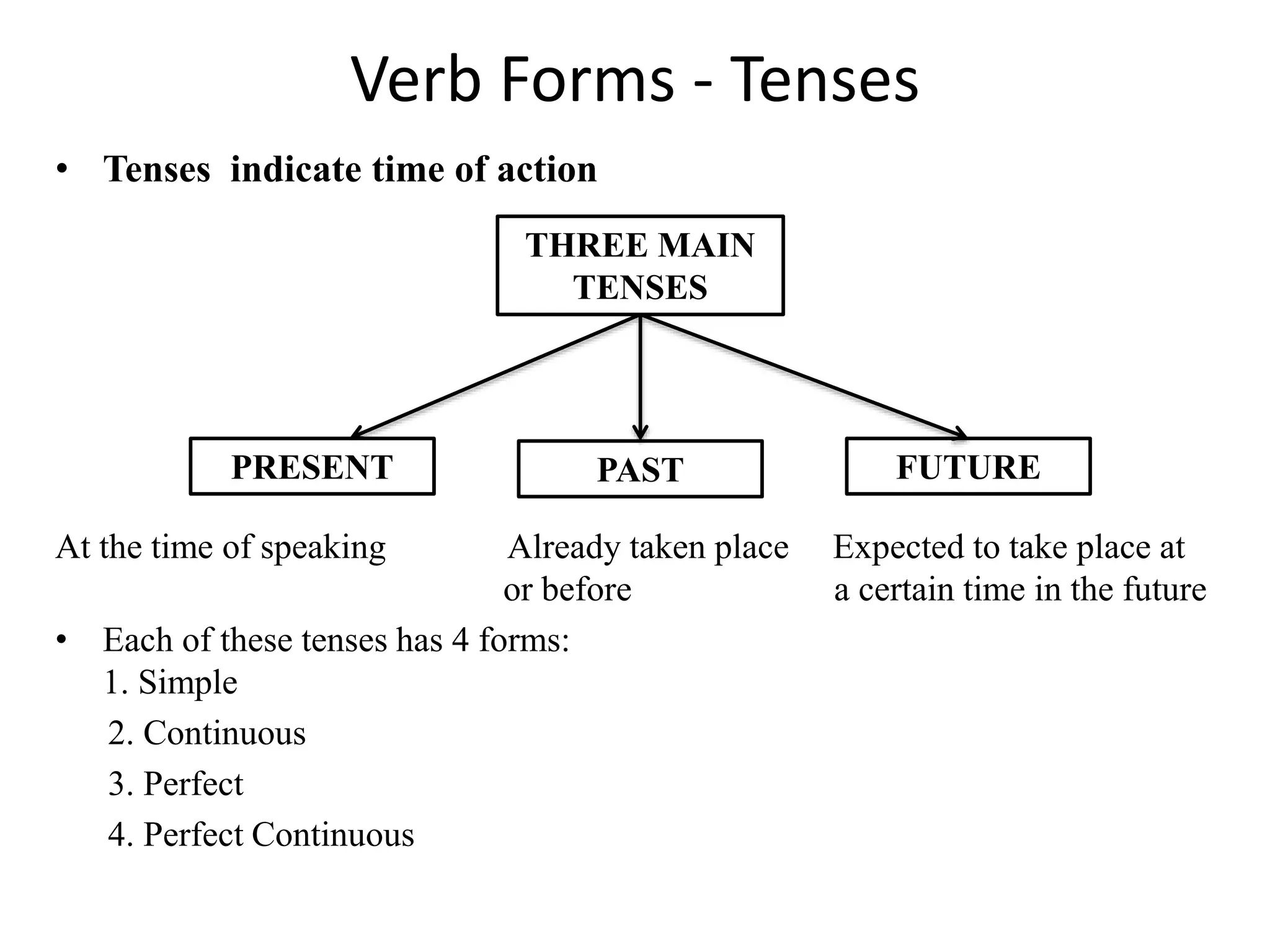
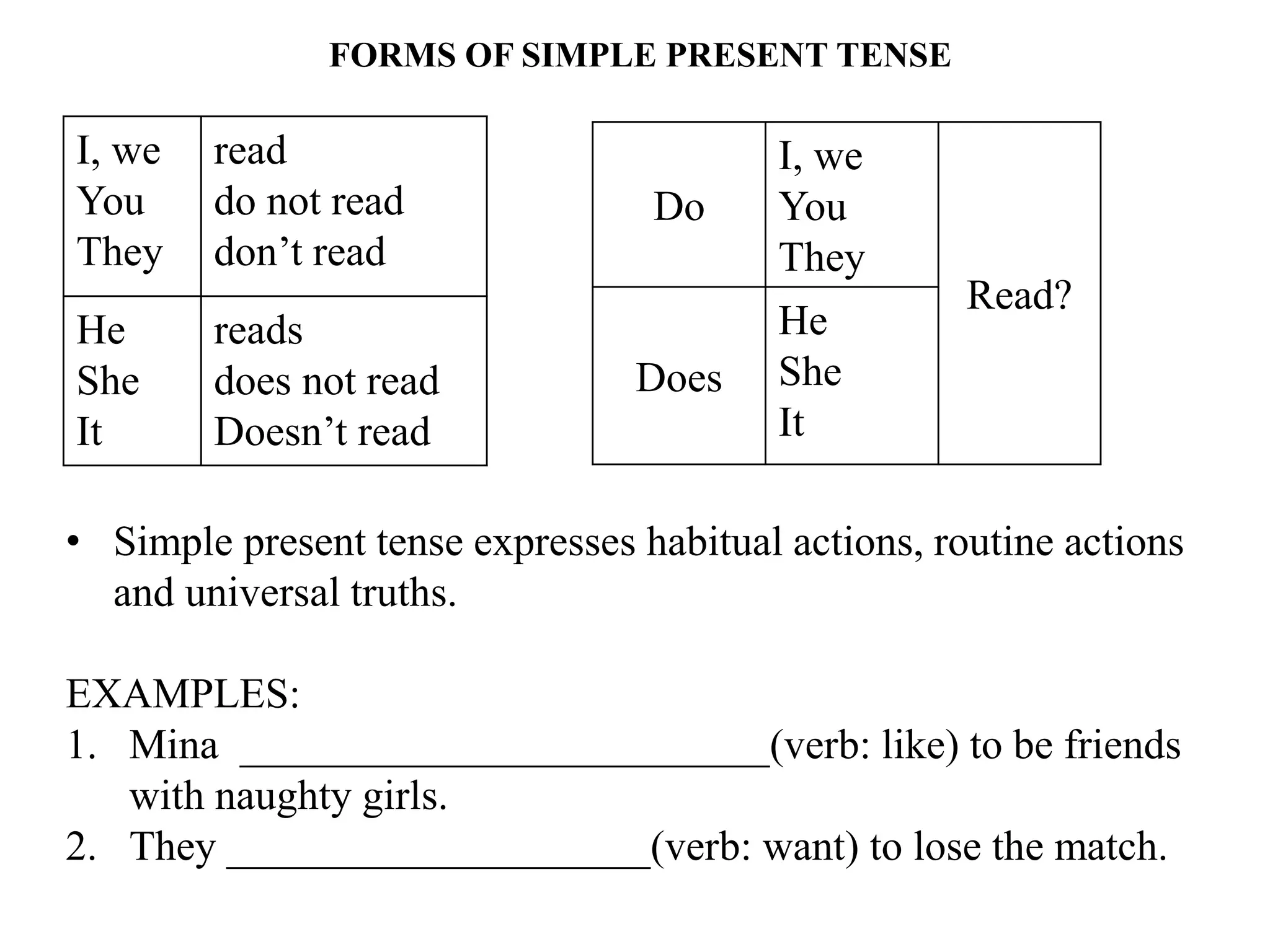
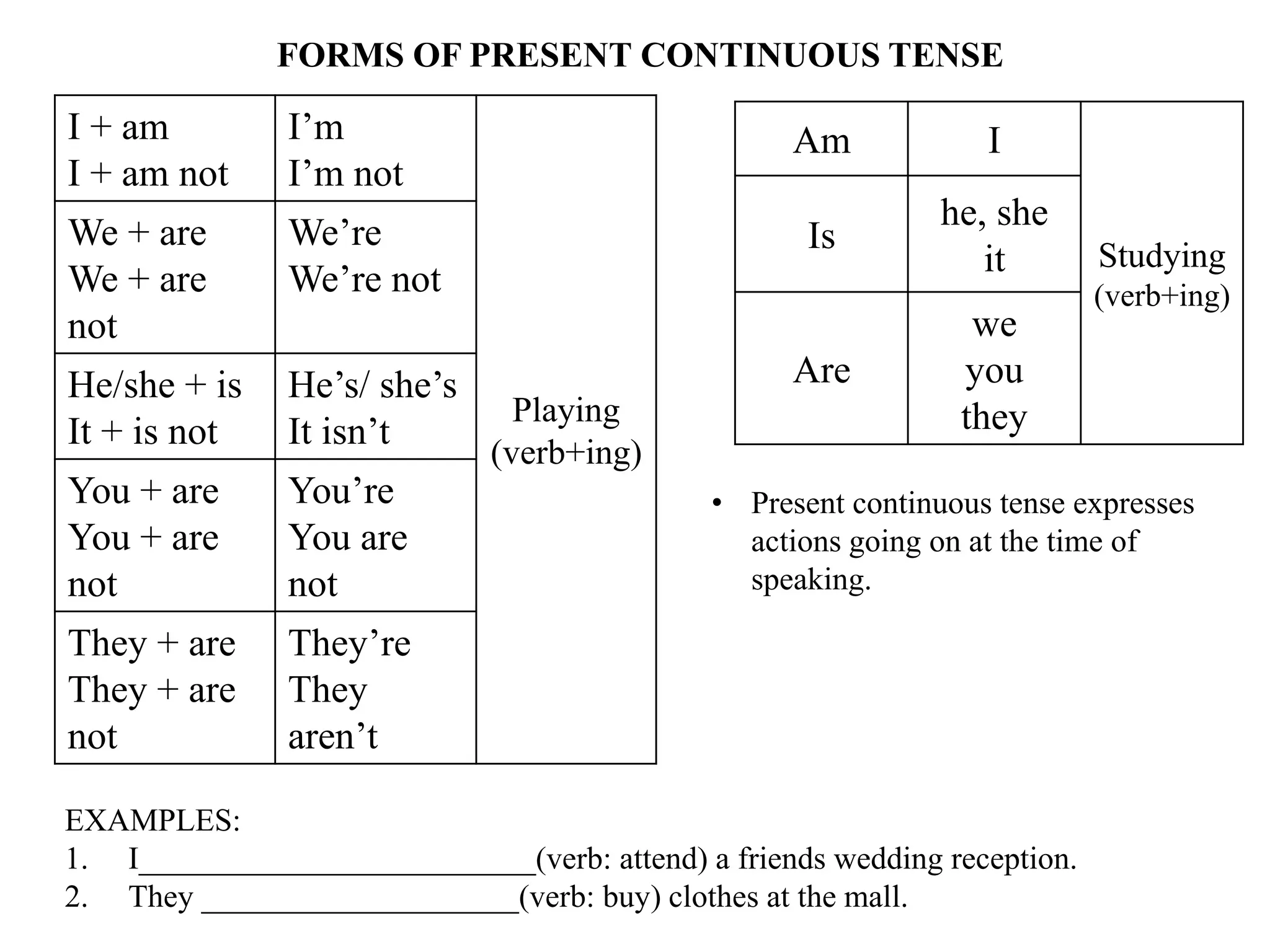
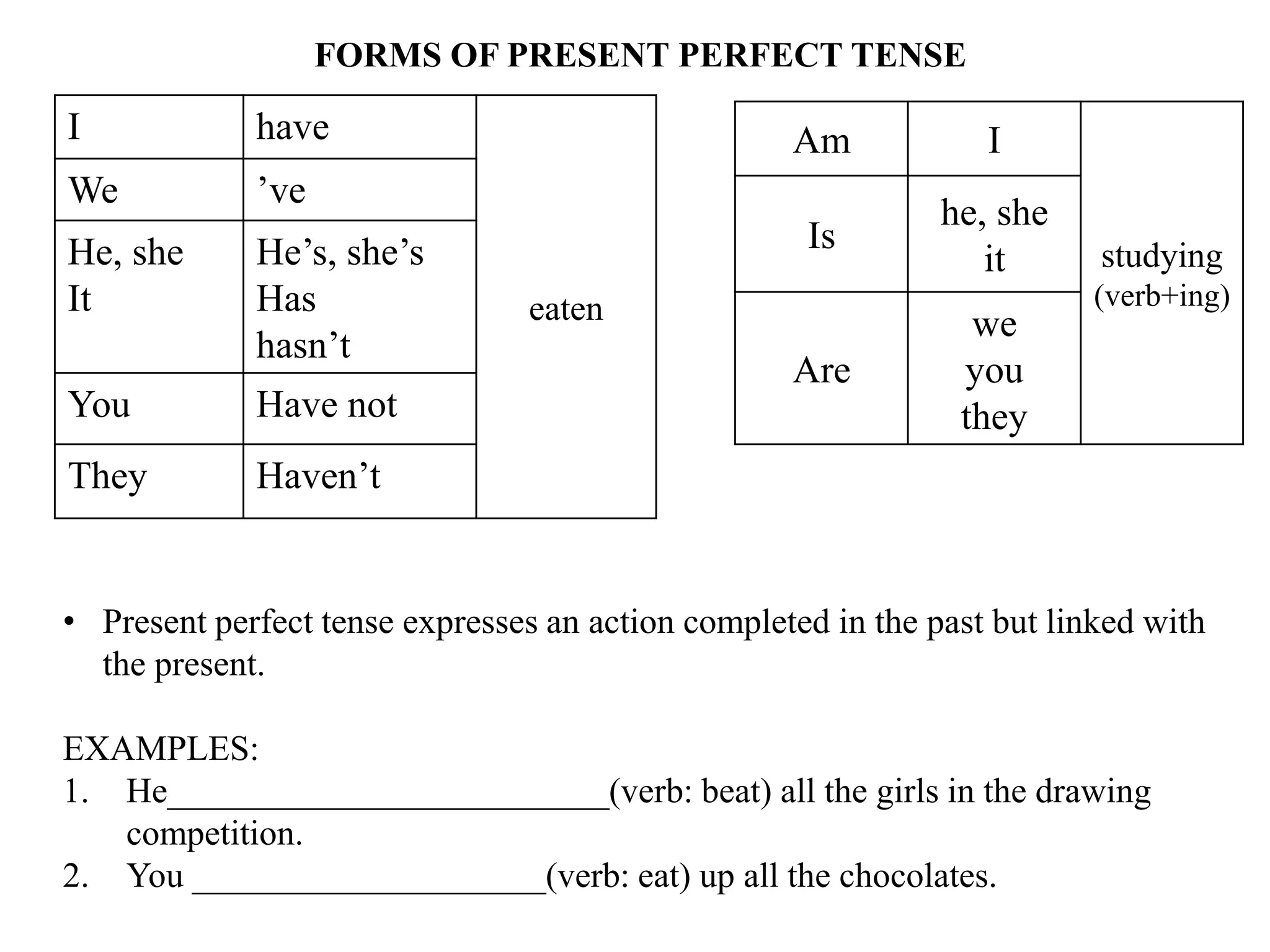
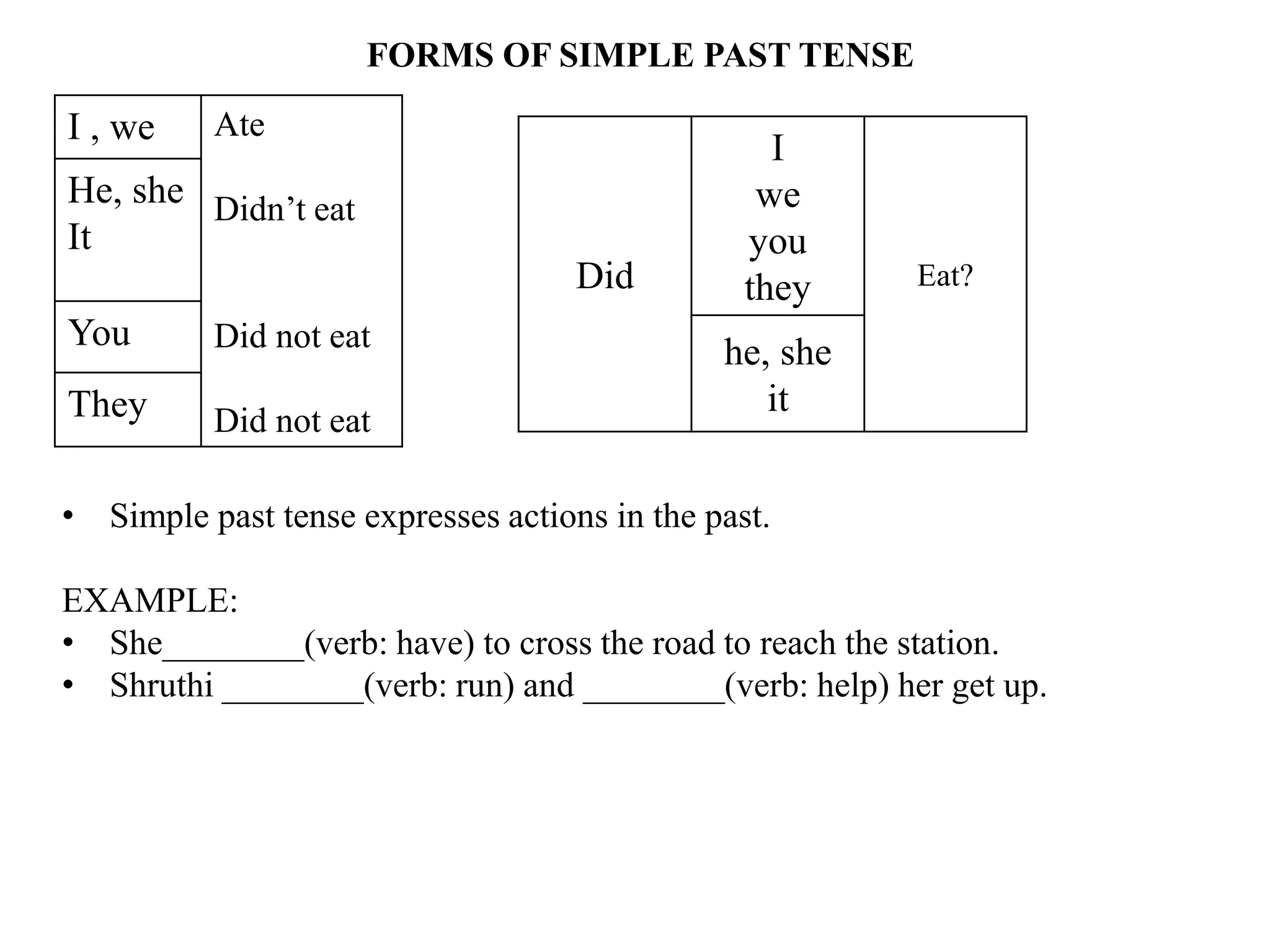
