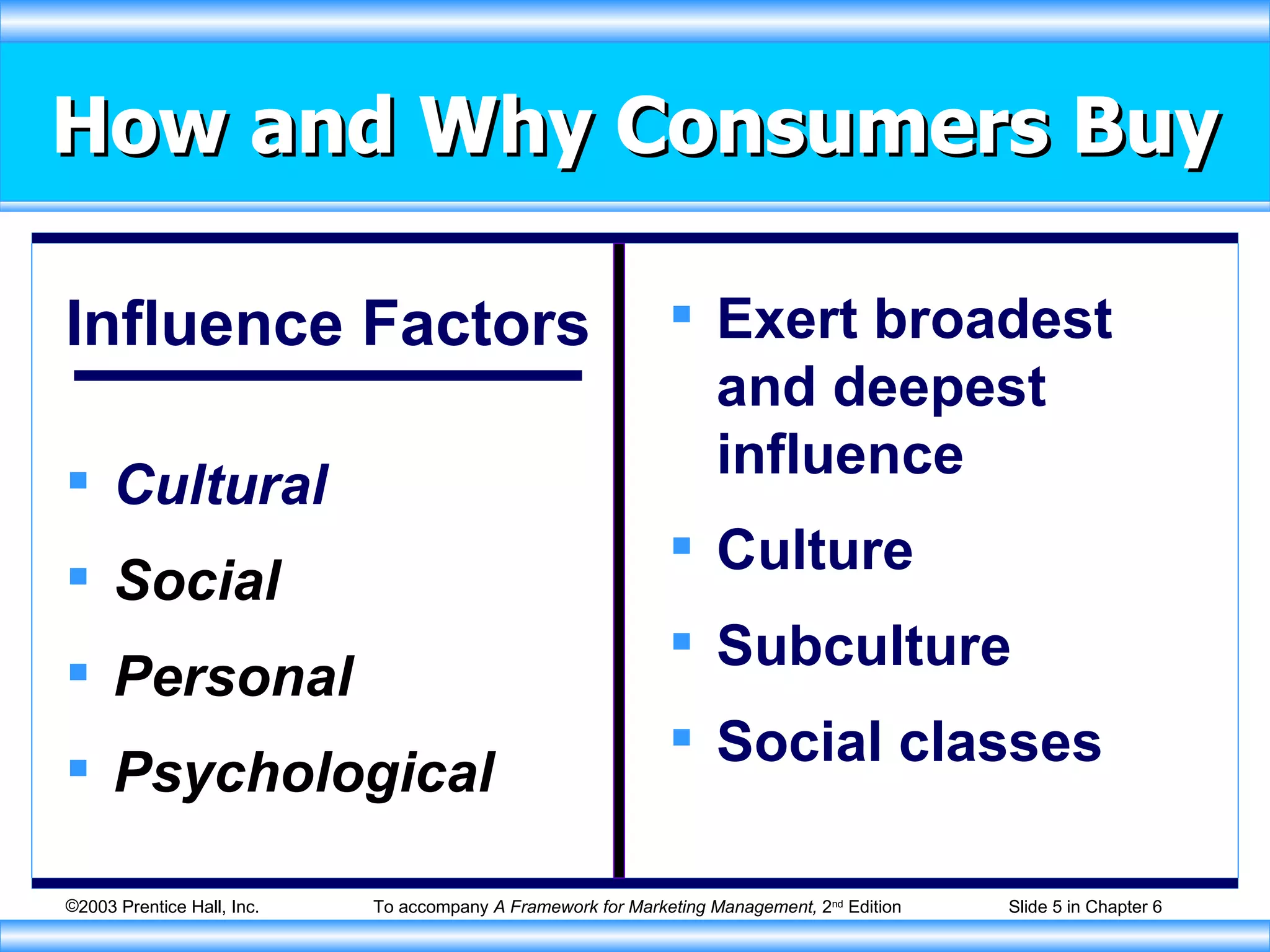
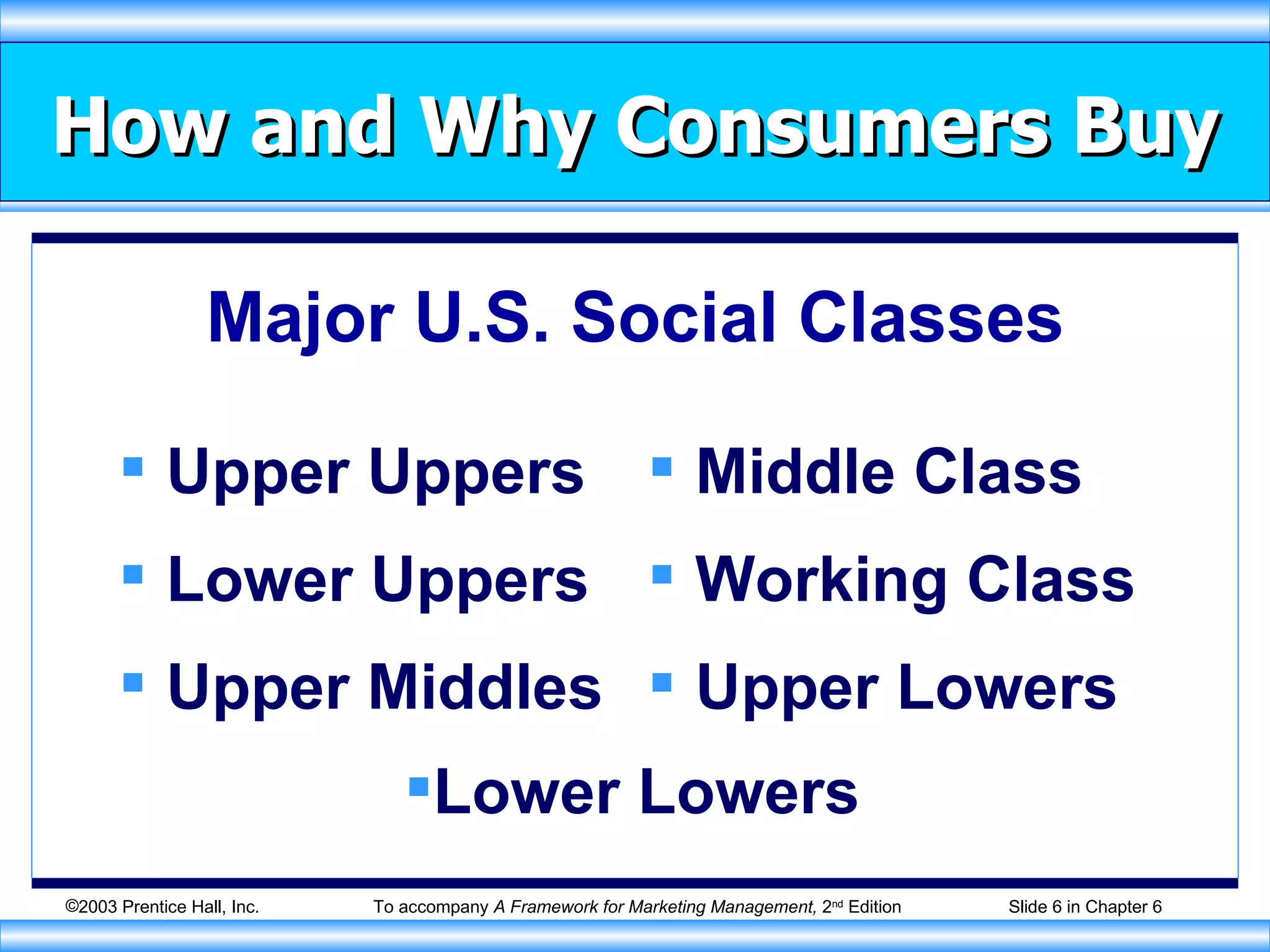
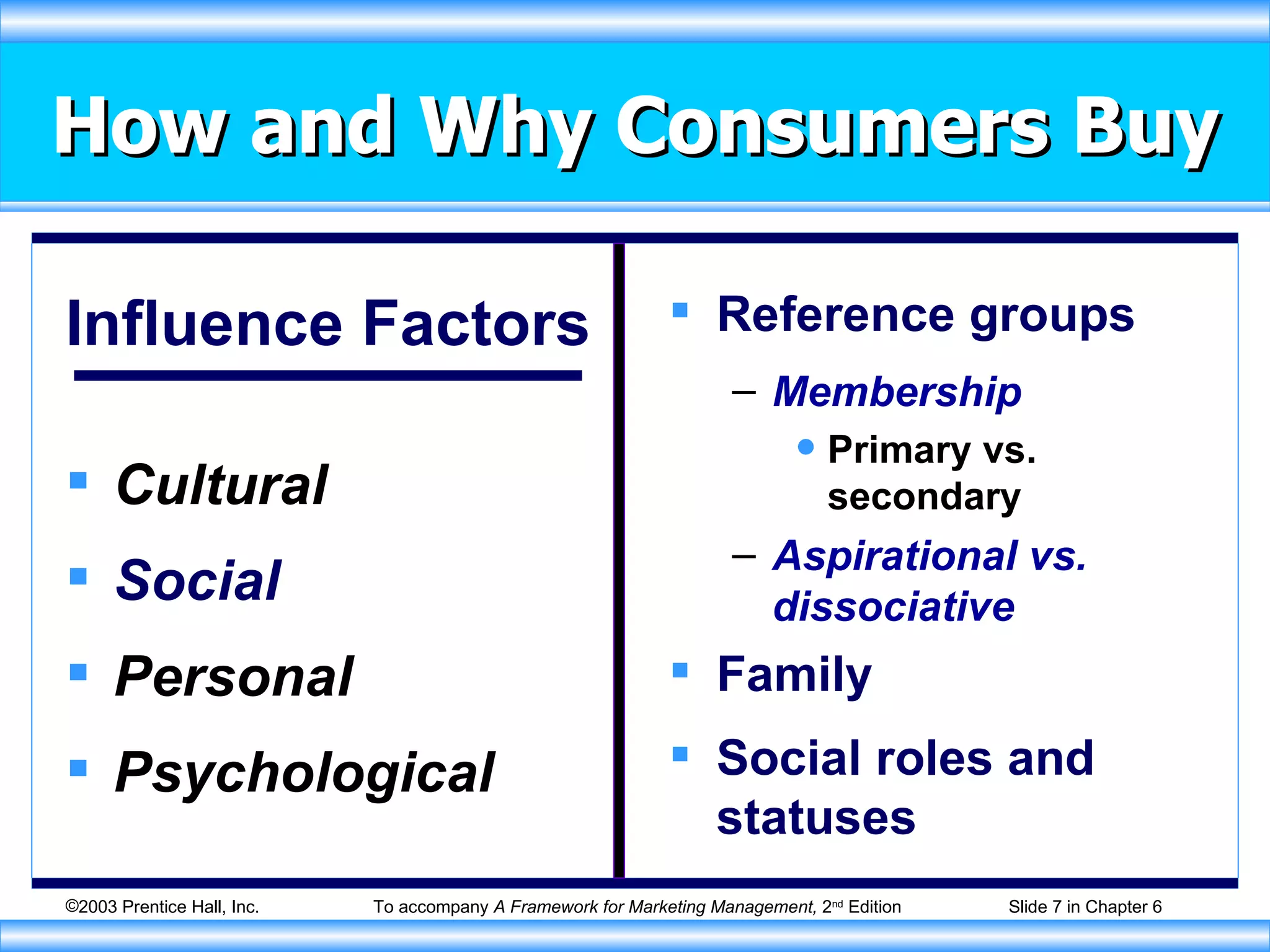
