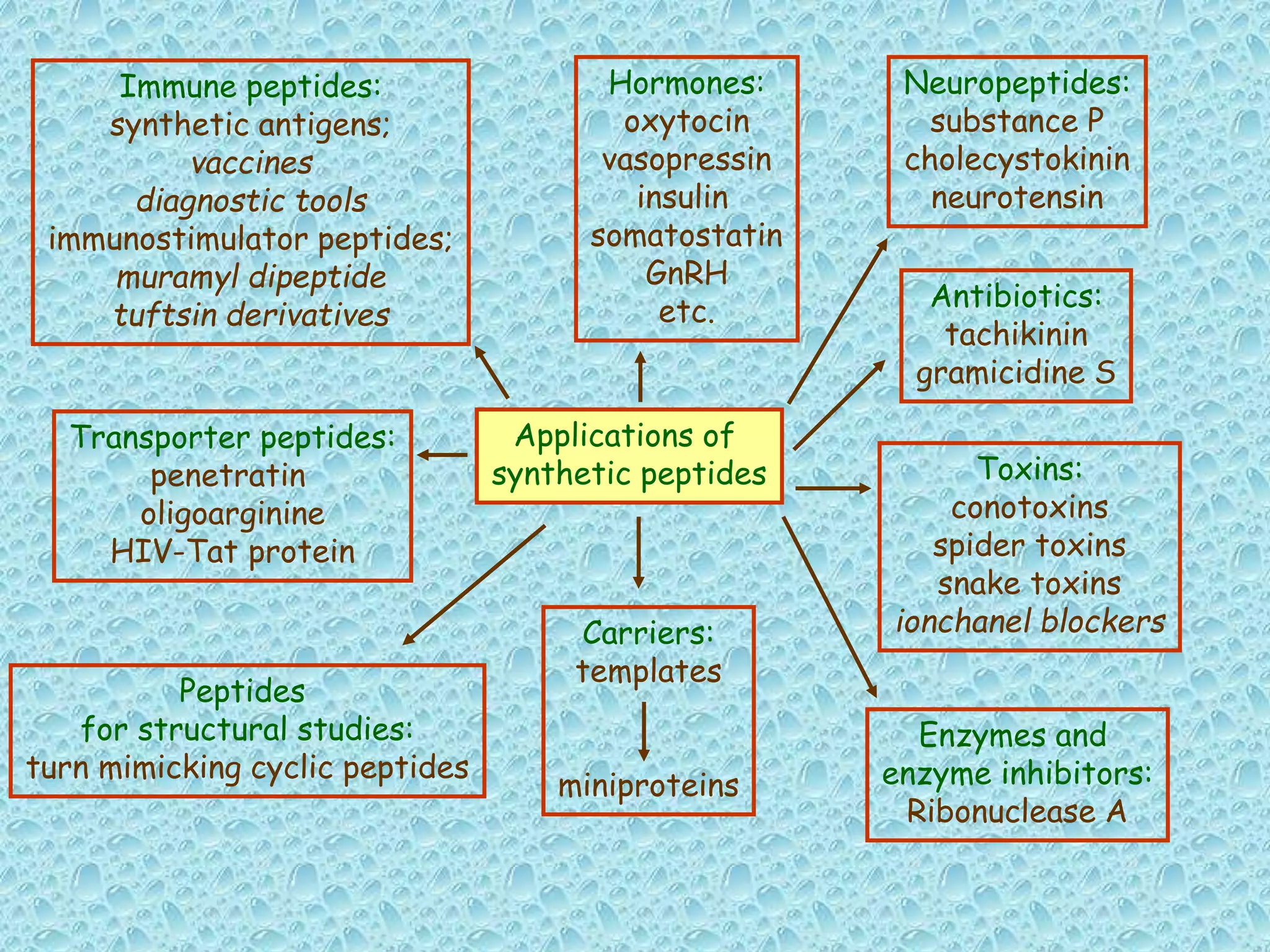
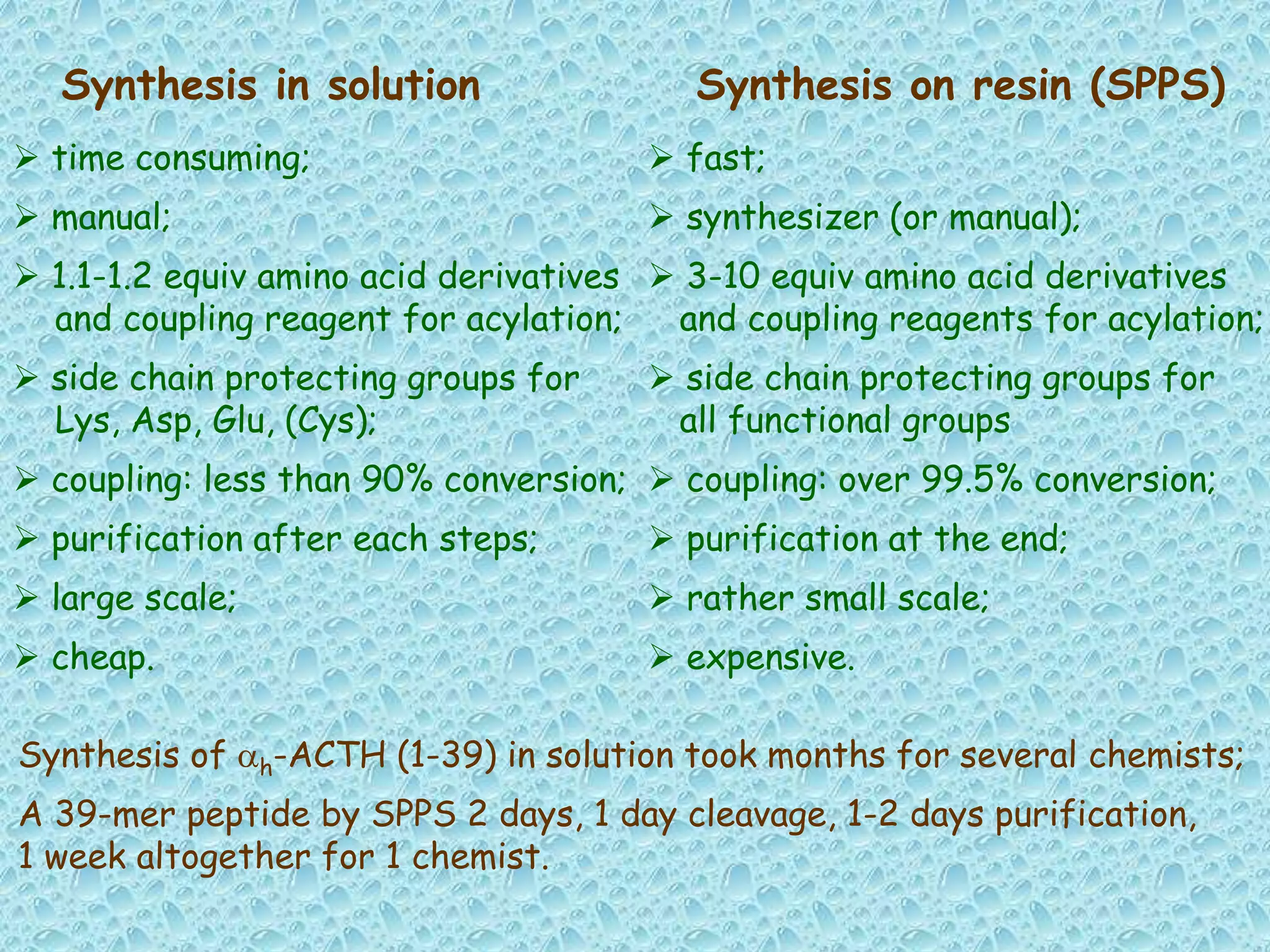
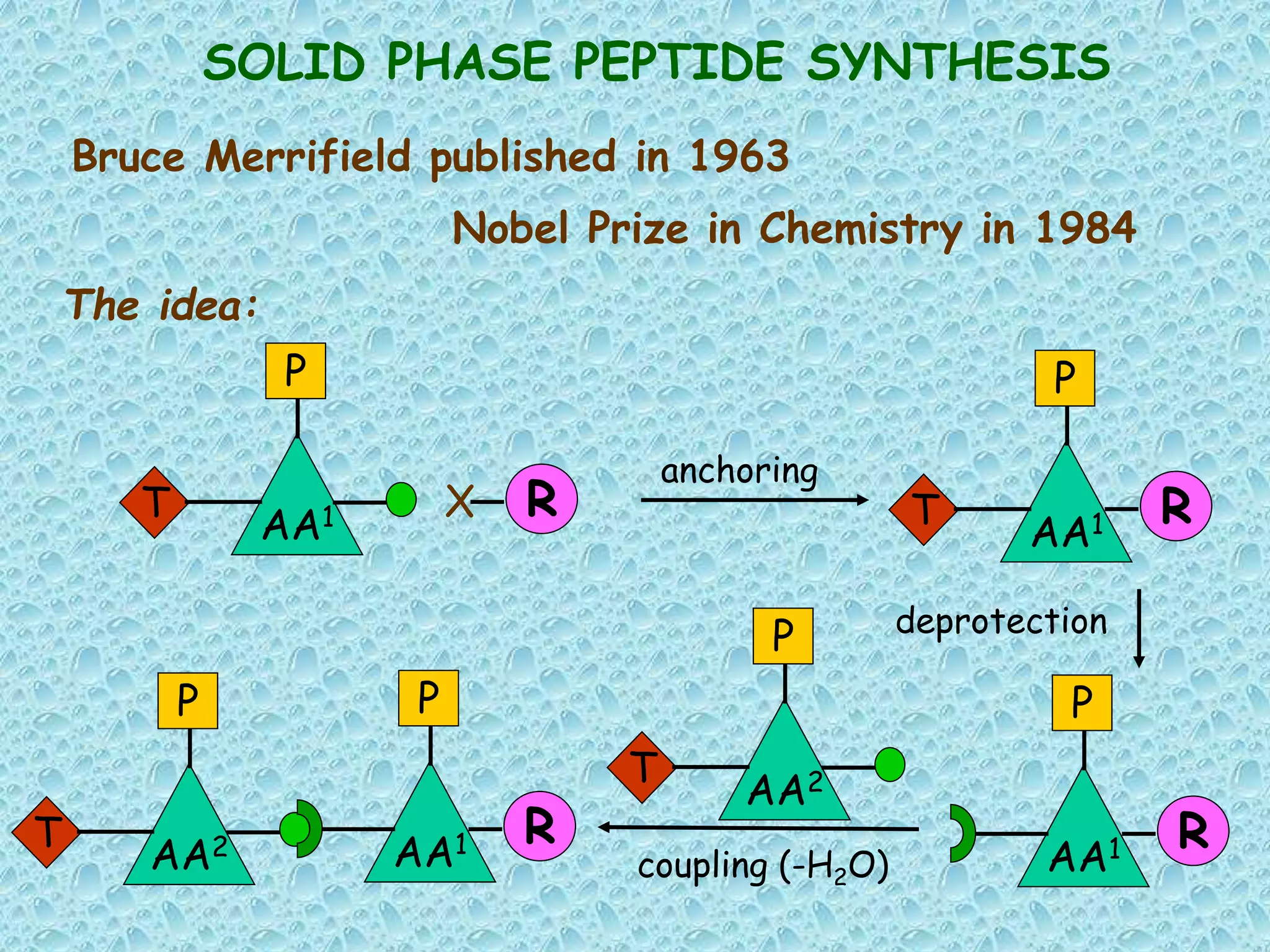
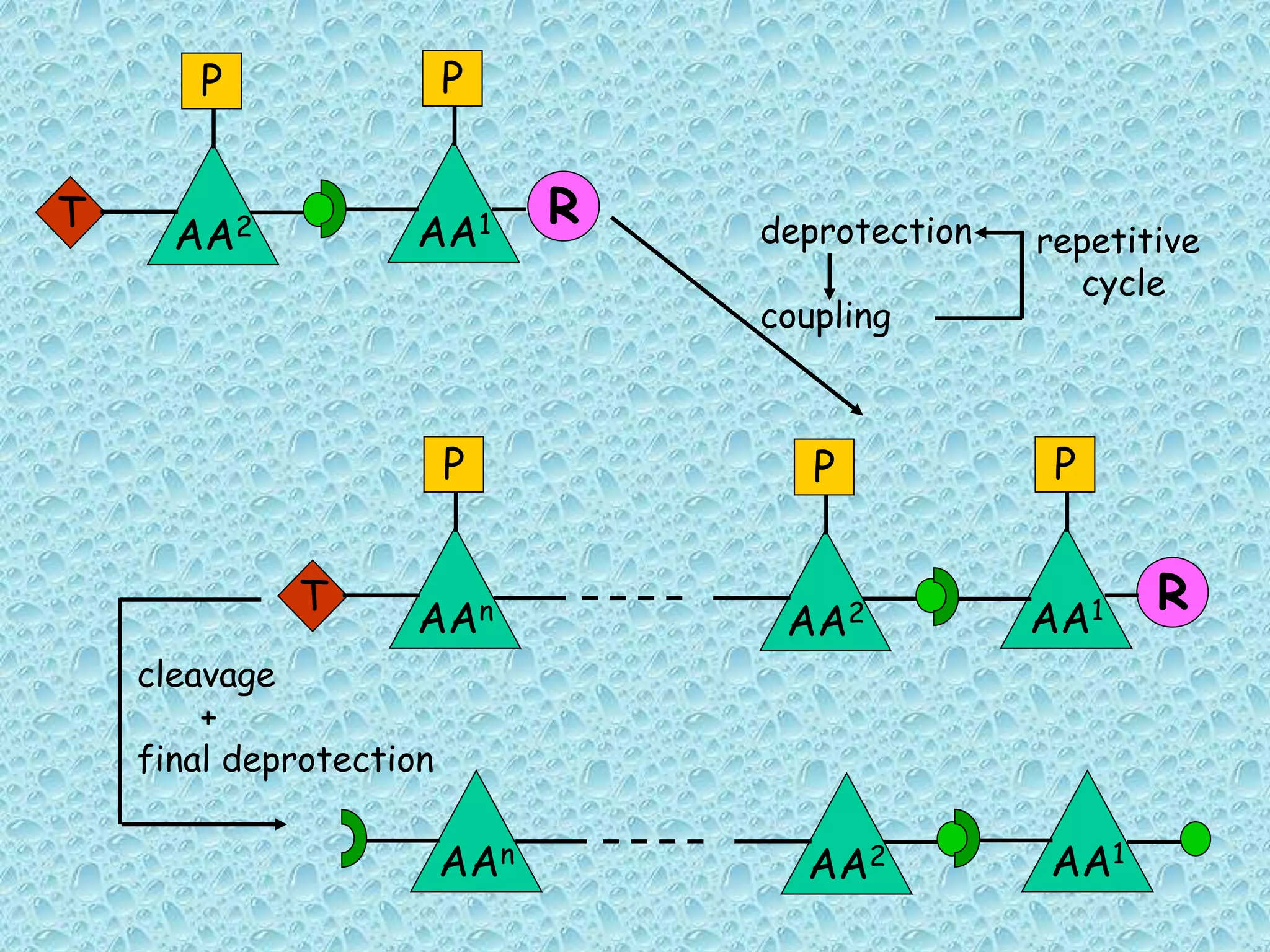
