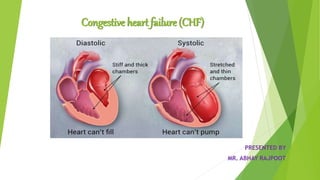
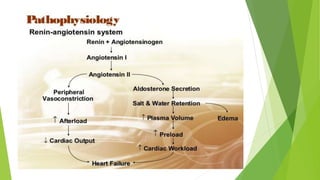
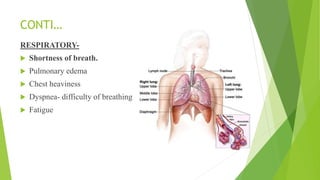
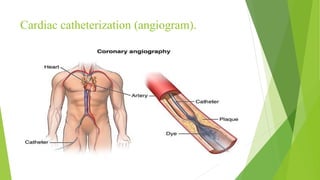
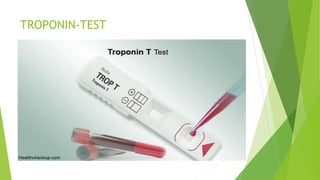
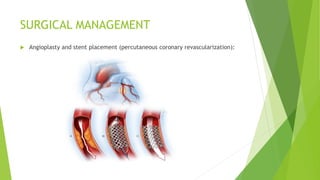
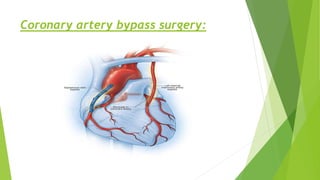
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a chronic condition characterized by the inefficient pumping of the heart due to fluid buildup. In India, its prevalence due to risk factors like coronary heart disease and obesity is estimated between 1.3 to 4.6 million, with symptoms that include shortness of breath, chest pain, and fatigue. Management involves lifestyle modifications, medications like nitrates and beta-blockers, and possible surgical interventions.