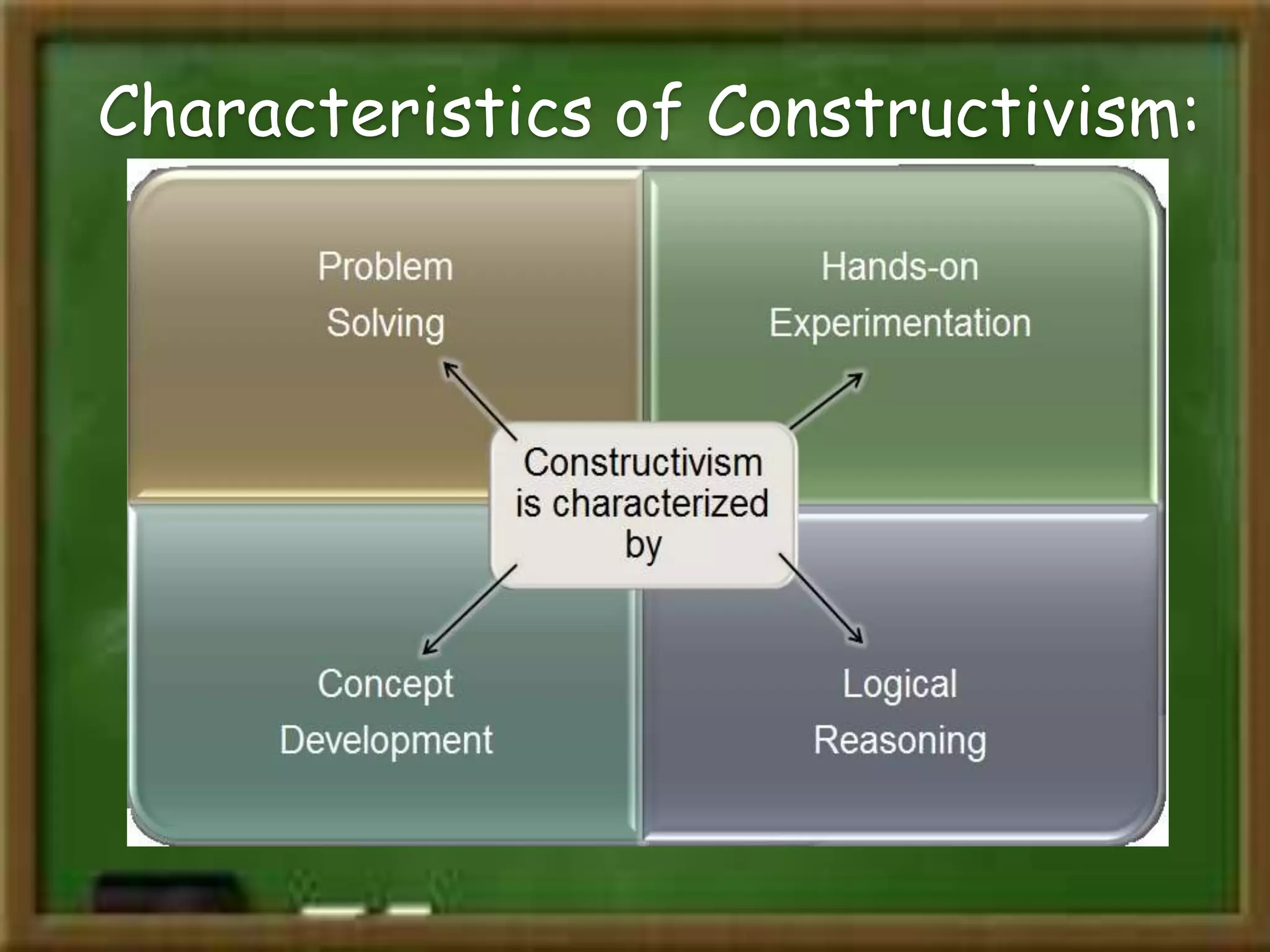
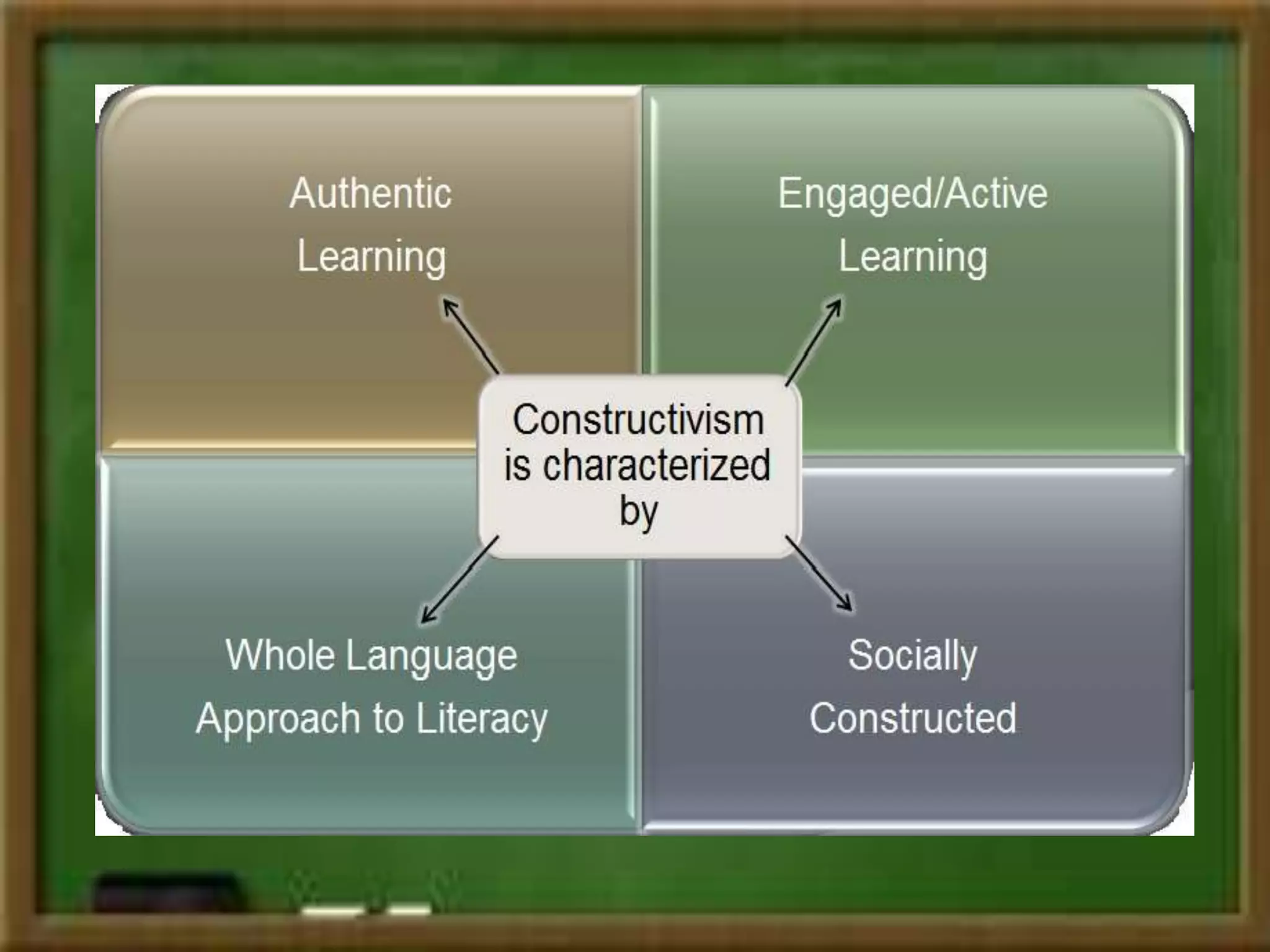
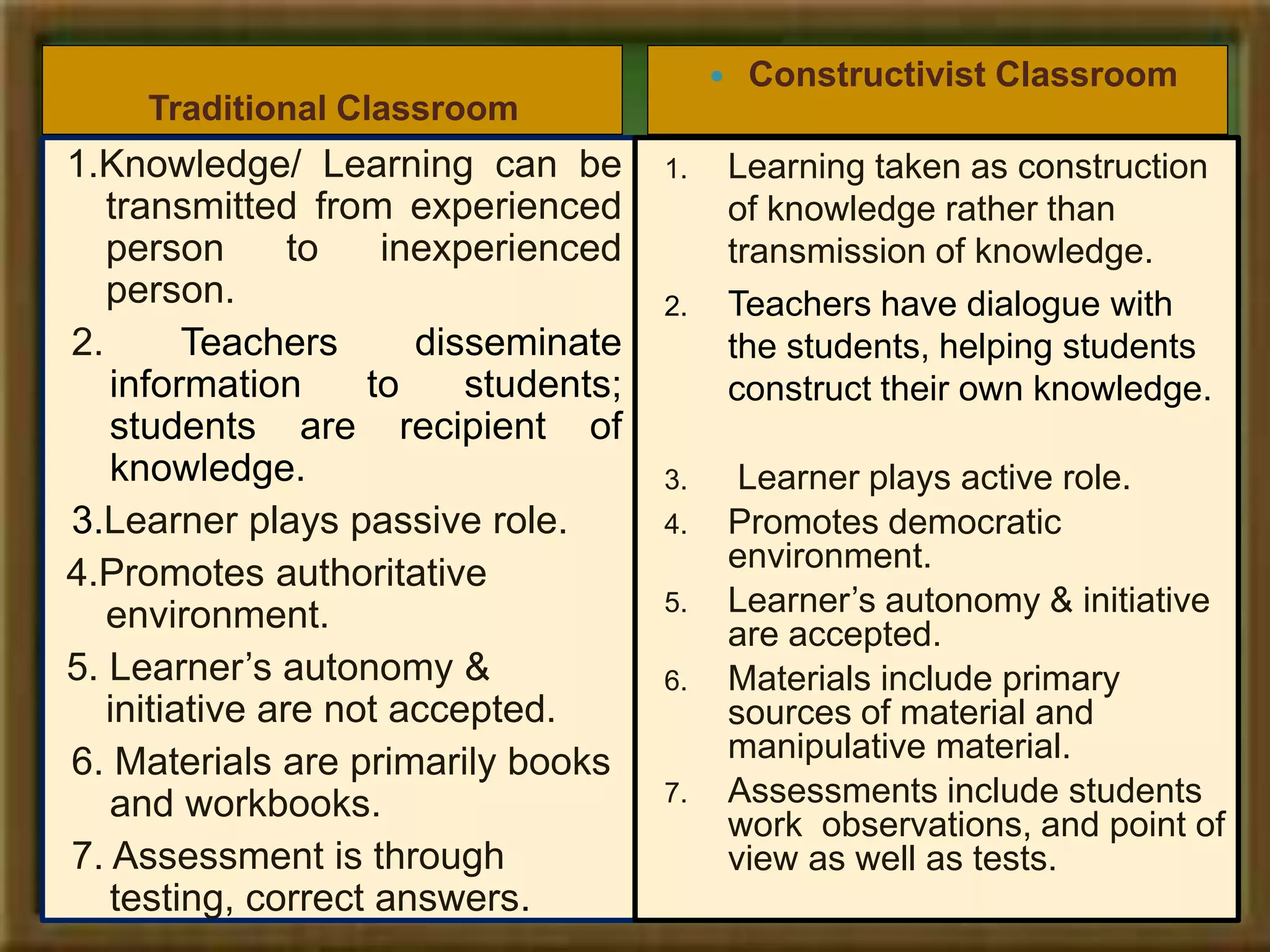