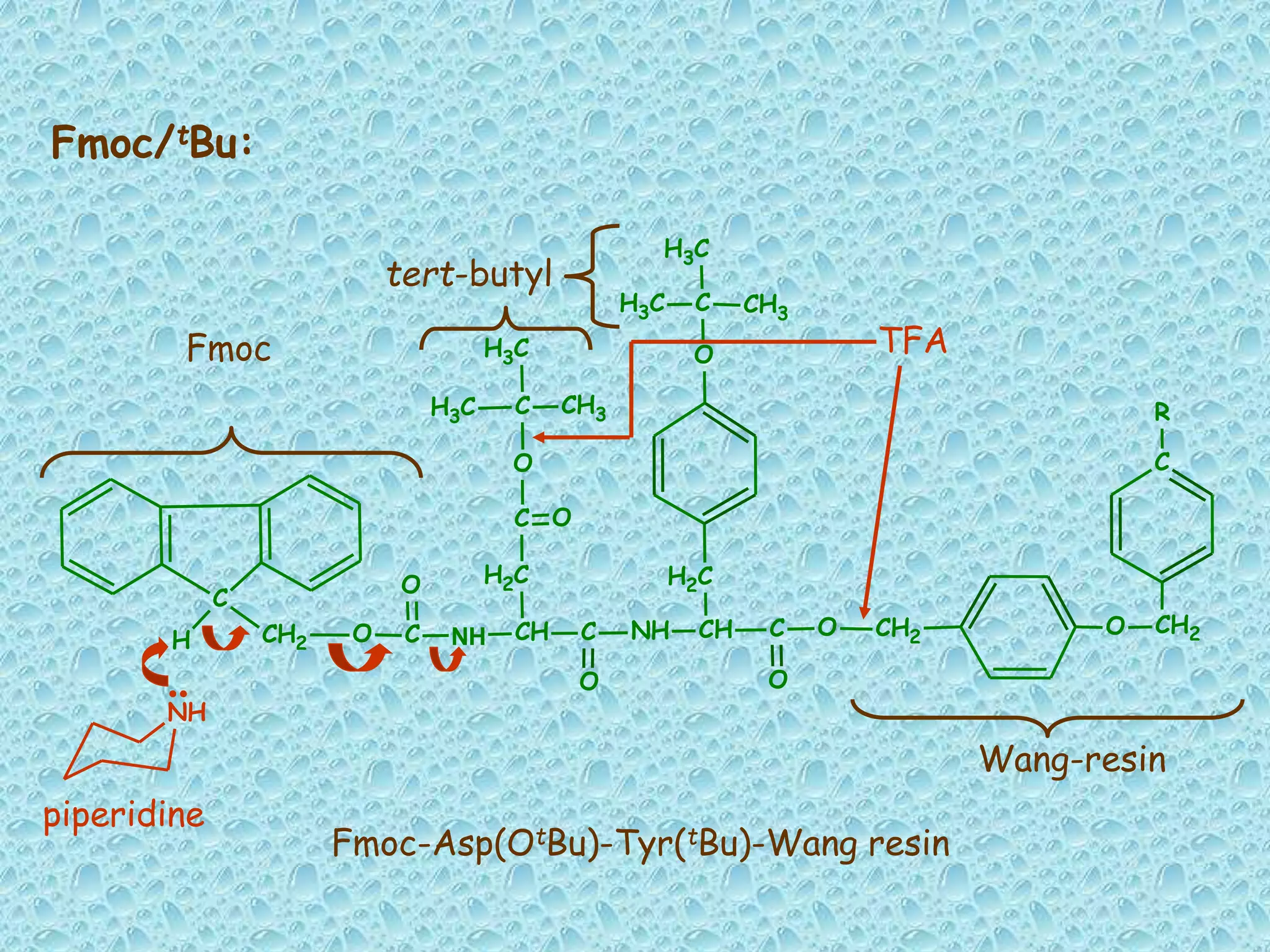
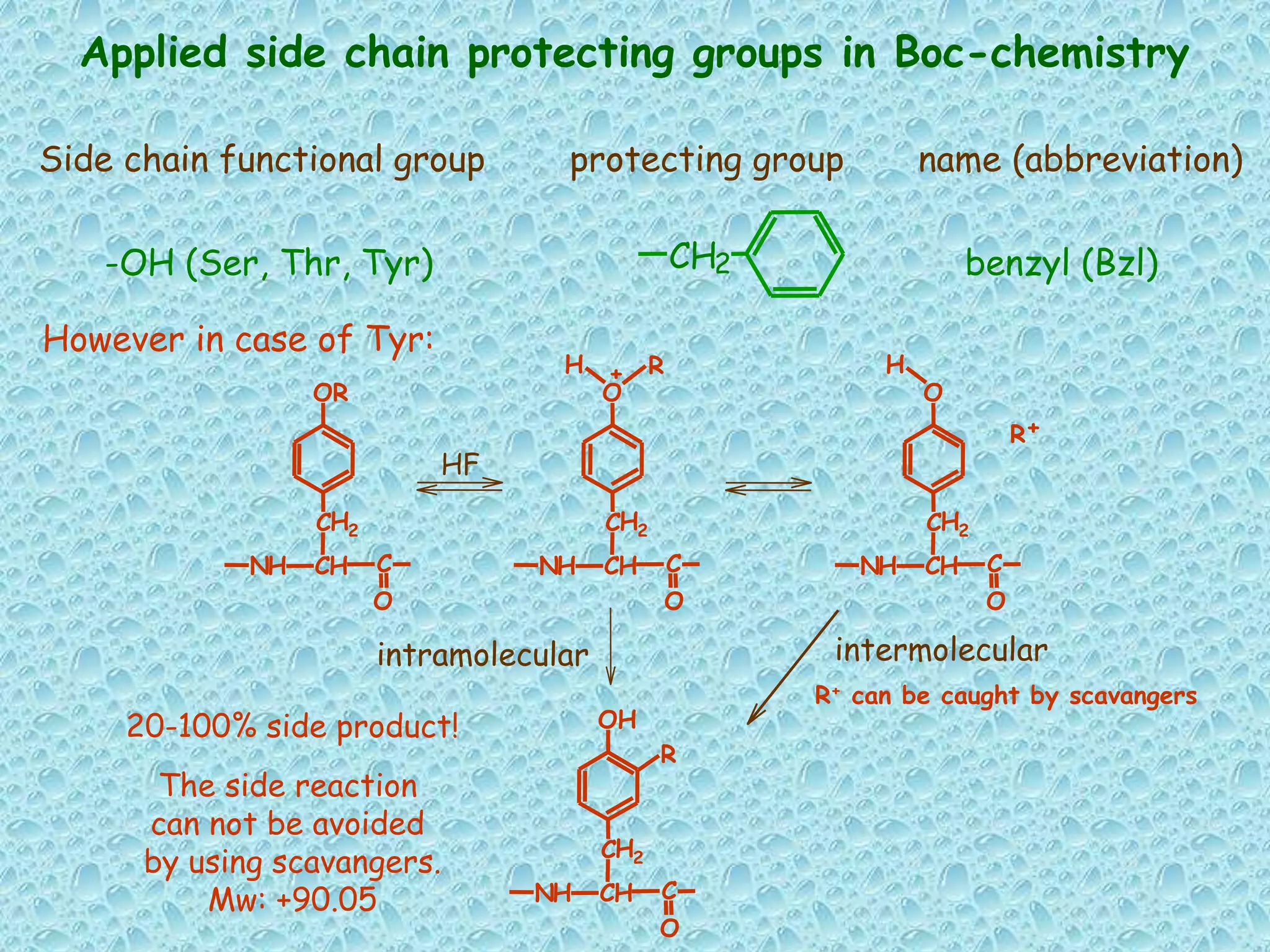
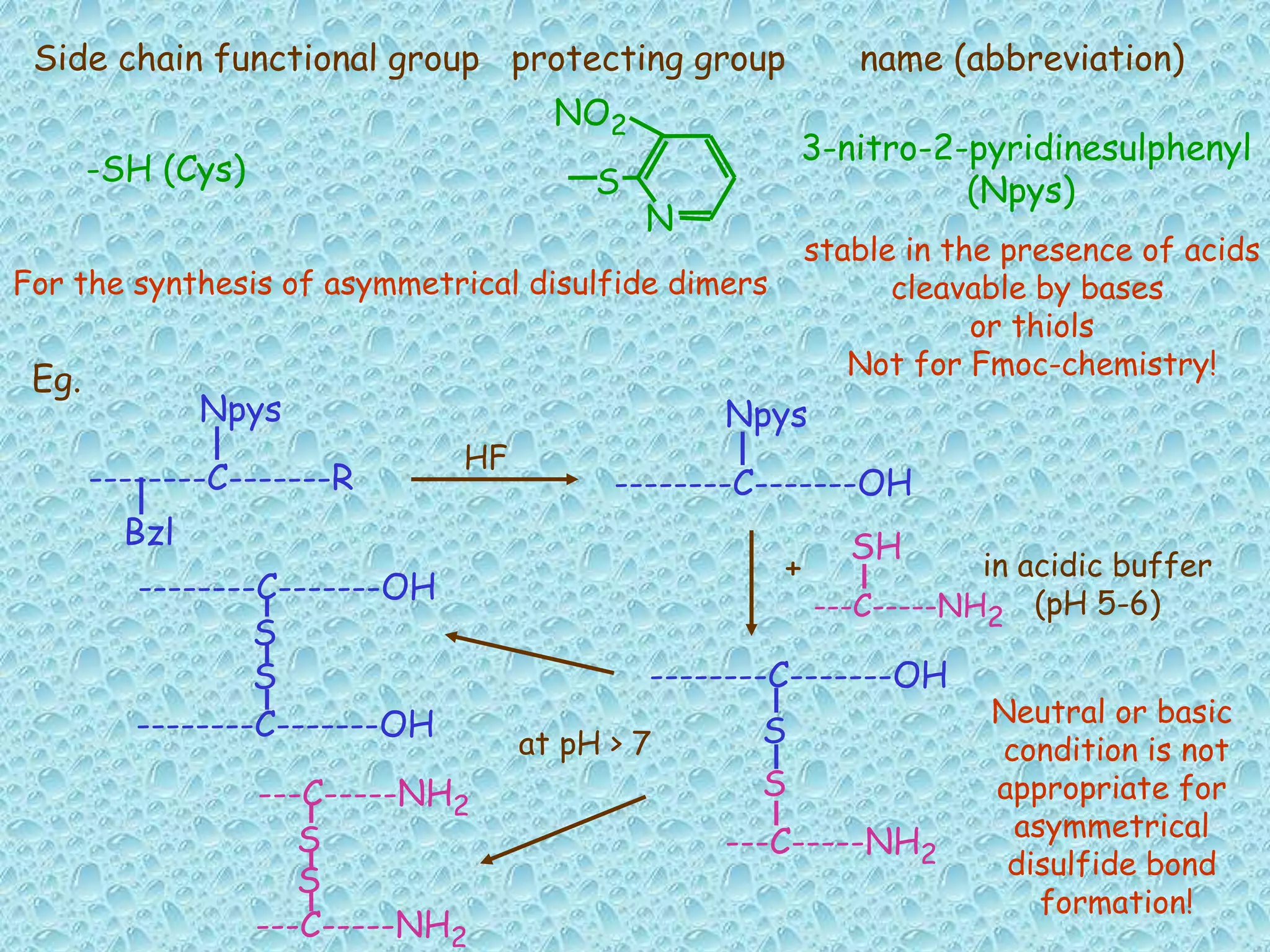
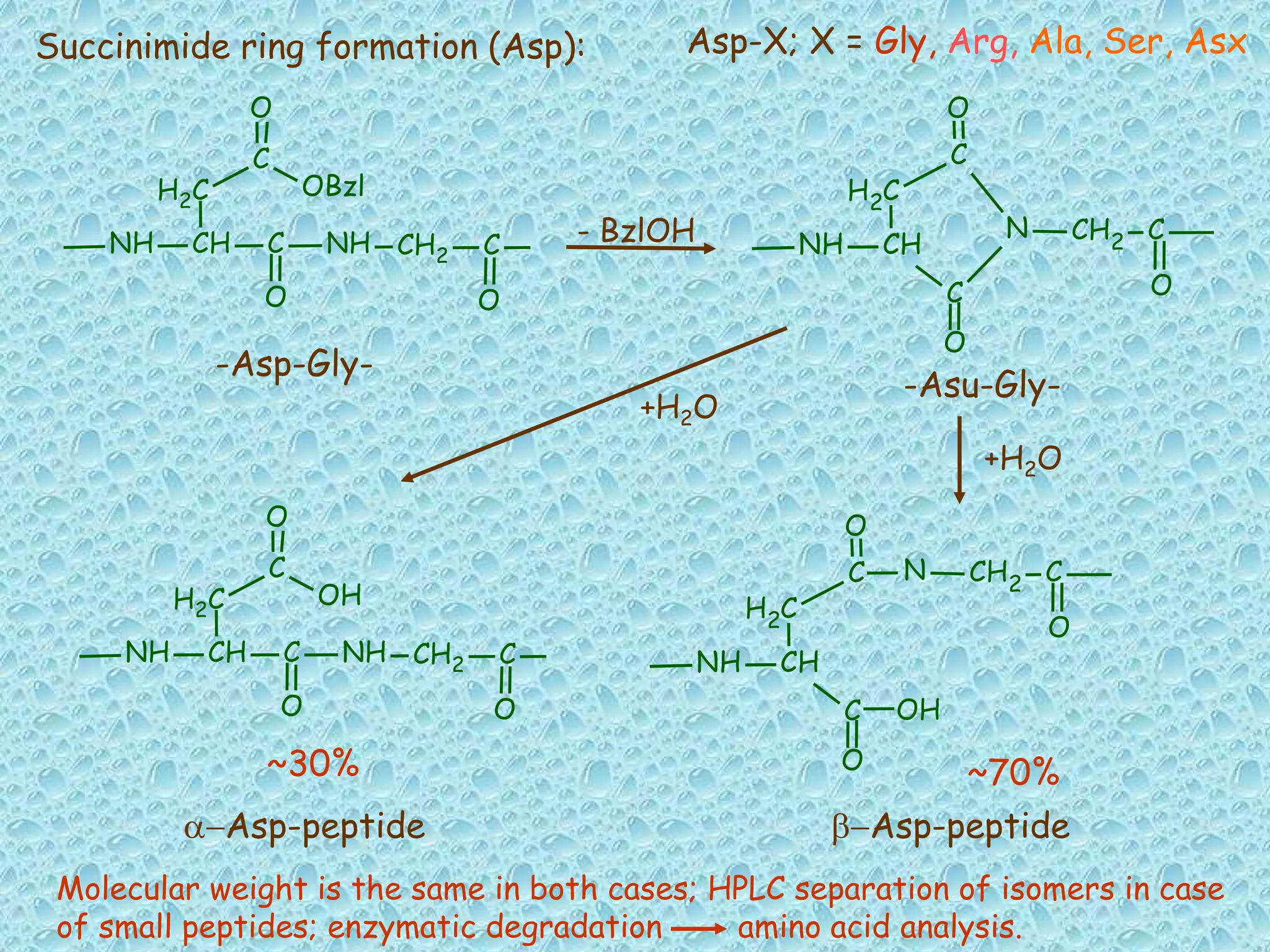
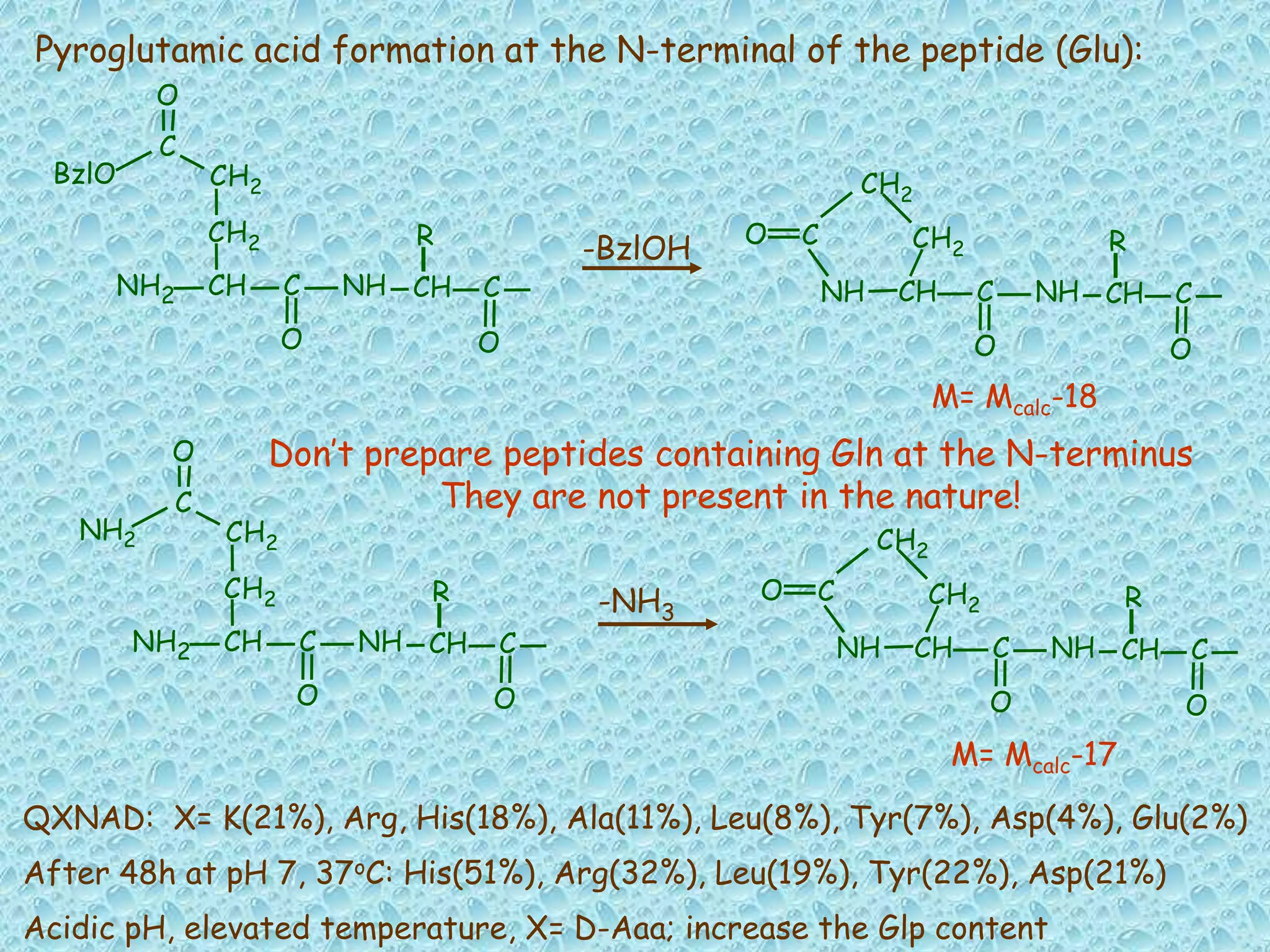
