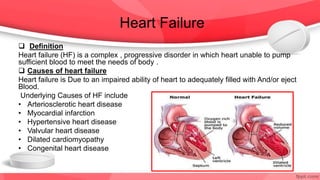
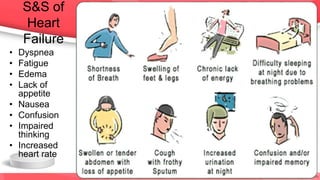
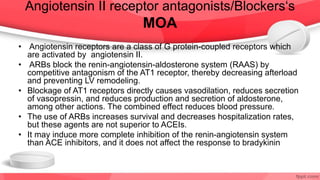
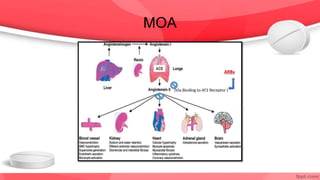
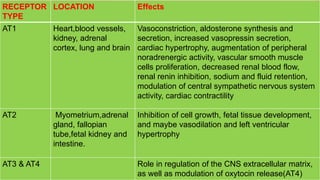
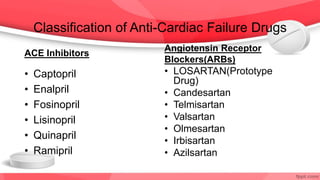
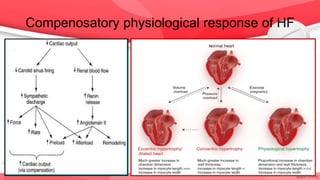
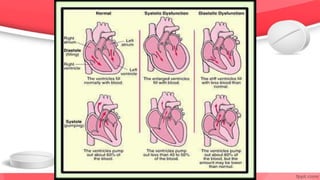
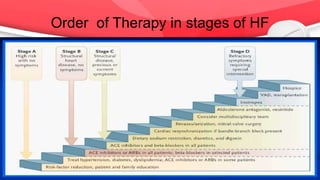
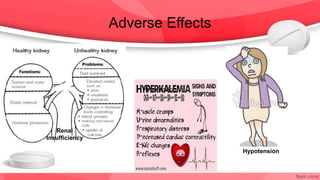
This document provides an overview of drugs for congestive heart failure. It defines heart failure as the heart's inability to pump sufficient blood to meet the body's needs. Causes include diseases like atherosclerosis, heart attacks, and hypertension. Signs and symptoms include dyspnea, fatigue, edema, and confusion. Angiotensin receptor blockers work by competitively blocking angiotensin II receptors, reducing blood pressure, afterload, and remodeling of the left ventricle. Common drug classes discussed are ACE inhibitors, ARBs, diuretics, beta-blockers, and aldosterone antagonists. Stages of heart failure and appropriate therapies are also covered.