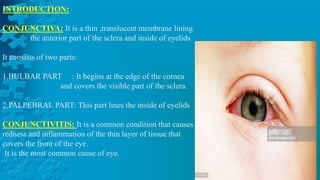
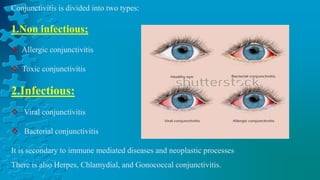
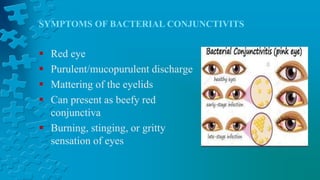
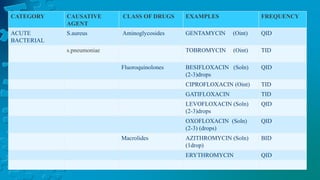
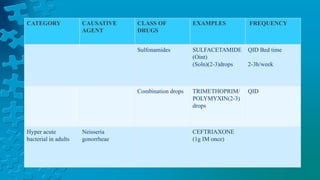
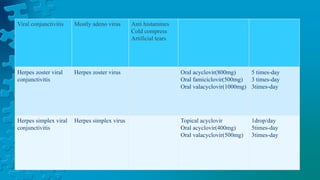
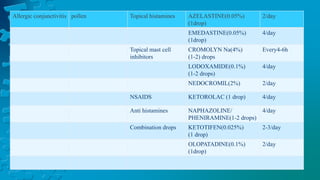
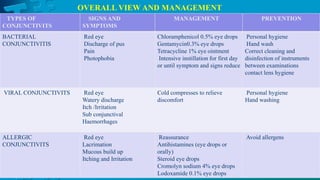
The document provides a detailed overview of conjunctivitis, including its definition, causes, types, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. It categorizes conjunctivitis into infectious and non-infectious types and describes specific conditions like allergic and bacterial conjunctivitis. Preventive measures and references for further reading are also included.