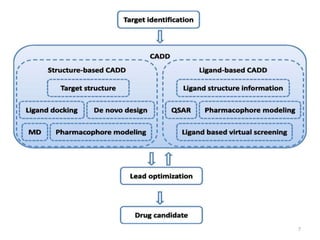
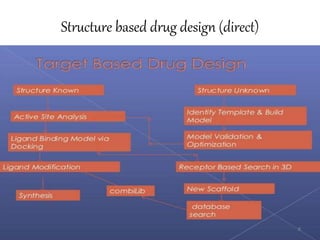
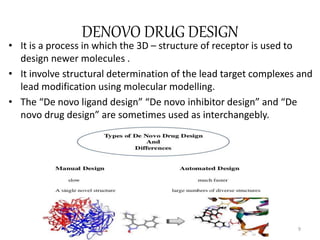
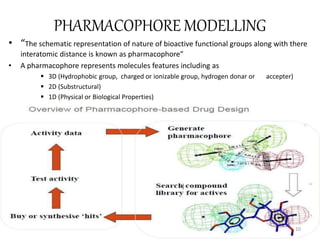
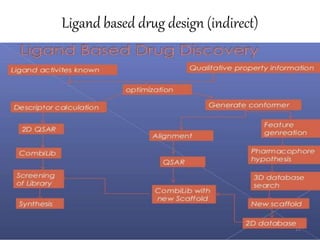
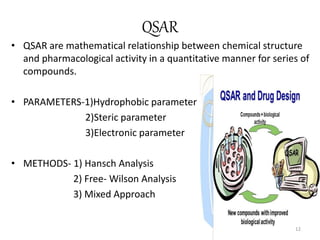
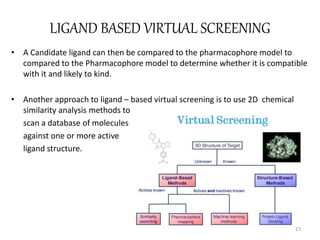
The document provides an overview of the history and development of drug design and medicinal chemistry, detailing significant milestones from the early extraction of compounds to the advent of computer-aided drug design (CADD). Key concepts discussed include various drug design techniques such as structure-based and ligand-based methods, pharmacophore modeling, and quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR). The application of these techniques aids in lead generation, optimization of drug properties, and understanding receptor-ligand interactions.