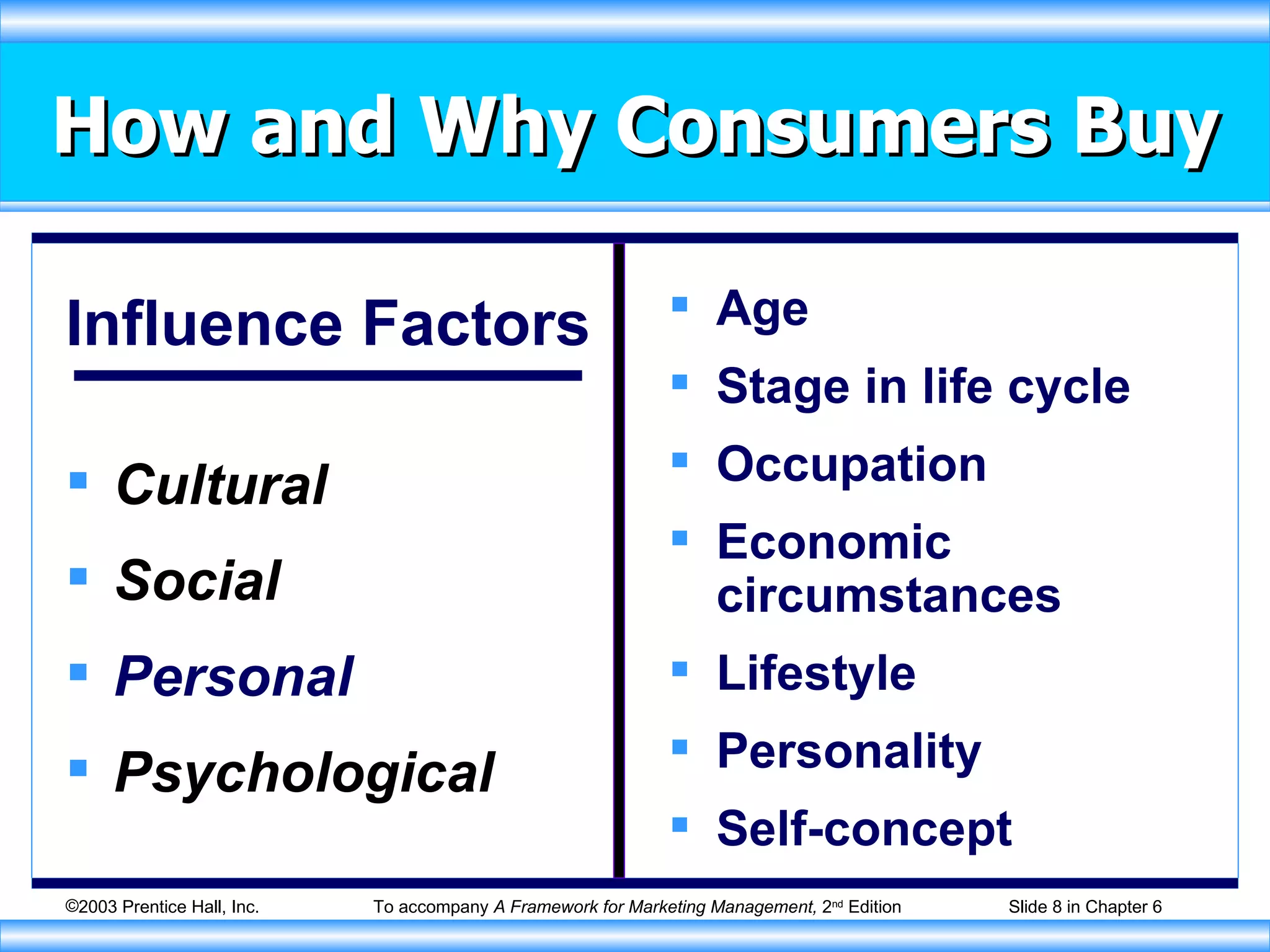
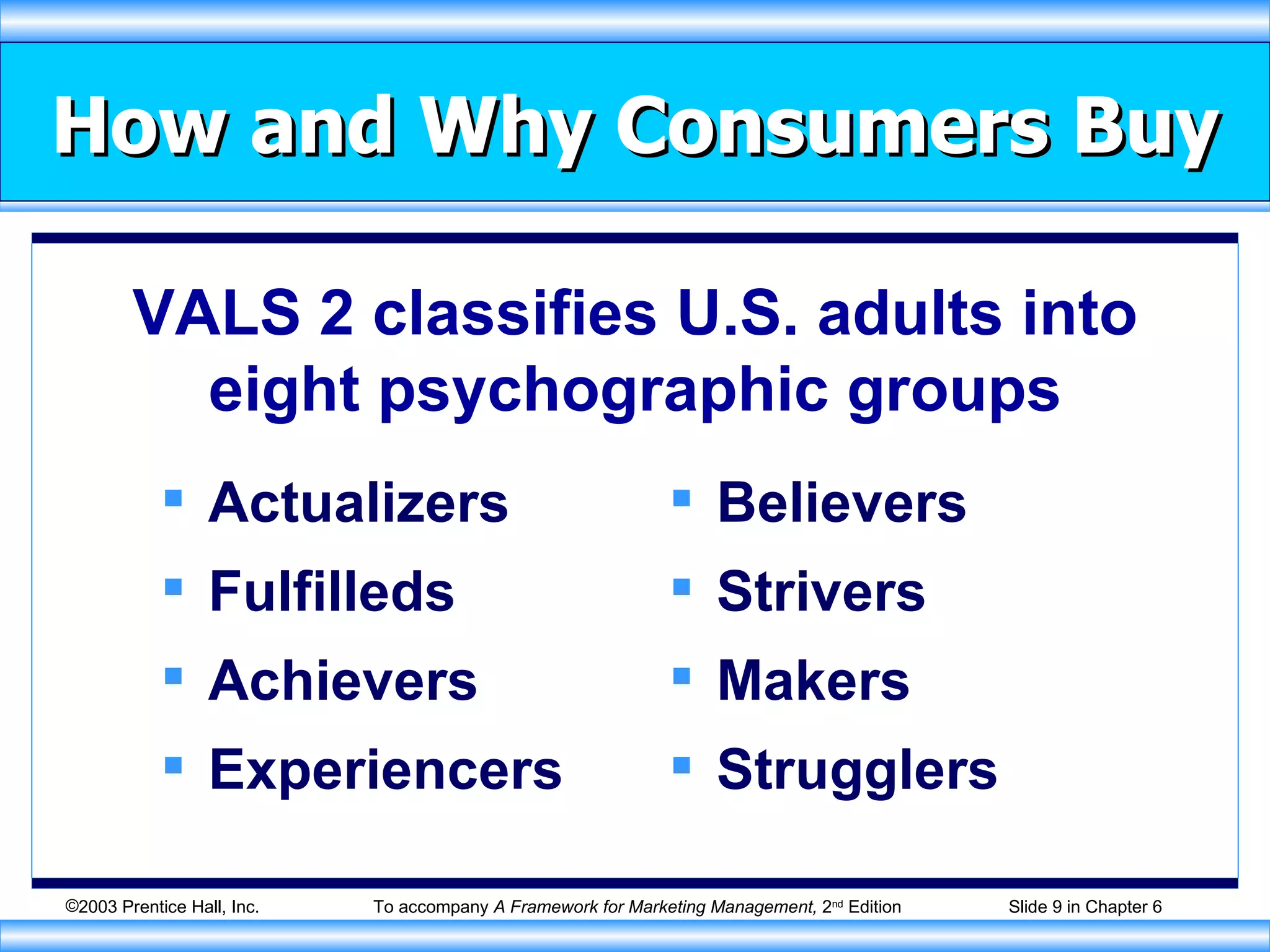
