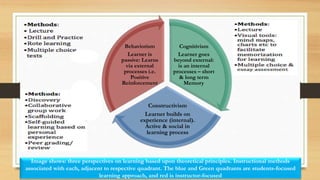
This document discusses three learning theories: behaviorism, cognitivism, and constructivism. Behaviorism sees learning as changes in observable behavior and focuses on external conditioning processes. Cognitivism views learning as an internal process of acquiring and organizing cognitive structures through memory, rules, and thinking. Constructivism posits that learners construct knowledge by working to solve realistic problems. Each theory provides a different perspective on the learning process and informs different instructional approaches, with behaviorism focusing on external reinforcement, cognitivism on developing cognitive abilities, and constructivism emphasizing hands-on, student-centered active learning.