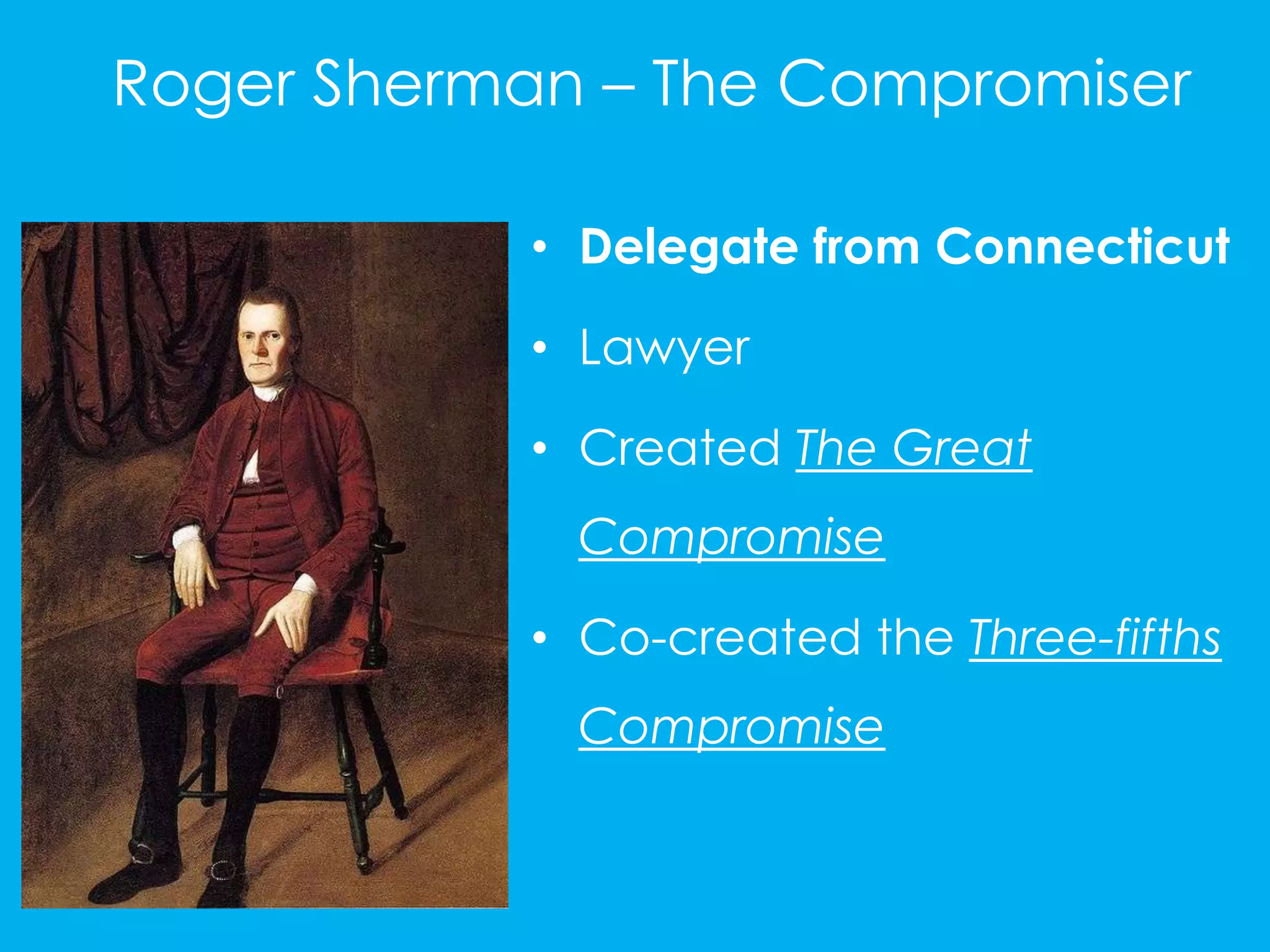
The 1787 Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia debated major issues around representation of states in the new federal government. The Virginia Plan proposed representation based on population, favoring large states, while the New Jersey Plan proposed equal representation for each state, favoring small states. Roger Sherman created the Great Compromise, establishing a bicameral Congress with proportional representation in the House and equal representation in the Senate. They also debated whether slaves should count toward state population. The Three-Fifths Compromise counted each slave as three-fifths of a person to determine taxes and representation.