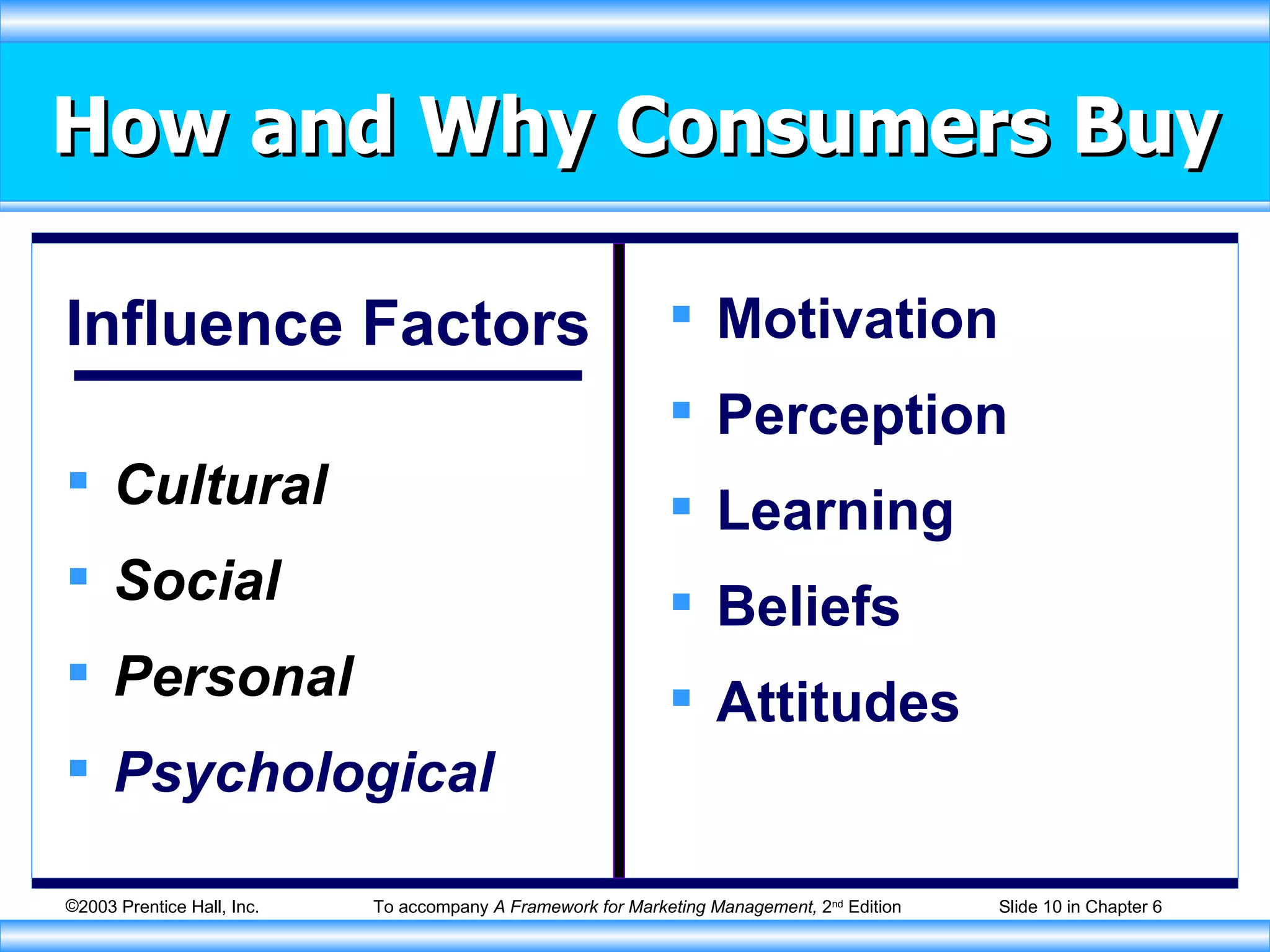
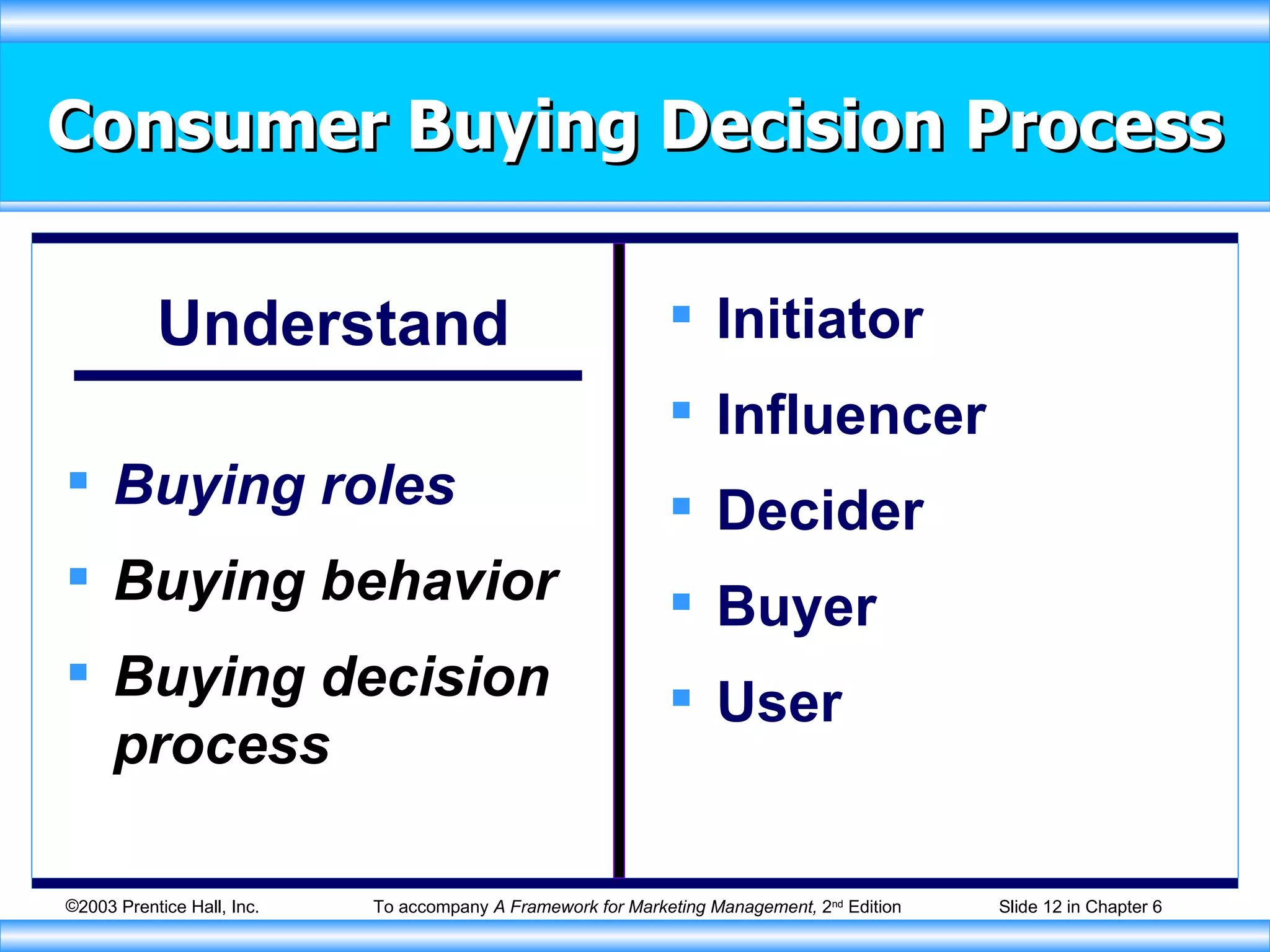
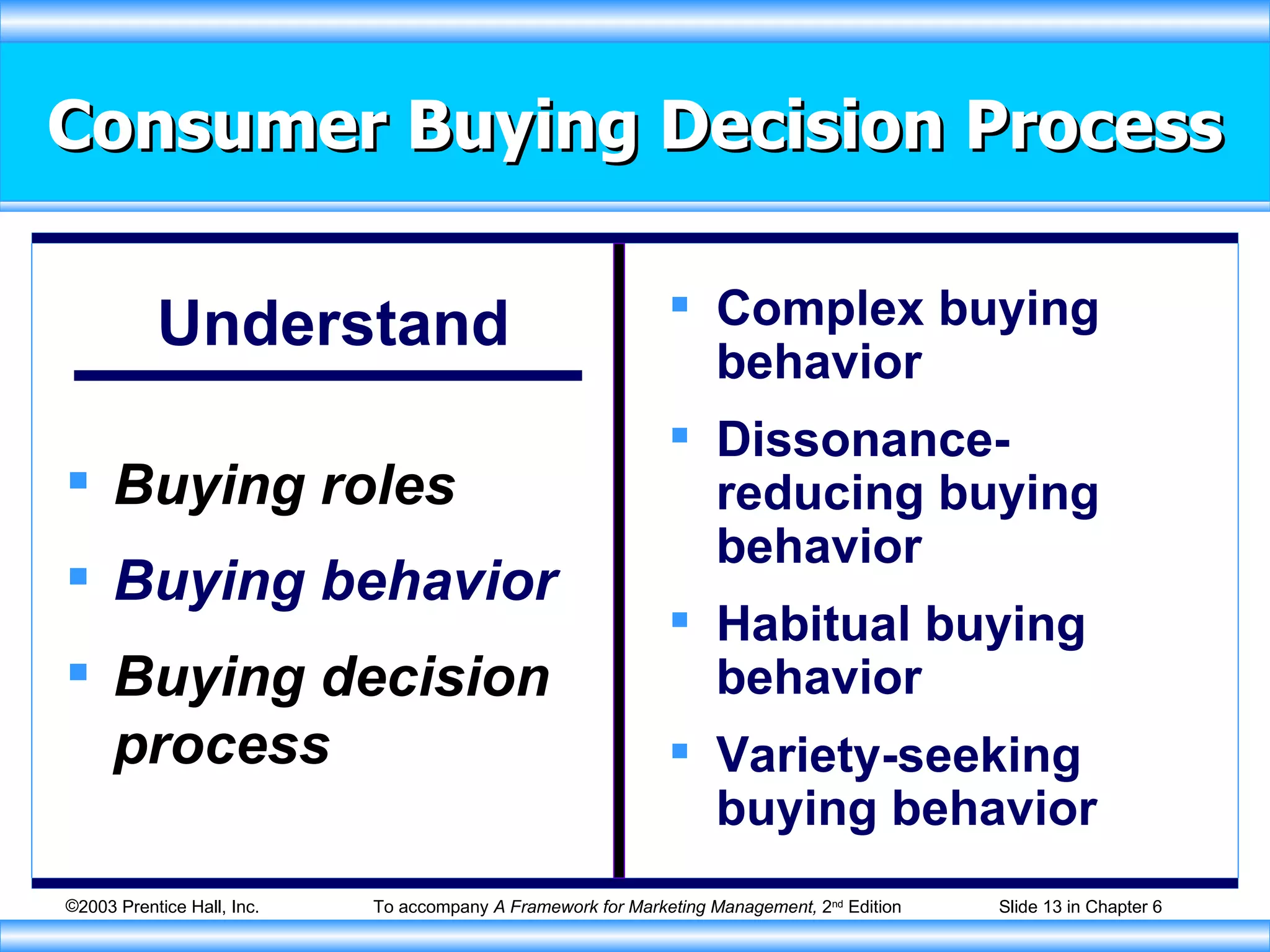
