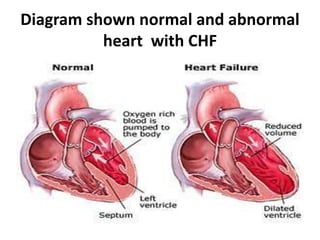
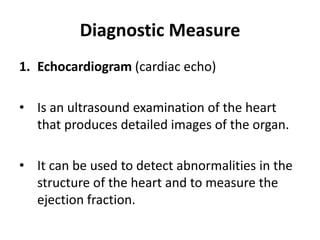
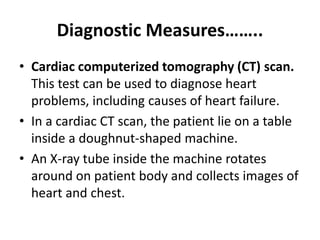
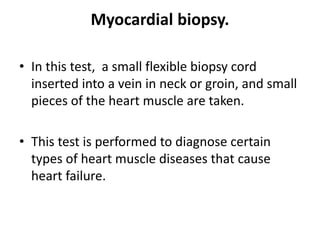
This document provides information on congestive heart failure (CHF), including its definition, causes, risk factors, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnostic measures, nursing management, treatment, and prevention. CHF is defined as the heart's inability to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. Common causes include coronary artery disease, heart attacks, valve disease, and hypertension. Diagnostic tests include echocardiograms, electrocardiograms, stress tests, and blood tests. Treatment involves medications to reduce workload on the heart and control symptoms, while prevention focuses on controlling risk factors like high blood pressure.