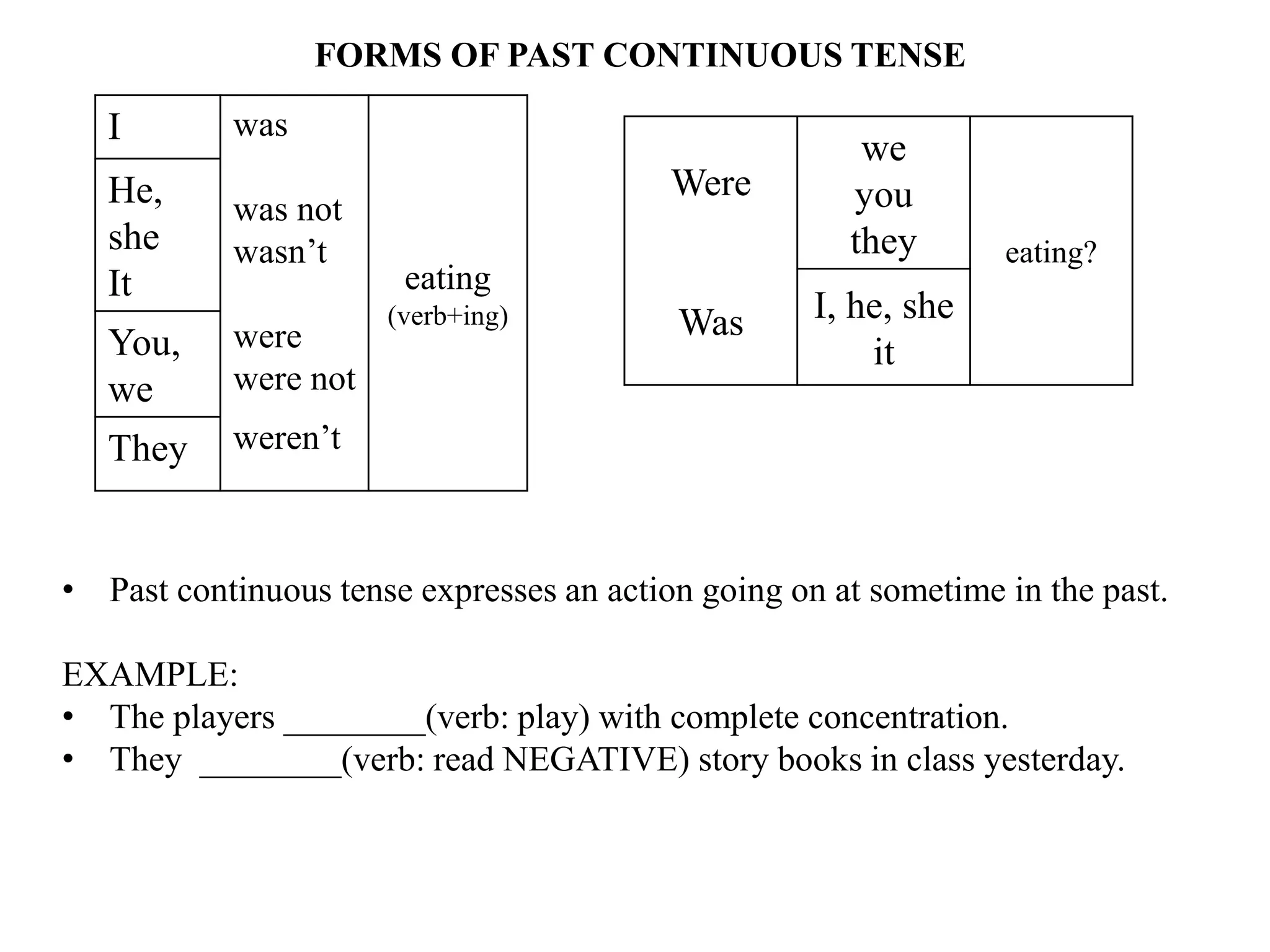
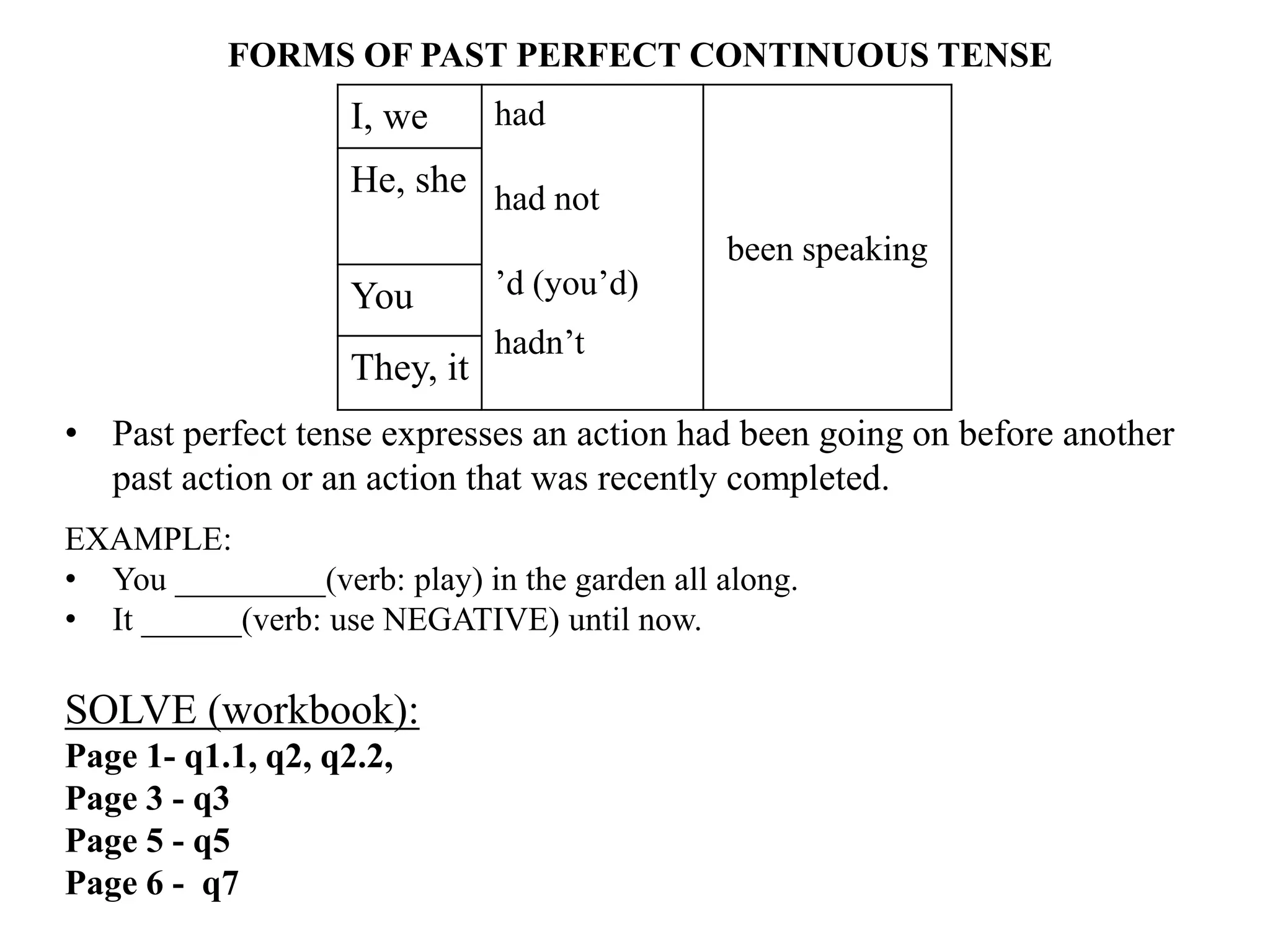
The document provides an overview of verb forms and tenses for Class 9 English grammar, including details on simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous tenses across present, past, and future. It explains how each tense is structured, its specific uses, and includes examples for clarity. Additionally, it references workbook exercises for practice.




![The Verb - To Have
Forms of To Have
Present Past Continuous
I / you / we / they have had having
he / she / it has had having
• As a main verb “to have” implies the meaning of possession.
• For example: “I have a job.”
• The verb “to have” is used as an auxiliary verb to help other verbs create the
perfect tense.
- auxiliary verb have [+ past participle]
• For example, “I have read a lot of books,”
• It does not take the continuous form "I having" - for that we have to use the
auxiliary verb be.
• For example: “I am having a shower.”
SOLVE (workbook):
Page 7 – q8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/verbformsclass9cbse-140502225136-phpapp02/75/Verb-forms-tenses-class-9-cbse-12-2048.jpg)

