This document discusses the consumer decision process, with a focus on problem recognition and information search. It covers:
1) The stages of the consumer decision process, including problem recognition where consumers realize a gap between their actual and desired situation.
2) Factors that influence problem recognition like situational changes, marketing influences, and a consumer's actual vs desired state.
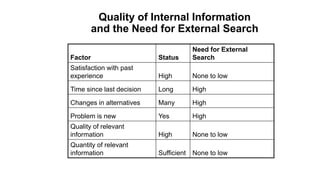
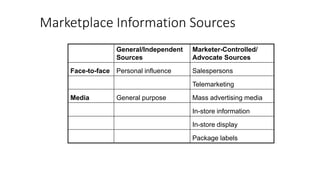
3) The different types of information search consumers engage in, including internal search using memory and external search of different sources.
4) Situational and individual factors that influence information search, and strategies consumers use to limit their search like using evoked sets of alternatives.