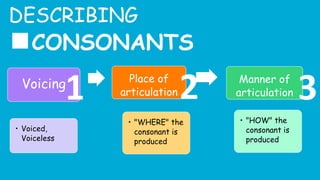
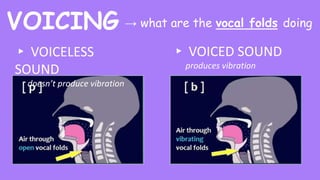
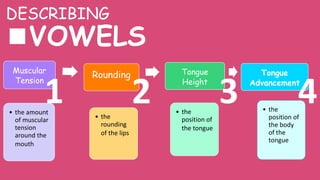
This document provides information about describing consonants and vowels in the English language. It discusses the key aspects of consonants, including voicing, place of articulation, and manner of articulation. It describes 9 places of articulation for consonants, including bilabial, labiodental, interdental, alveolar, and velar. It also outlines 7 manners of articulation such as plosives, fricatives, and nasals. For vowels, it covers muscular tension, rounding, tongue height, and tongue advancement as the main factors for distinguishing vowels. Examples are provided to demonstrate different consonant and vowel sounds.

![PLACE OF ARTICULATION
→ where the constriction of airflow takes place
1.BILABIAL
both lips come together
Active ▹ Lower lip
Passive ▹ Upper lip
[p] as in "purse" and "rap”
[b] as in "back" and "cab”
[m] as in "mad" and "clam”
[w] as in "wet" and "how”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160329123926/85/Consonants-and-Vowels-4-320.jpg)
![PLACE OF ARTICULATION
2.LABIODENTAL :
curling your lower lip back and
raising it to touch your upper teeth
Active ▹ Lower lip
Passive ▹ Upper teeth
[f] as in "fall" and “half”
[v] as in "vine" and "have"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160329123926/85/Consonants-and-Vowels-5-320.jpg)
![PLACE OF ARTICULATION
3. INTERDENTAL :
placing tip of tongue against
upper teeth
Active ▹ Tip of
tongue
Passive ▹ Upper teeth
[θ] as is "thick" and "bath”
[ð] as in "the" and "rather"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160329123926/85/Consonants-and-Vowels-6-320.jpg)
![PLACE OF ARTICULATION
4. ALVEOLAR :
The tongue tip touches the
alveolar ridge.
Active ▹ Tip of tongue
Passive ▹ Alveolar ridge
[n] as in "no" and "man”
[t] as in "tab" and "rat”
[d] as in "dip" and "bad”
[s] as in "suit" and "bus”
[z] as in "zit" and "jazz”
[l] as in "luck" and "full"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160329123926/85/Consonants-and-Vowels-7-320.jpg)
![PLACE OF ARTICULATION
5. ALVEO-PALATAL :
The tongue tip touches the
back of the alveolar ridge.
Active ▹ Tip of tongue
Passive ▹ the hard palate
[ ʃ ] as in "shoot" or "brash"
[ʒ] as in "vision" or "measure”
[tʃ ] as in "chick" or "match"
[dʒ] as in "jam" or "badge”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160329123926/85/Consonants-and-Vowels-8-320.jpg)
![PLACE OF ARTICULATION
6.RETROFLEX :
The tongue tip is curled up toward
the hard palate.
Active ▹ Tip of tongue
Passive ▹ The hard palate
[r] as in “run" and “rabbit”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160329123926/85/Consonants-and-Vowels-9-320.jpg)
![PLACE OF ARTICULATION
7.PALATAL :
The front of the tongue touches
the hard palate.
Active ▹ The front of the
tongue
Passive ▹ The hard palate
[j] as in "yes" and “beyond”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160329123926/85/Consonants-and-Vowels-10-320.jpg)
![PLACE OF ARTICULATION
8.VELAR :
the back of the tongue touches the
soft palate, or velum.
Active ▹ the back of the
tongue Passive ▹ the soft palate
[ŋ] as in "going" and "uncle”
[k] as in "kite" and "back”
[g] as in "good" and "bug”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160329123926/85/Consonants-and-Vowels-11-320.jpg)
![PLACE OF ARTICULATION
9.GLOTTAL :
The opening between the vocal folds
is narrow enough to create some
turbulence in the airstream flowing
past the vocal folds.
[h] as in "hi" and “horse"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160329123926/85/Consonants-and-Vowels-12-320.jpg)
![Plosives or Stop
▷ the air quickly builds up pressure
behind the articulators and then
releases in a burst.
[p] [b] [t]
[d] [k] [g]
→ how the airflow is constricted
MANNER OF ARTICULATION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160329123926/85/Consonants-and-Vowels-13-320.jpg)
![Fricative
▷The air has to be forced through
a narrowchannel.
[f] [v] [θ]
[ð] [s] [z]
[ ʃ ] [ʒ] [h]
MANNER OF ARTICULATION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160329123926/85/Consonants-and-Vowels-14-320.jpg)
![Affricates
▷ a combination of a stop
and a fricative that make one
new sound. The sounds begin with
a stop and end in a fricative.
[tʃ] [dʒ]
MANNER OF ARTICULATION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160329123926/85/Consonants-and-Vowels-15-320.jpg)
![▷ the air pass through
your nose.
[m] [n] [ŋ]
MANNER OF ARTICULATION
Nasal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160329123926/85/Consonants-and-Vowels-16-320.jpg)
![▷ Two articulators come
close together but not
quite close enough to
create air turbulence.
[w] [ j ] [r]
MANNER OF ARTICULATION
Approximants
▷ The tongue blocks the
middle of your mouth so
that air has to pass
around the sides.
[ l ]
Lateral Approx.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160329123926/85/Consonants-and-Vowels-17-320.jpg)
![EXERCISE ► CONSONANTS
TABOO
[təˈbuː]
THROW
[θrəʊ]
SINGER
[ˈsɪŋə]
Voiced — Bilabial — Plosive
Voiceless — Interdental — Fricatives
Voiced — Velar — Nasal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160329123926/85/Consonants-and-Vowels-18-320.jpg)
![EXERCISE ► VOWELS
THROUGH
[θruː]
STAND
[stand]
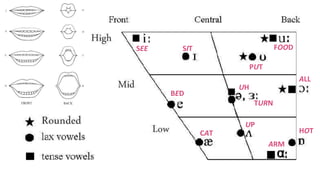
Tense — Rounded — High — Back
Lax — Unrounded — Low — Front
http://cambridgeenglishonline.com/Phonetics_Focus/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160329123926/85/Consonants-and-Vowels-21-320.jpg)