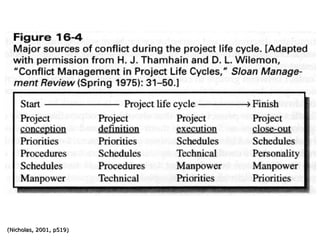
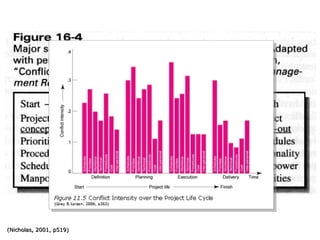
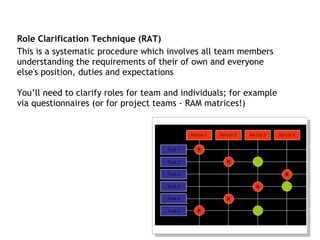
The document discusses various topics related to conflict management. It defines conflict and describes its sources and components. It outlines consequences of conflict, both good and bad. Conflict handling styles like avoiding, compromising, competing, accommodating, and collaborating are presented. The document also discusses responding to grievances, nature of stress, and strategies for managing stress at the organizational and individual level. Managing conflict, addressing grievances, and reducing stress are important for team and project success.