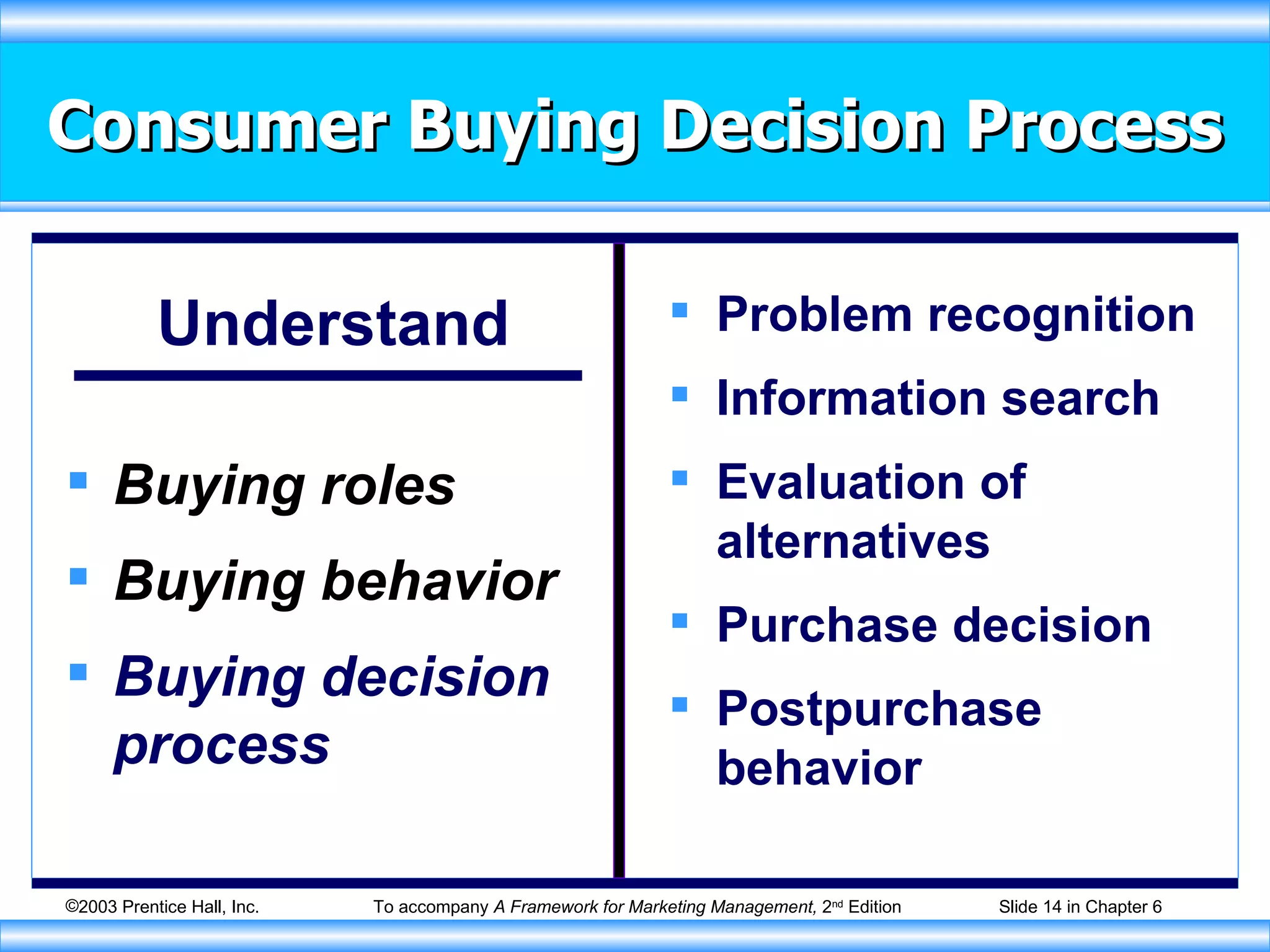
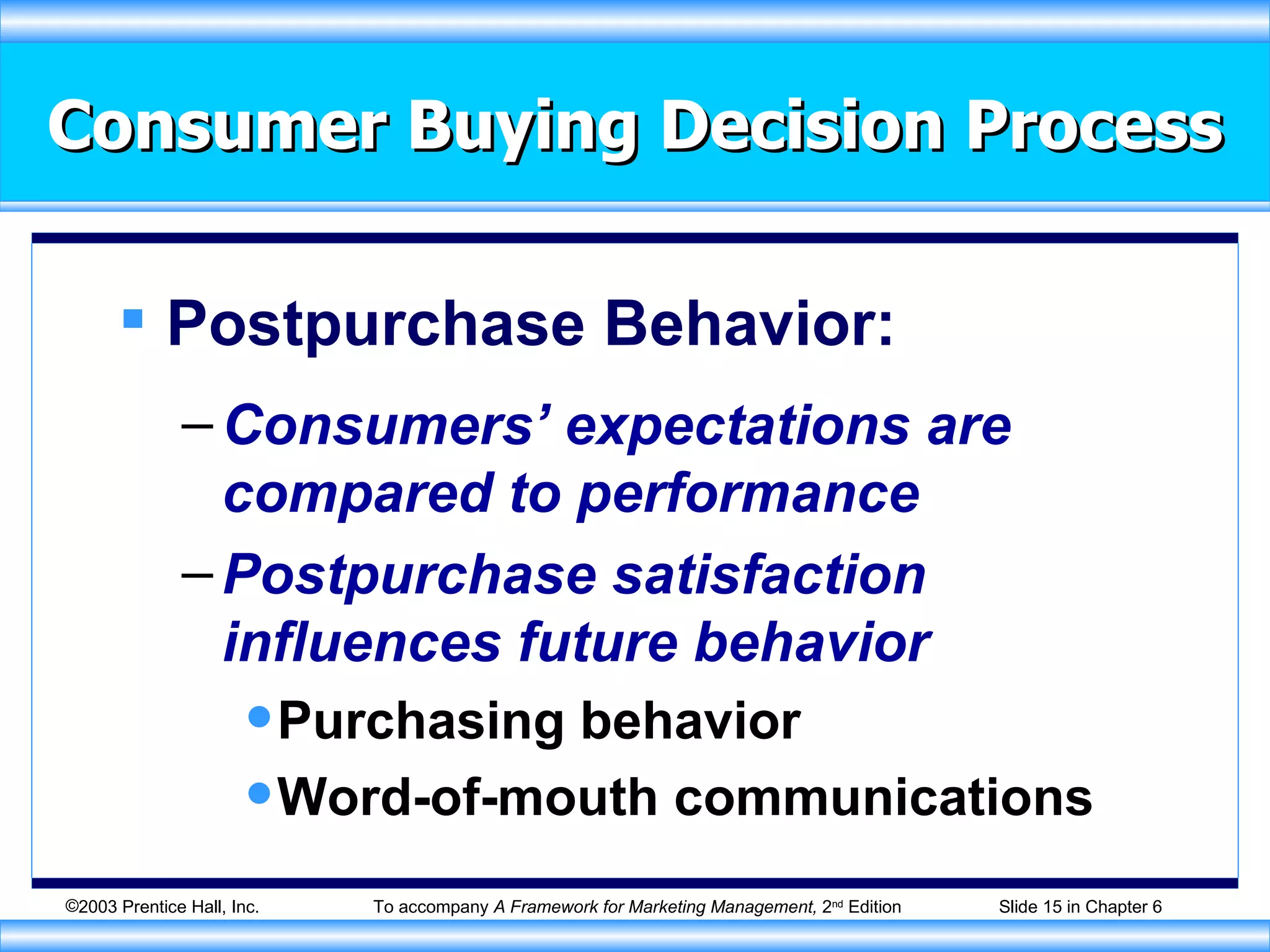
The document discusses factors that influence consumer buying behavior and the consumer decision-making process. It outlines that consumer behavior is shaped by cultural, social, personal, and psychological factors. It also describes the stages consumers go through in the buying process, including problem recognition, information search, evaluation, purchase, and post-purchase evaluation. Marketers need to understand these influences and stages to effectively market to consumers.