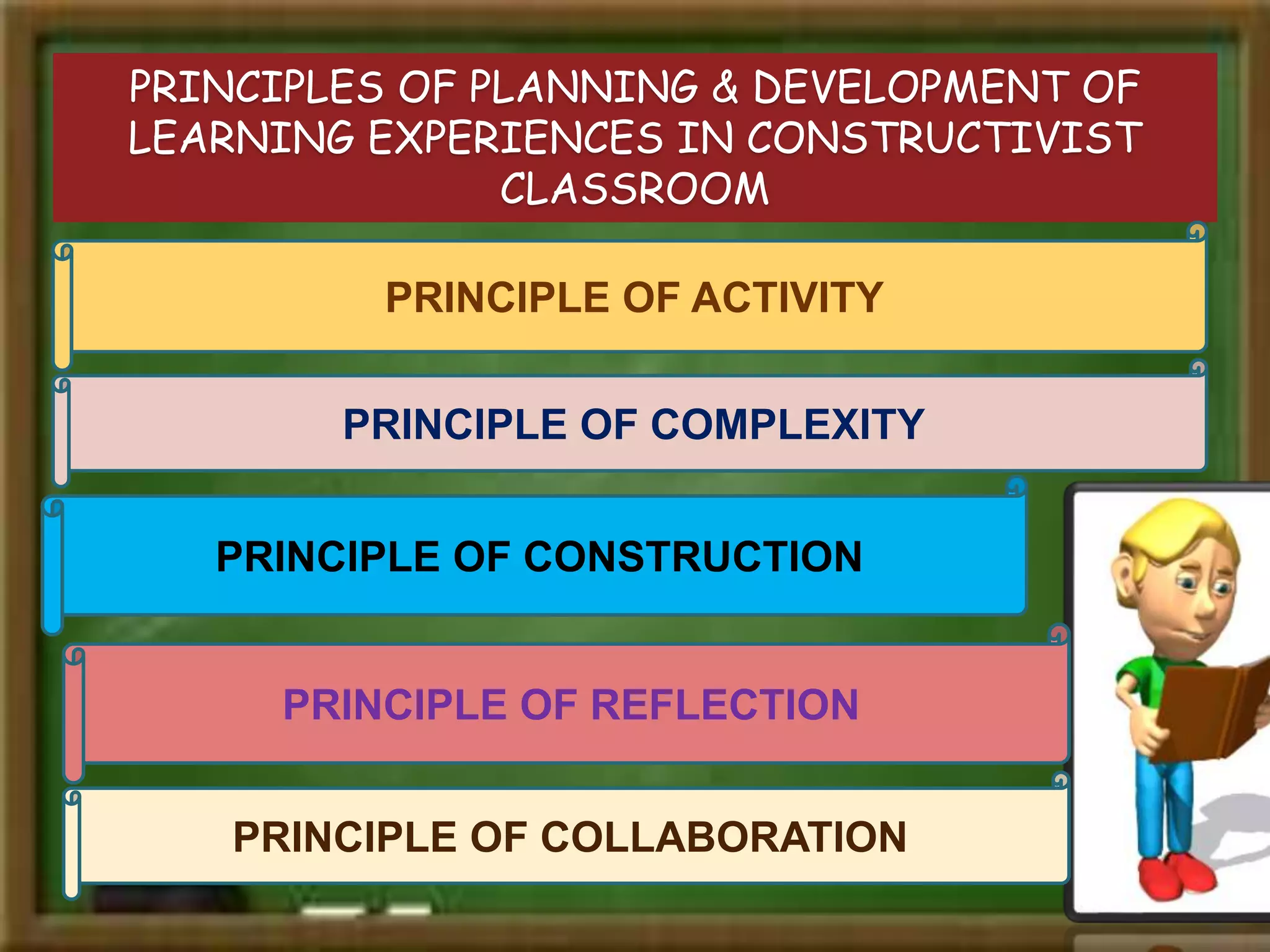
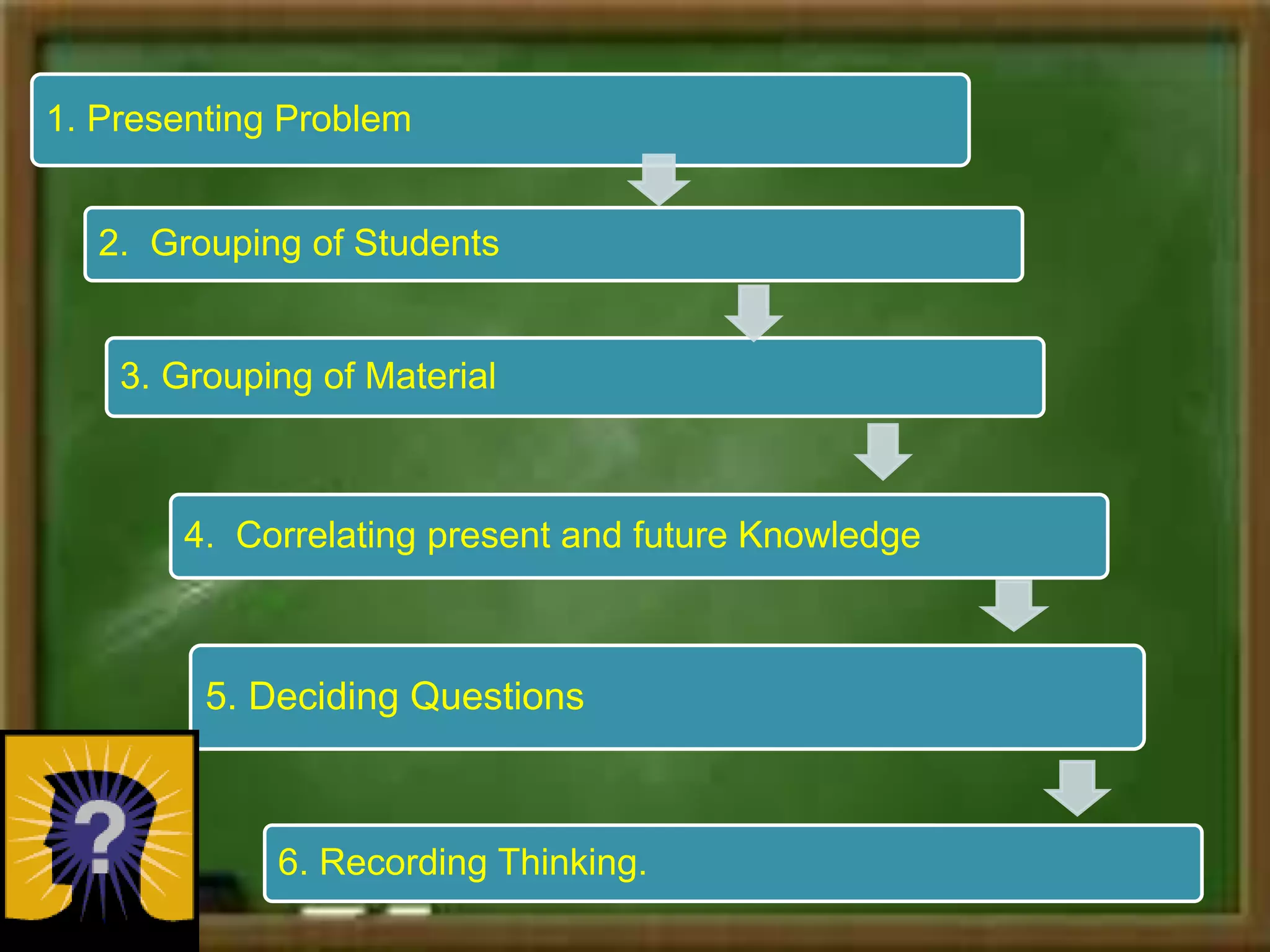
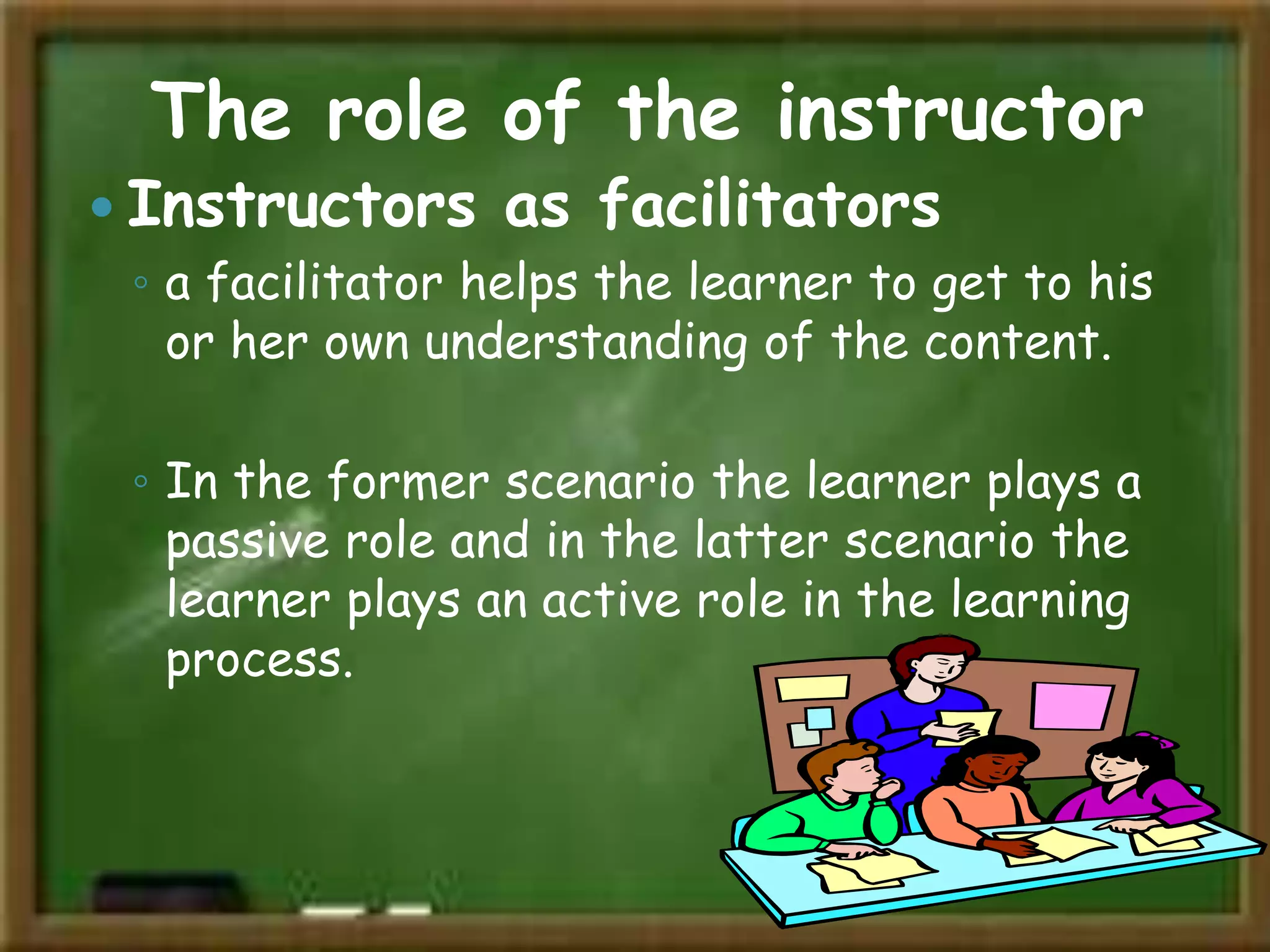
