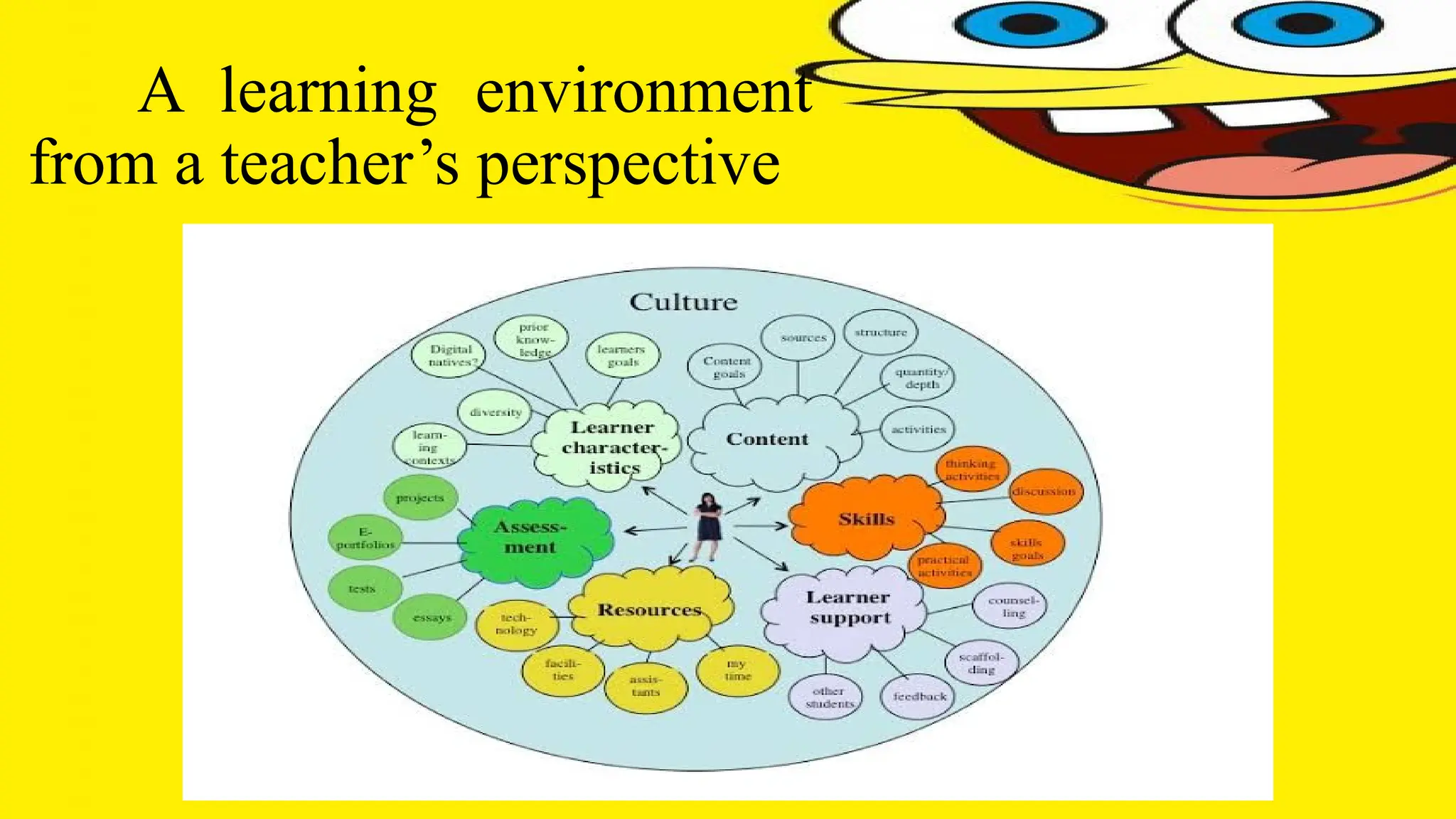
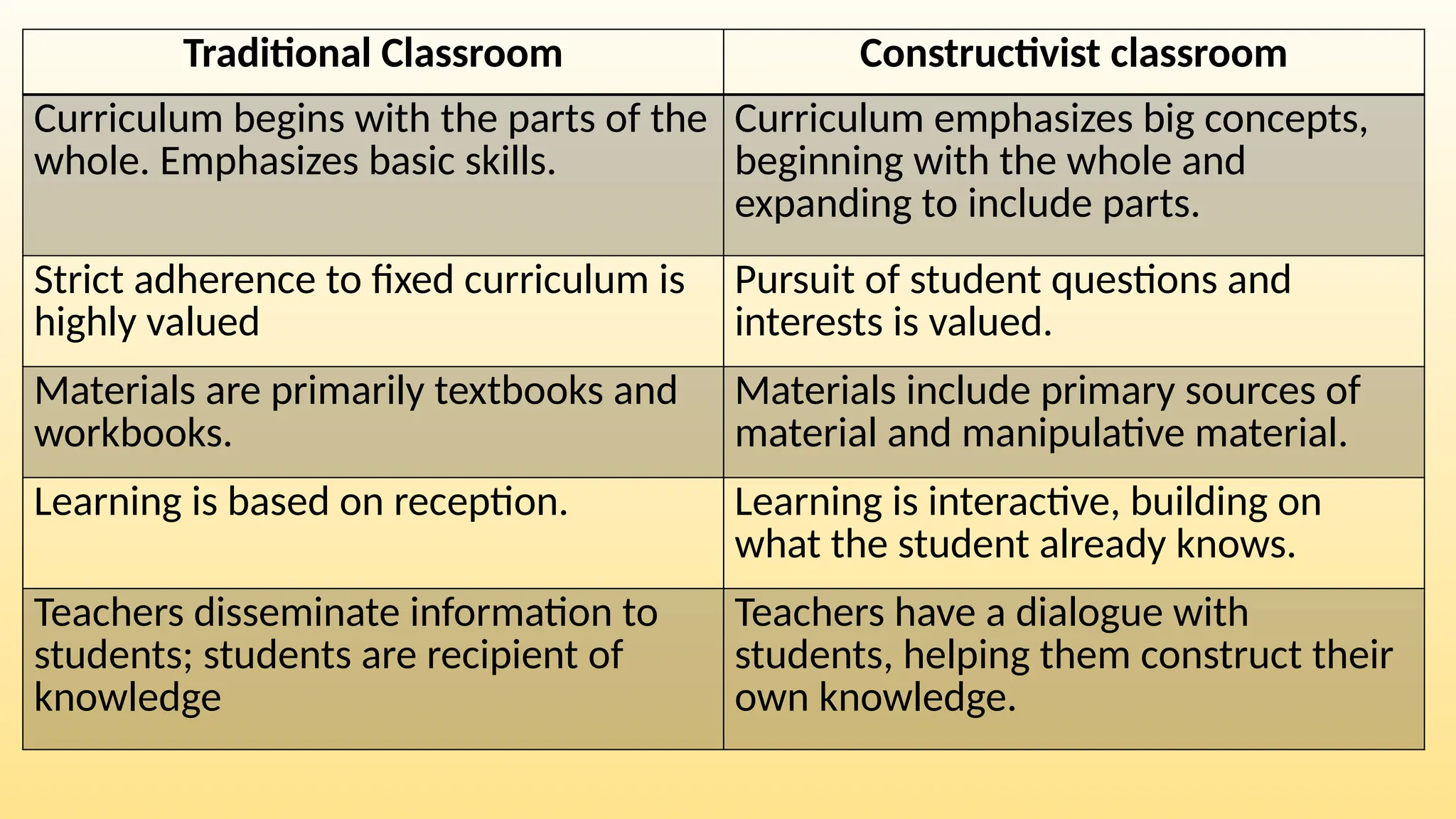
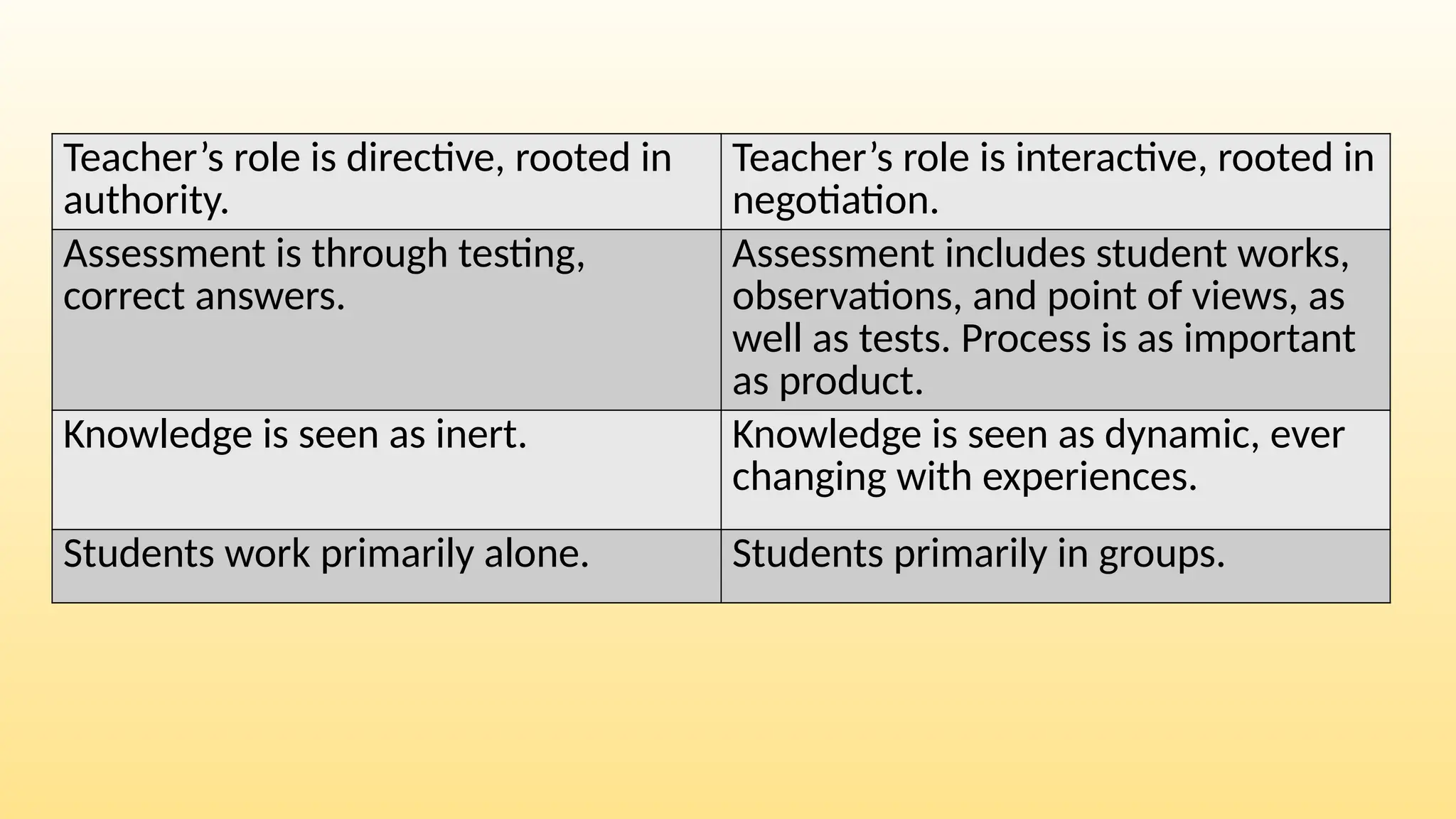
The document discusses the evolving concept of learning environments, emphasizing the shift from traditional to constructivist approaches influenced by theorists like Bruner, Vygotsky, and Piaget. Key principles of constructivism include active engagement, social interaction, and contextual learning, with technology playing a supportive role in facilitating these interactions. Teachers in a constructivist environment are seen as guides and mentors who design activities to help students construct their knowledge through dialogue and exploration.