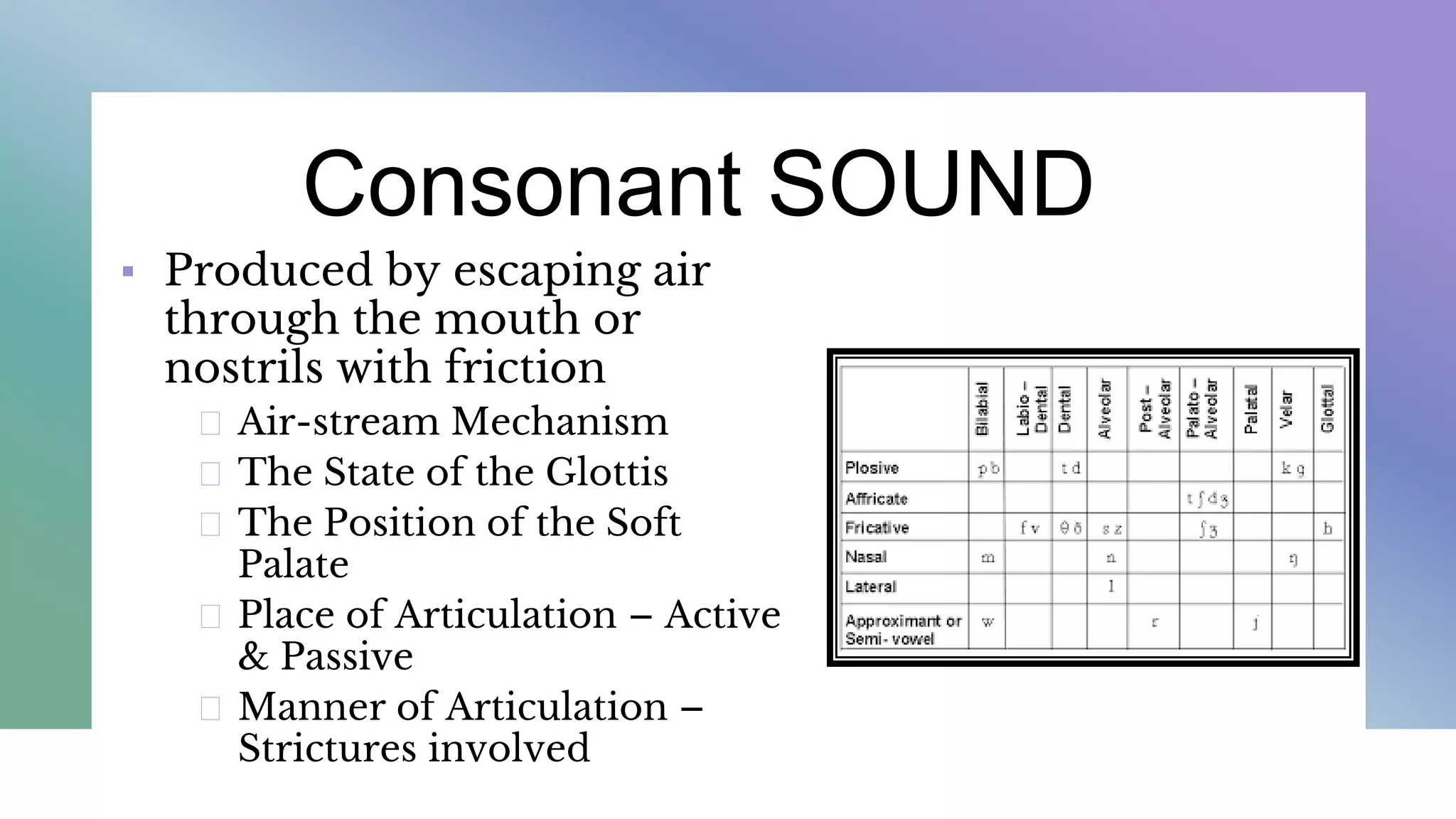
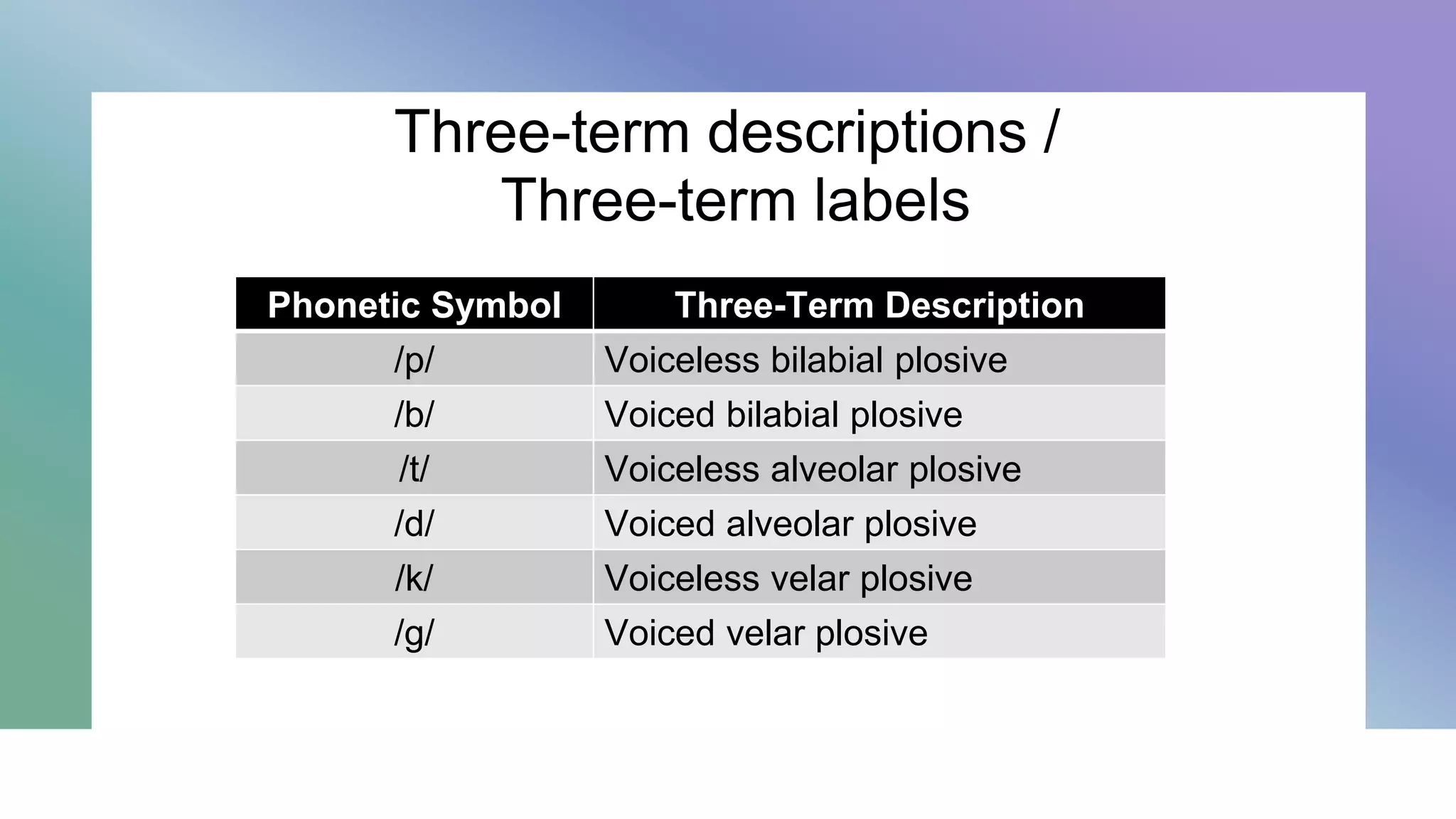
This document describes the classification and description of consonant sounds. It discusses the air-stream mechanism, state of the glottis, position of the soft palate, place of articulation (active/passive articulators), and manner of articulation (plosives, affricates, nasals, fricatives, continuants, laterals, trills) used to describe consonant sounds. It also provides examples of three-term descriptions for various consonant sounds using their state of the glottis, place of articulation, and manner of articulation.