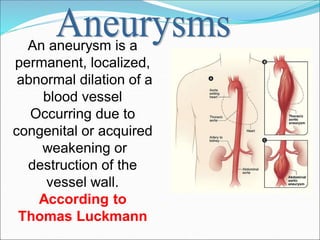
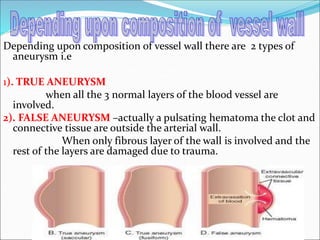
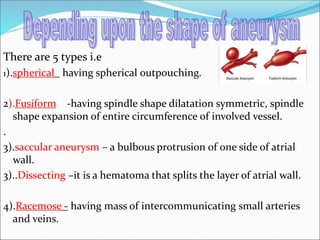
This document provides information about aneurysms and peripheral vascular disorders. It defines different types of aneurysms including true aneurysms, false aneurysms, berry aneurysms, and aortic aneurysms. The causes of aneurysms are discussed, including conditions like atherosclerosis, smoking, and genetic factors. Diagnostic tests for aneurysms including CT scans, MRI, and angiograms are outlined. Treatment options for aneurysms include medications to control risk factors, surgical procedures like endovascular coiling and stent grafting, and rehabilitation after brain injury from rupture. Complications from ruptured aneurysms like re-bleeding and hydrocephalus are also noted.