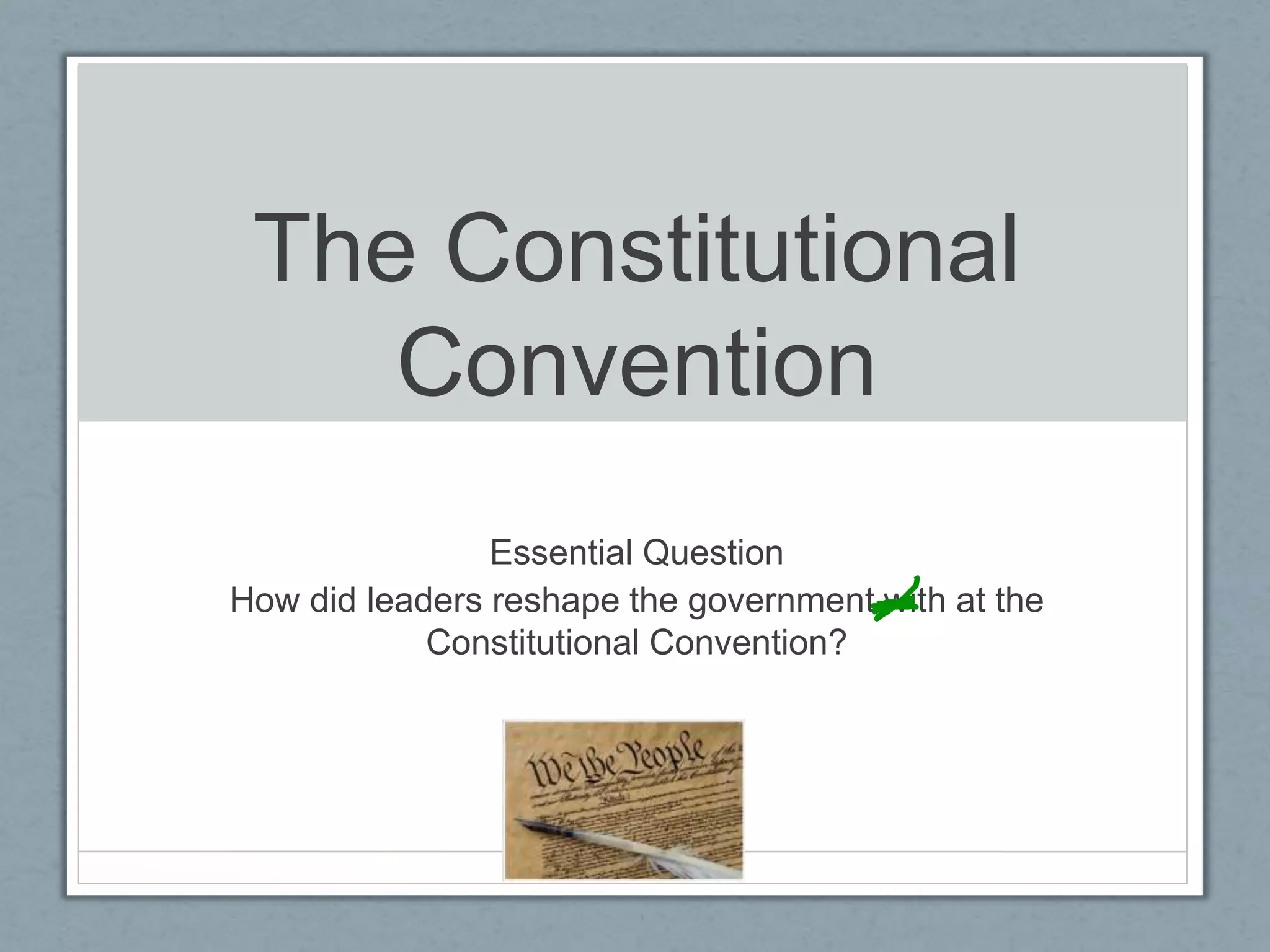
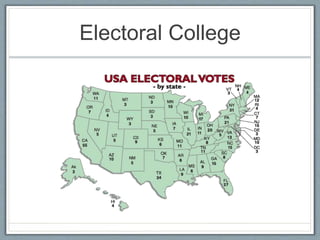
The Constitutional Convention was called to address issues with the weak central government under the Articles of Confederation. Delegates debated plans for the new government, including the Virginia Plan which proposed a two-house legislature based on population and the New Jersey Plan which proposed one house with equal state representation. The Great Compromise blended these ideas by creating a bicameral legislature with proportional representation in the House and two senators per state in the Senate. Additionally, the Three-Fifths Compromise was adopted to determine representation and taxation based on state populations, including counting slaves as three-fifths of a person. The convention also established the executive and judicial branches and a process for electing the president through the Electoral College