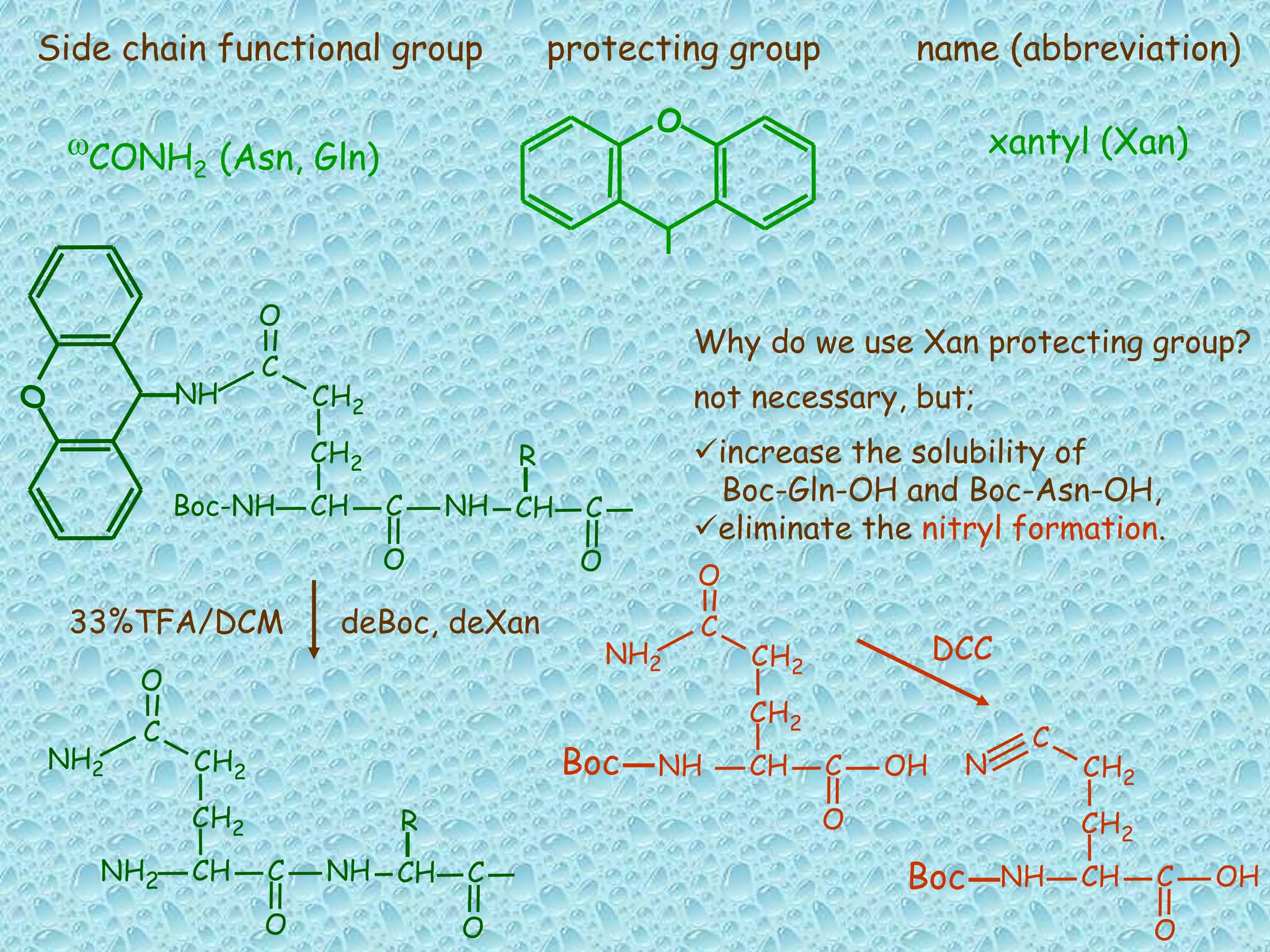
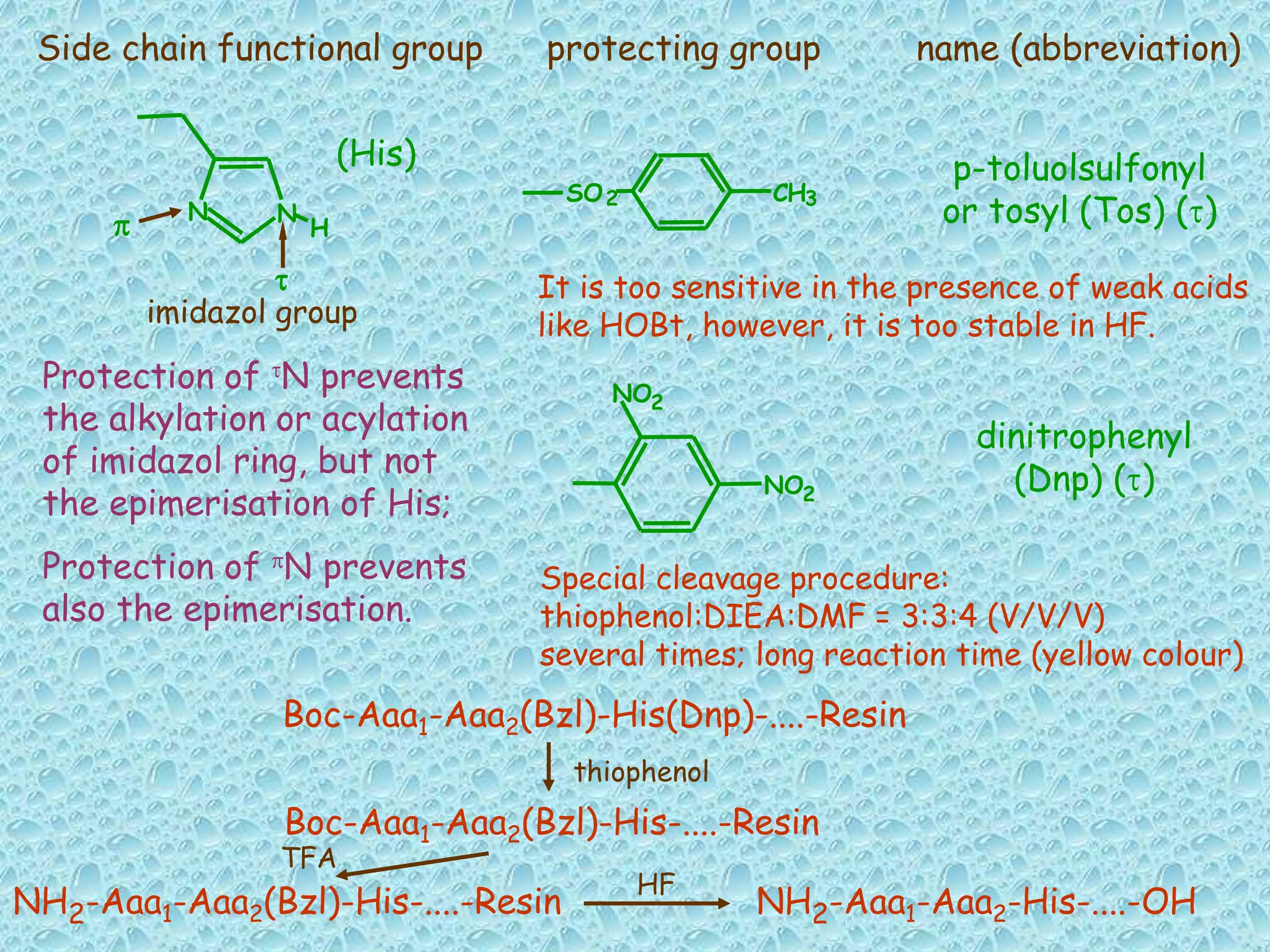
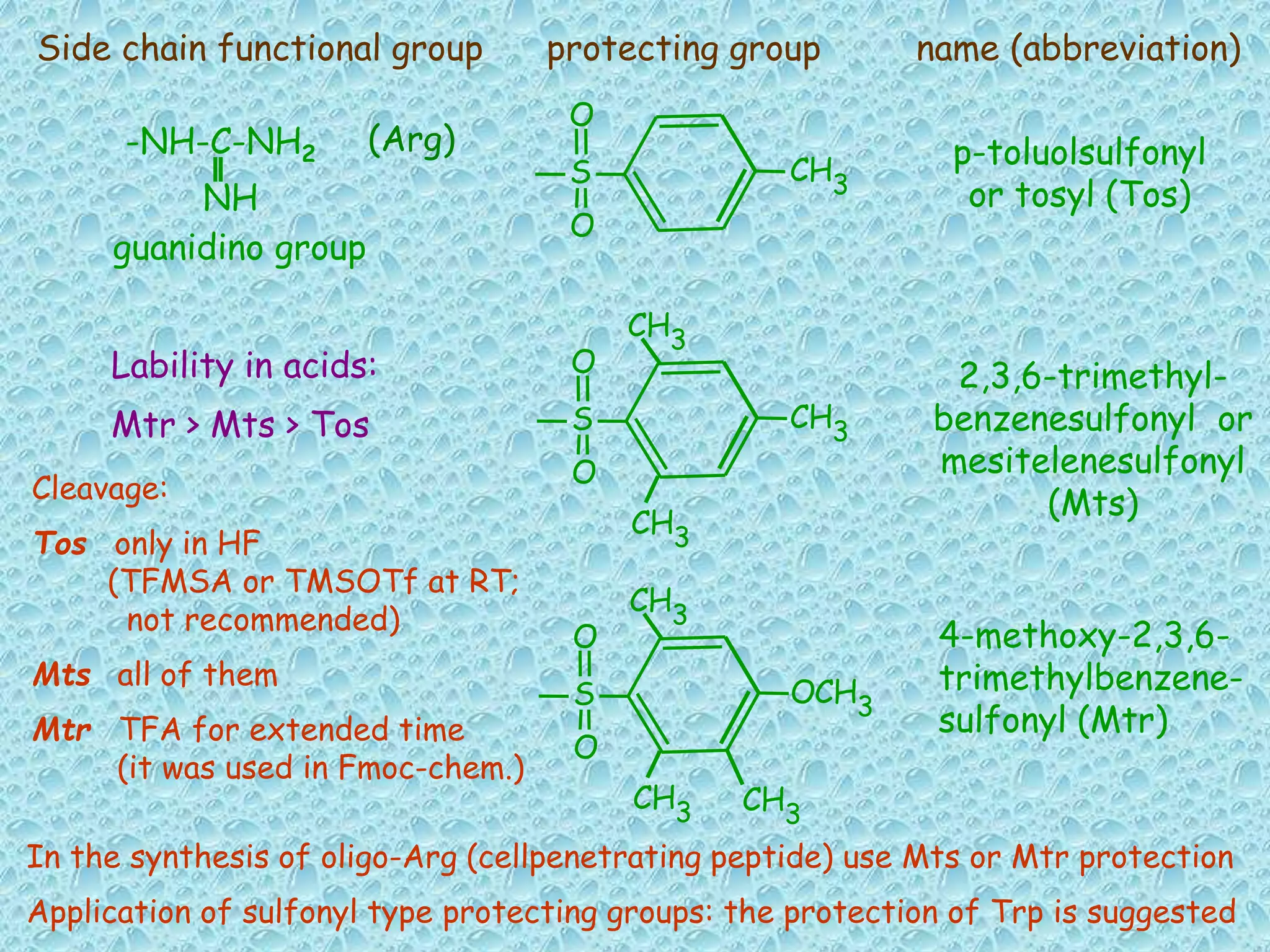
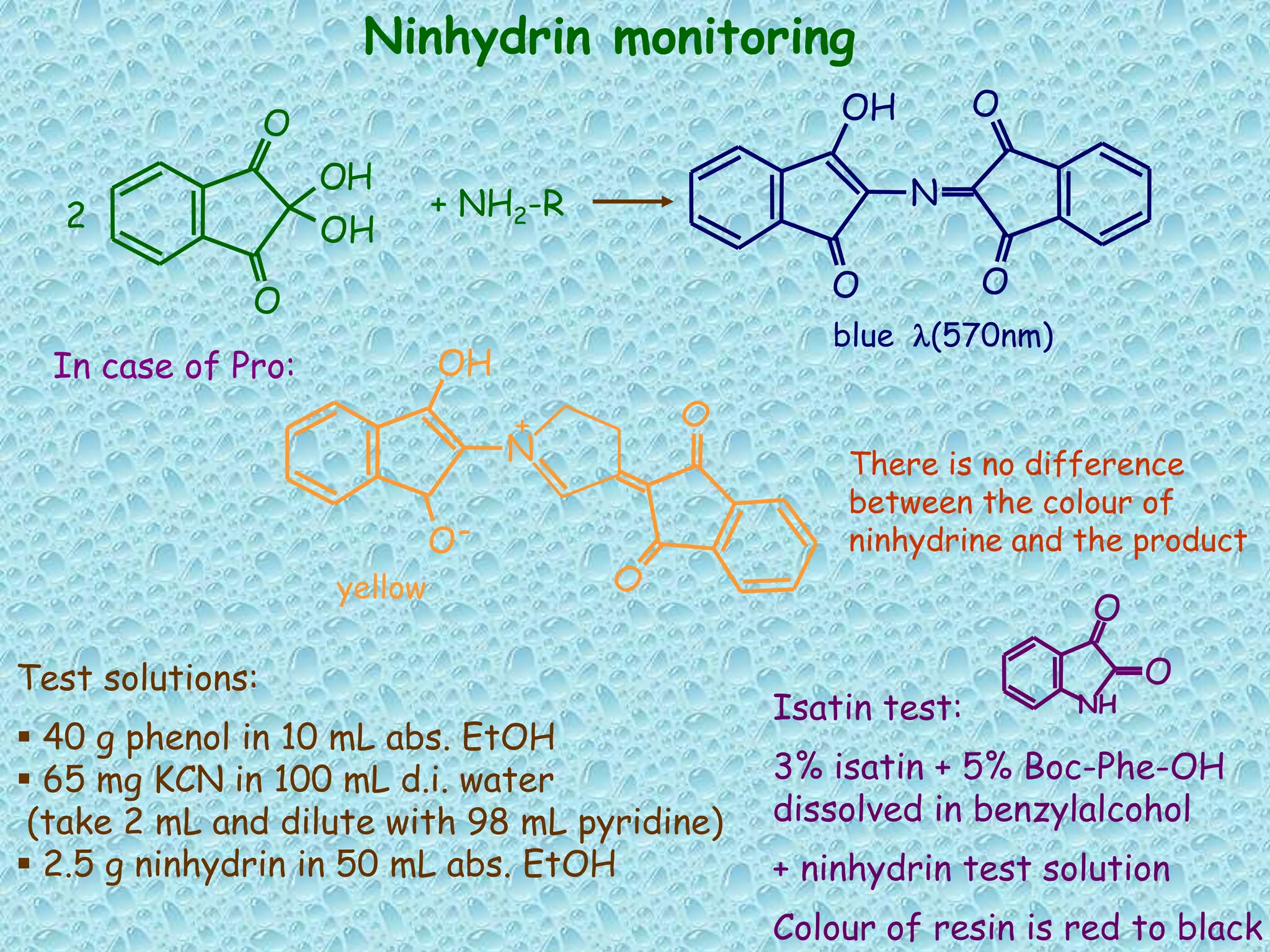