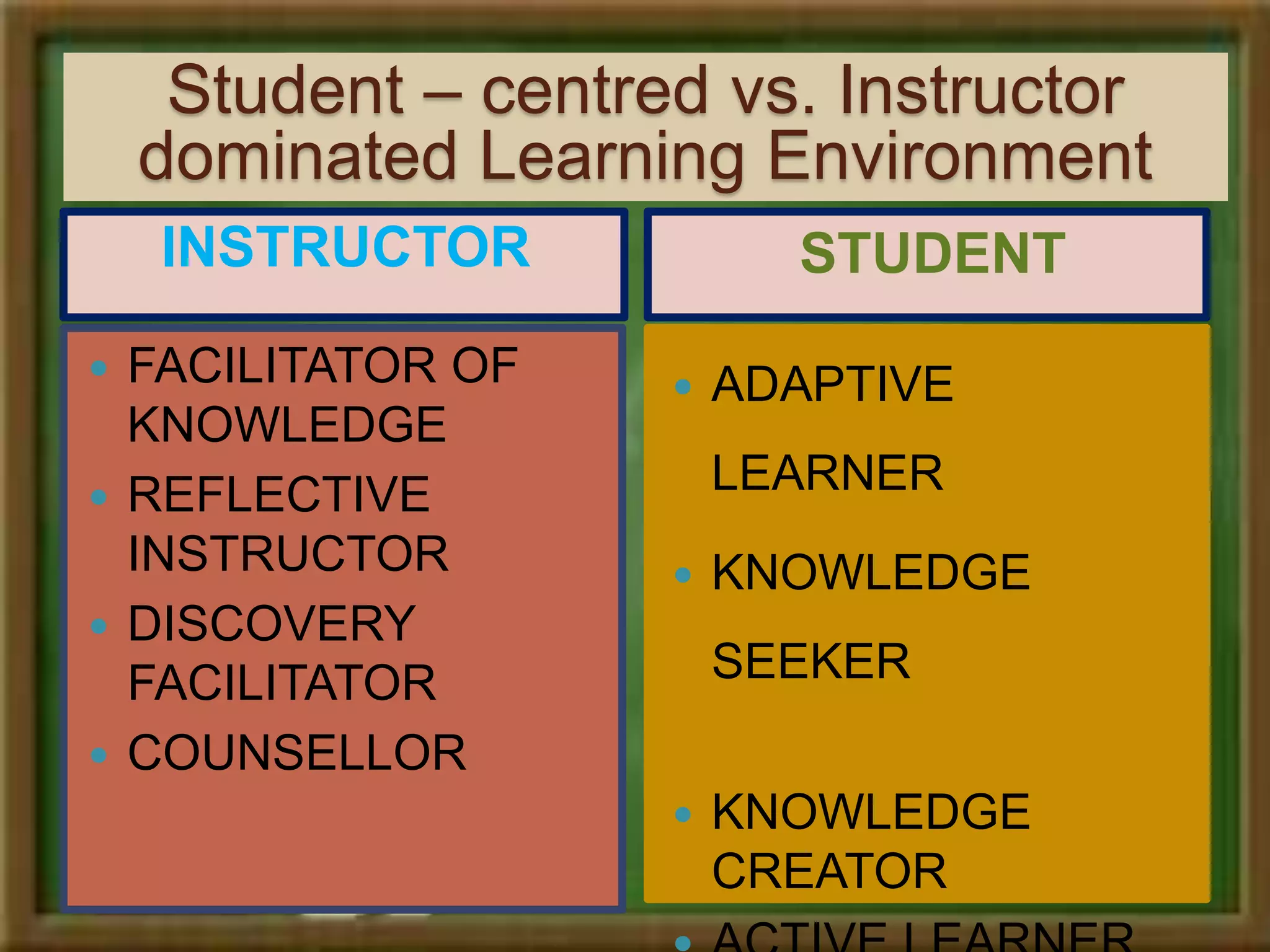
Constructivism is a theory of learning that states that individuals create or construct their own understanding and knowledge of the world through experiencing things and reflecting on those experiences. Key scholars who contributed to constructivism include Piaget, Vygotsky, and Bruner. There are two main views: individual constructivism which emphasizes individual construction of knowledge, and social constructivism which sees knowledge as constructed through social interactions. A constructivist classroom is learner-centered, uses open-ended learning activities, and positions the teacher as a facilitator rather than lecturer.