Embed presentation
Downloaded 95 times
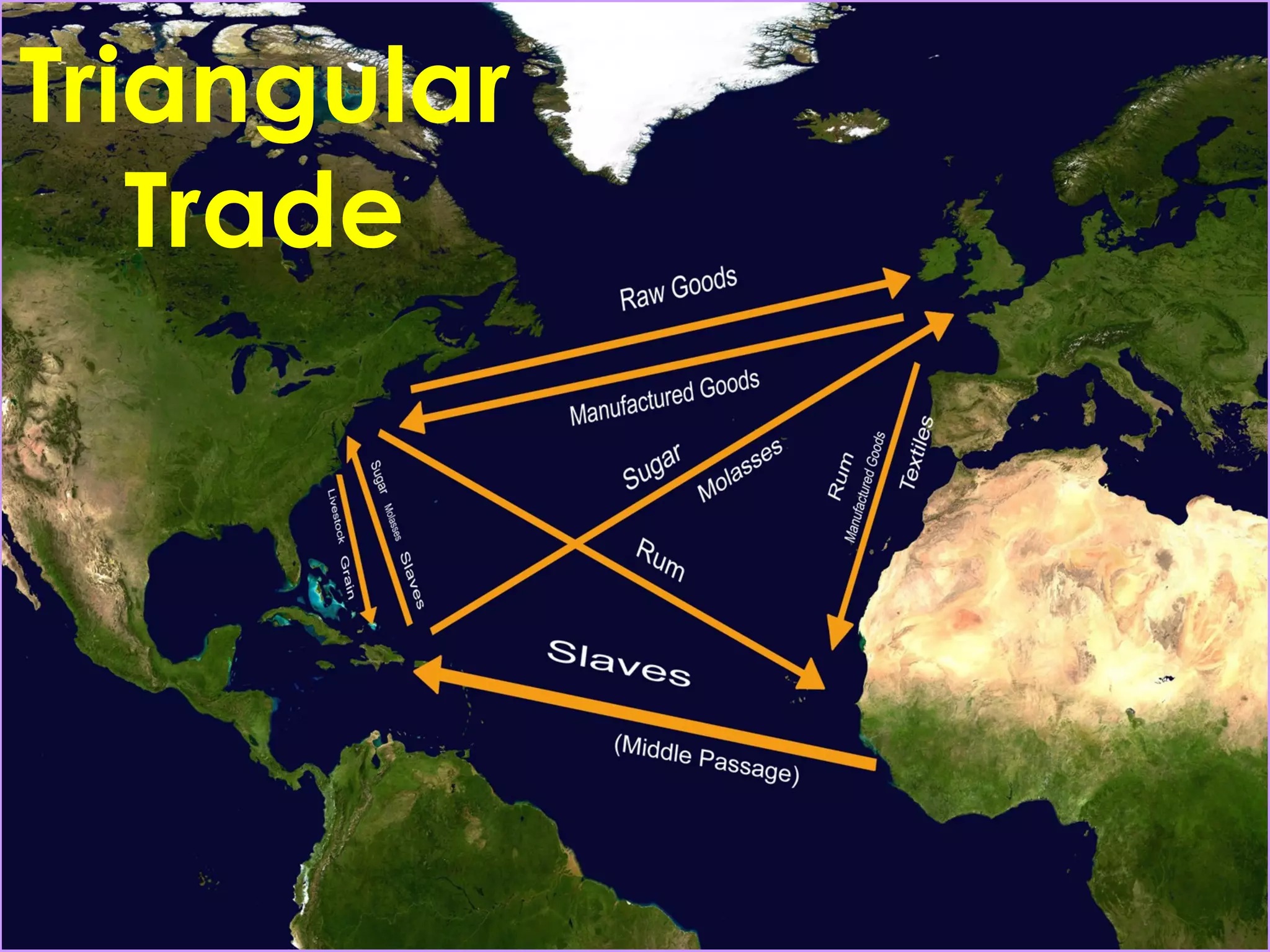




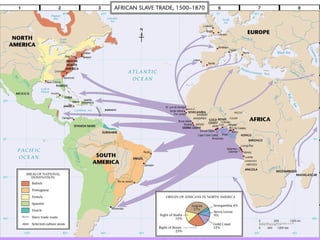

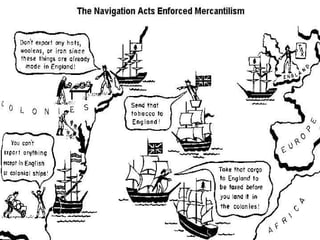
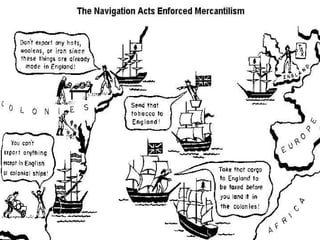
The document describes the triangular trade system that developed between England, its North American colonies, Africa, and the West Indies. Raw materials from the colonies were exported to England, where they were used to manufacture goods that were then shipped to Africa and the West Indies. Enslaved Africans purchased on the coast of Africa made up the third leg of the triangle, transported via the brutal Middle Passage to the colonies and West Indies to be sold and used as slaves, completing the cycle of trade. The system was driven by European mercantilist policies that aimed to accumulate wealth for the parent countries.