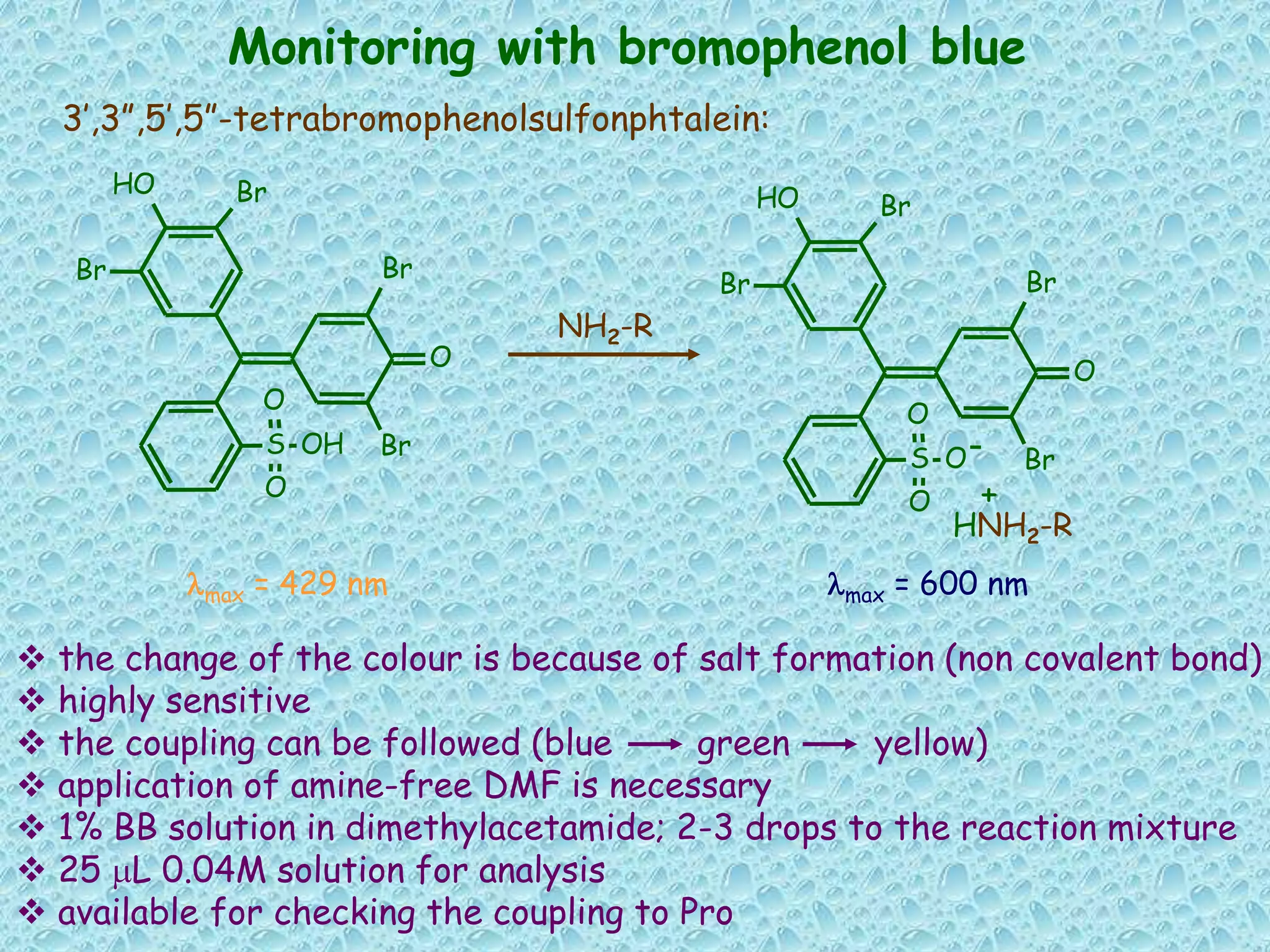
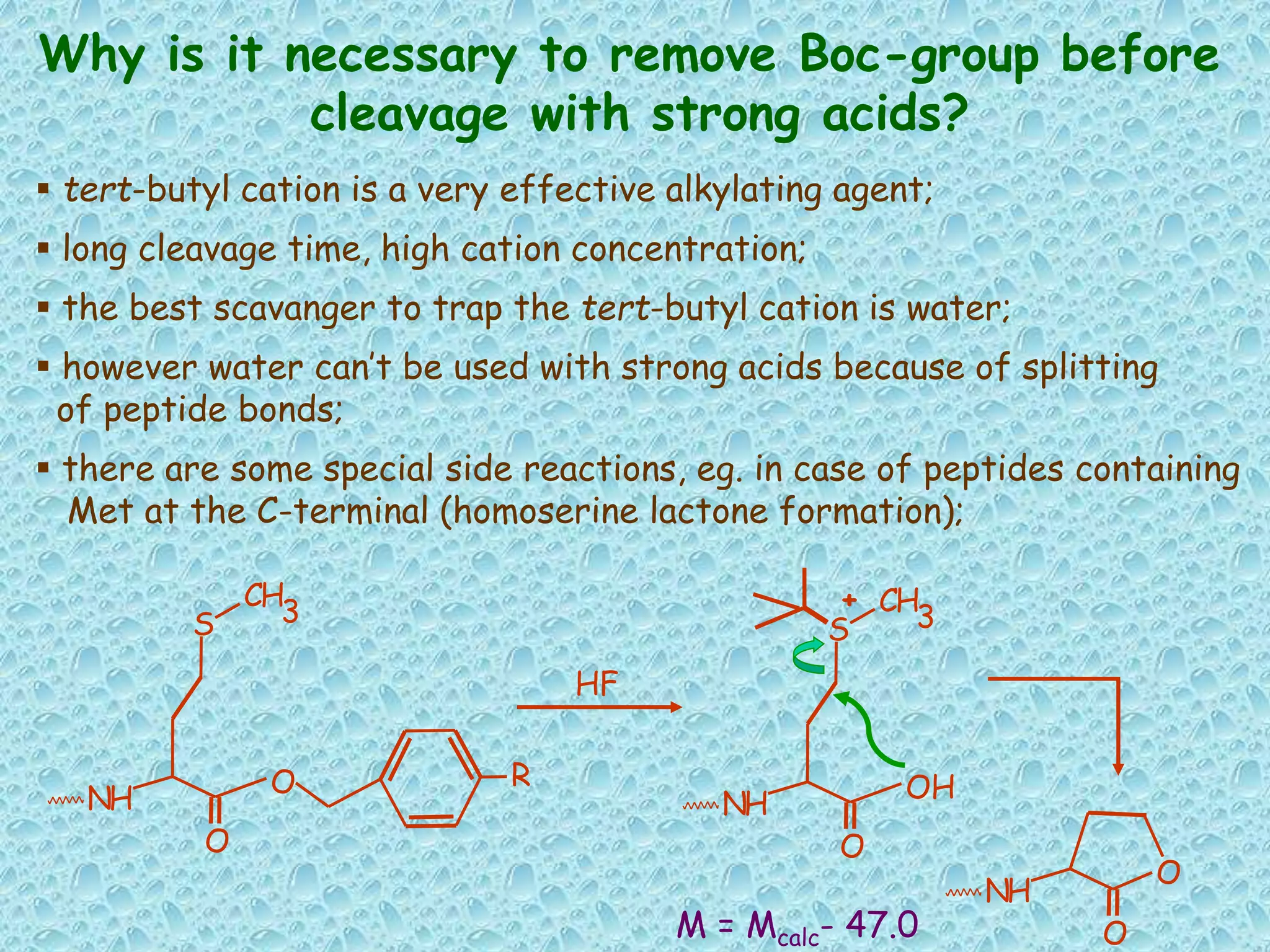
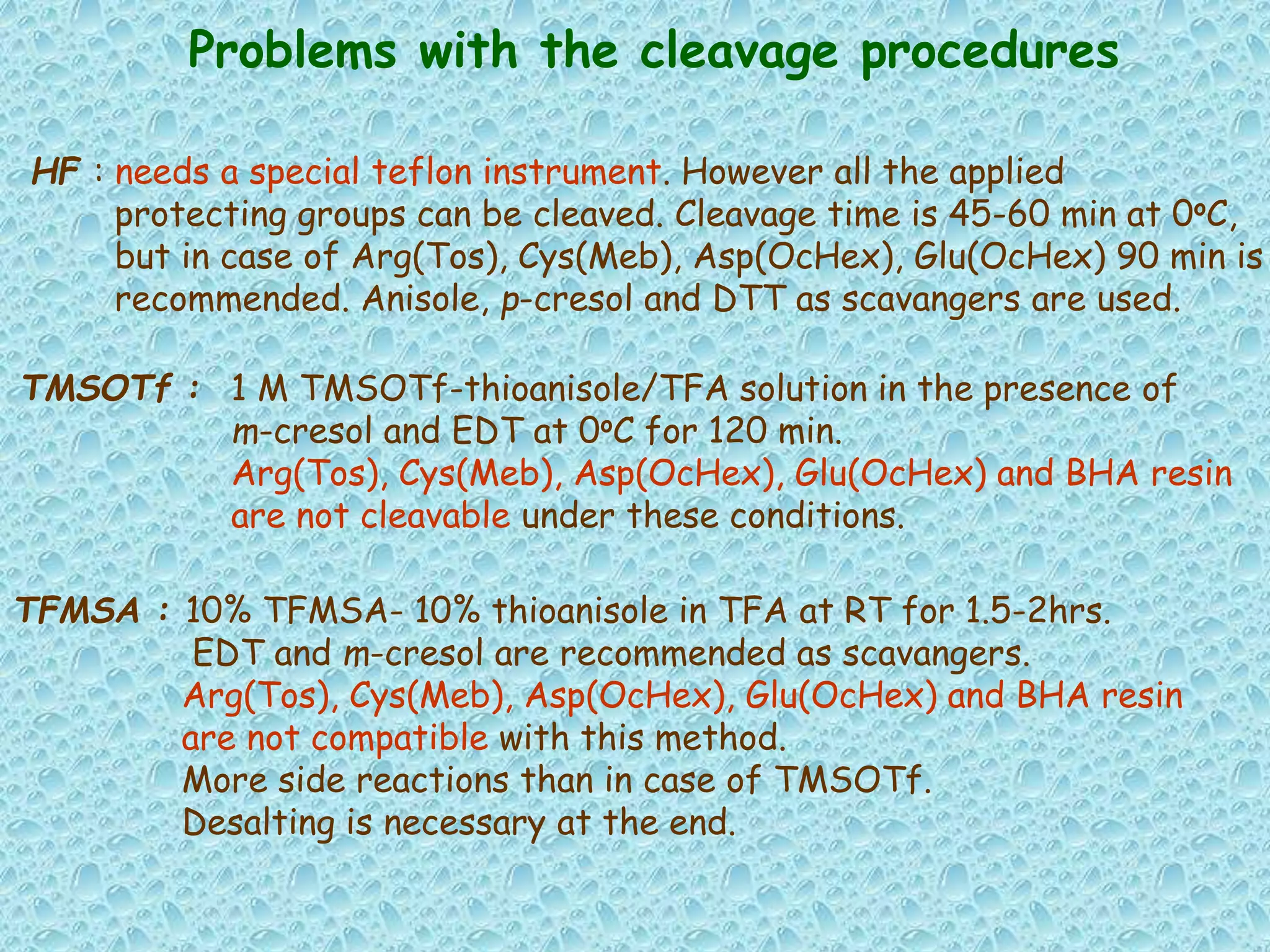
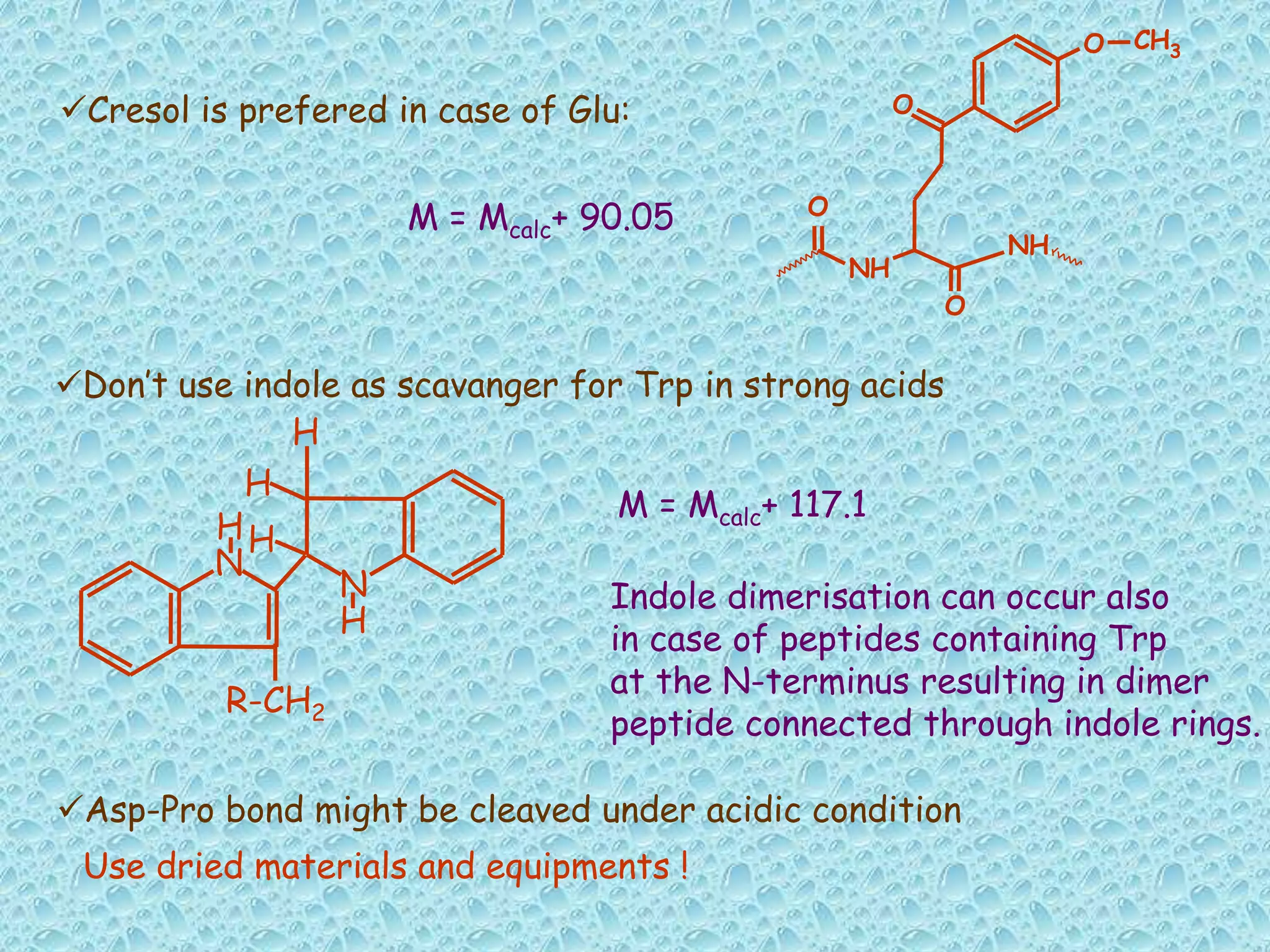
