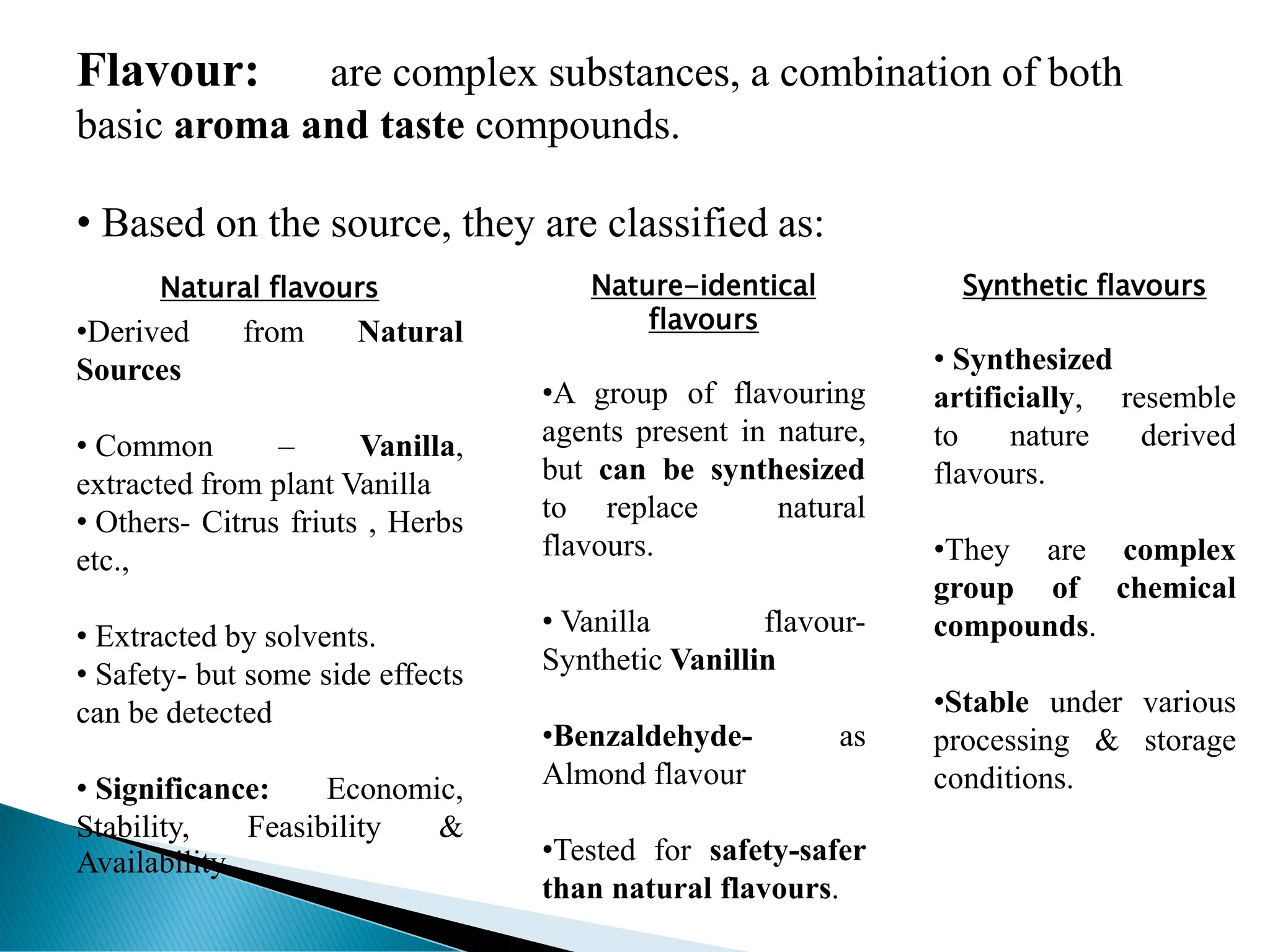
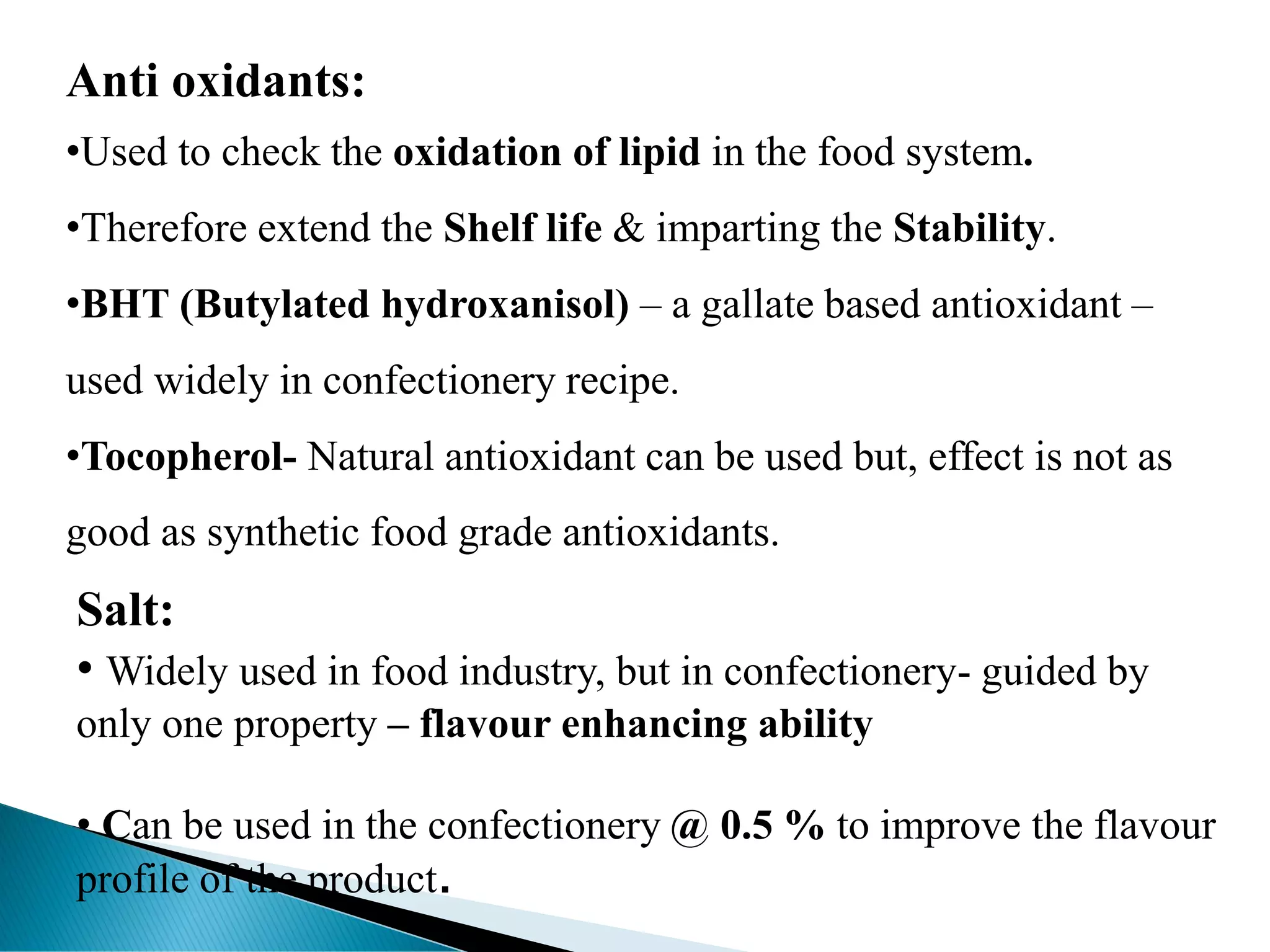
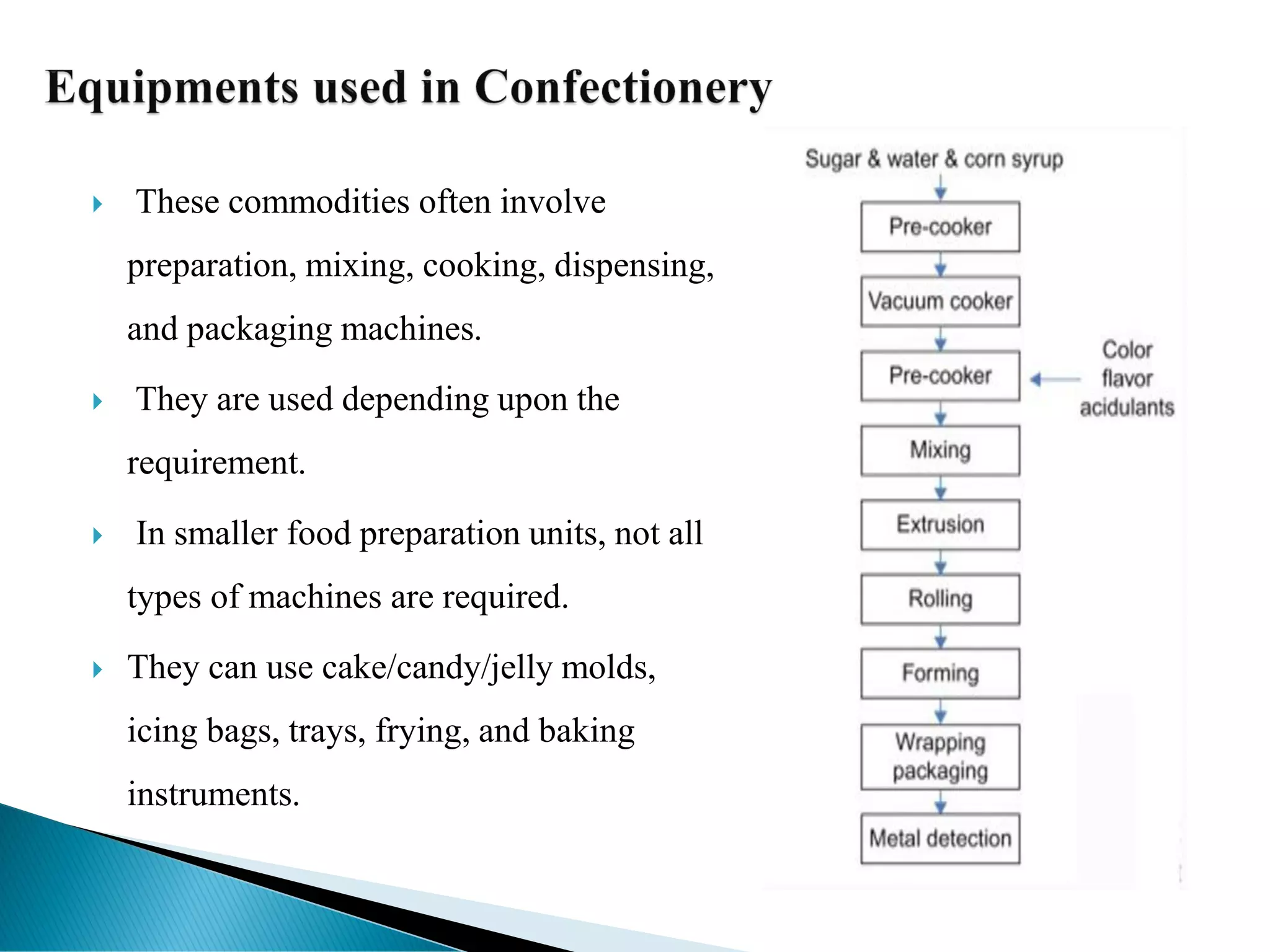
The document discusses different types of confectionery products. It begins by describing the various ingredients commonly used in making confections like sugars, dairy products, fats, hydrocolloids, emulsifiers, colors, flavors, and antioxidants. It then explains the different categories of confections - flour, sugar, chocolate, milk and other confections. Specific examples like toffee manufacturing process and popular Indian and international confections are also mentioned. The document provides detailed information on ingredients and processes involved in the confectionery industry.