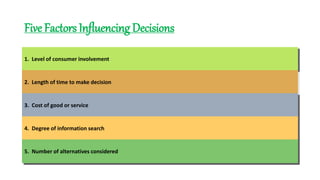
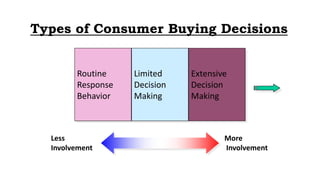
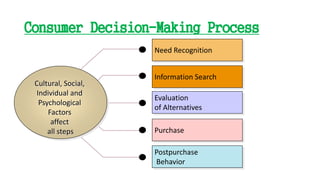
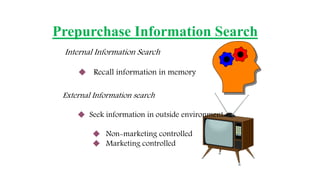
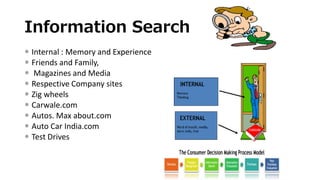
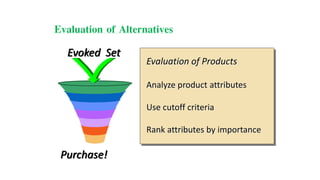
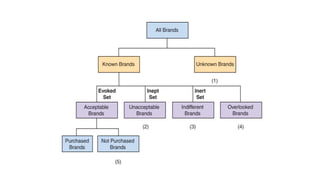
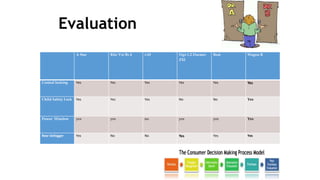
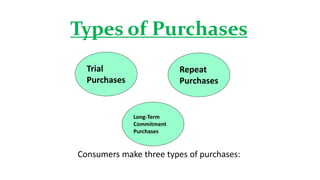
This document discusses the consumer decision making process. It outlines five factors that influence consumer decisions, as well as three levels of consumer decision making ranging from extensive problem solving to routine response behavior. The stages of the consumer decision making process are described, including need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase, and post-purchase behavior. An example consumer decision process for purchasing a new car is provided to illustrate these stages.