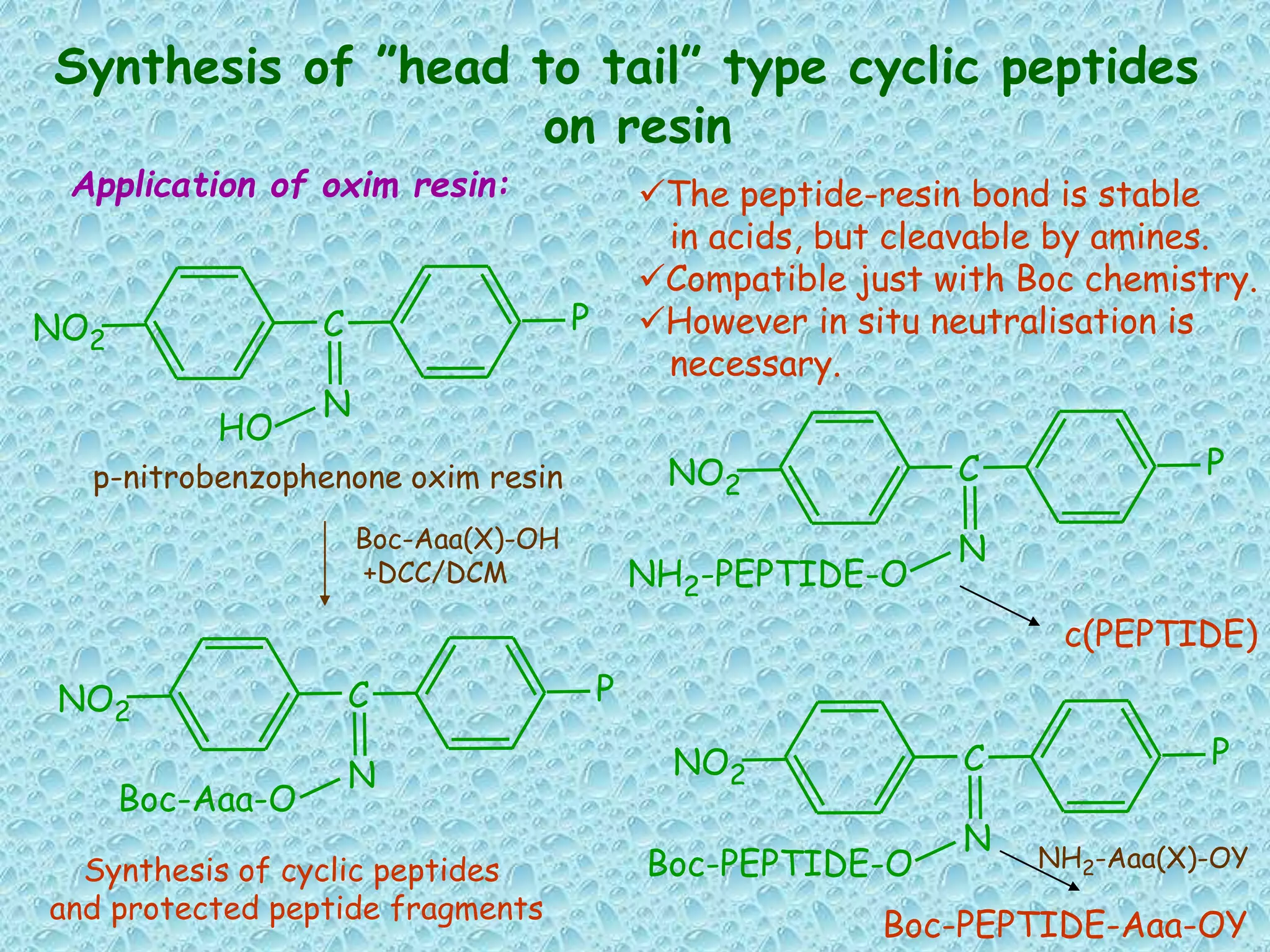
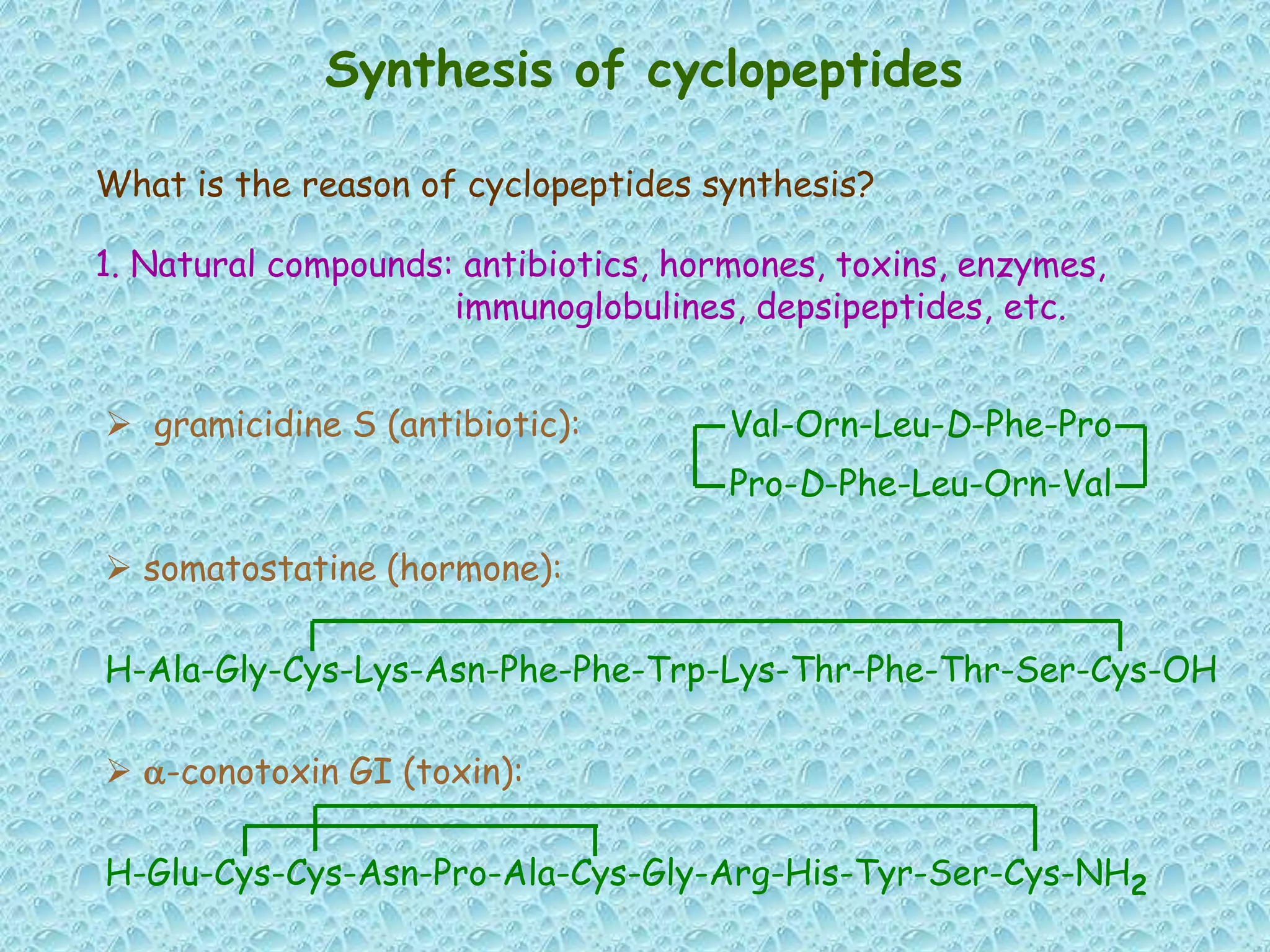
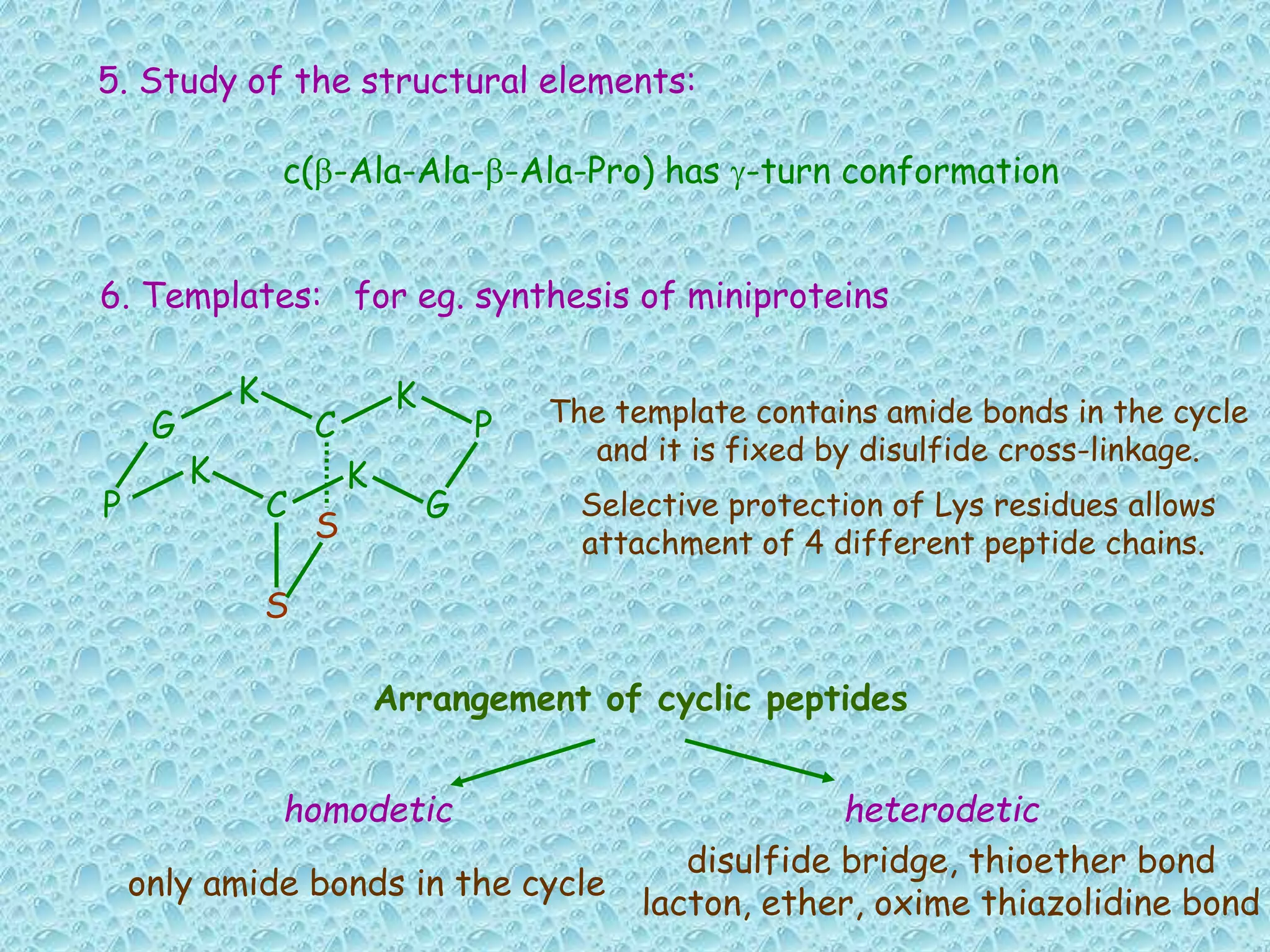
The document discusses solid phase peptide synthesis, focusing on the BOC/Bzl strategy and its applications in creating various peptides for medical uses, including immune peptides, hormones, neuropeptides, and drugs. It outlines the importance of peptide synthesis, the roles different resins and protecting groups play, as well as the comparison between solid-phase and solution synthesis techniques. The text highlights both the advantages and limitations of peptides as drugs, noting the significant market potential and the increasing number of synthetic peptides being introduced as pharmaceuticals.