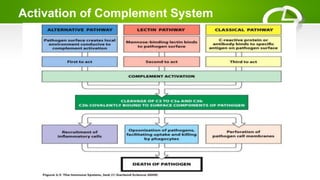
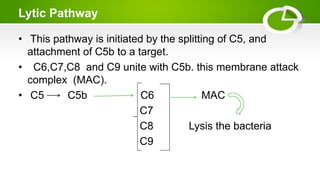
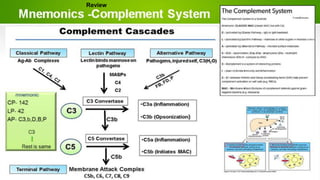
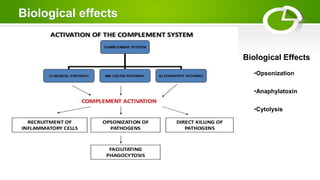
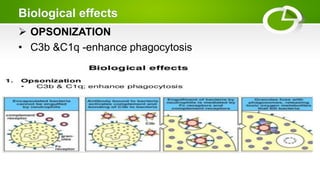
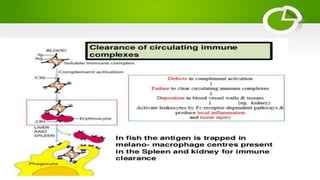
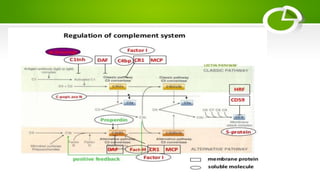
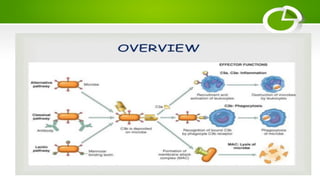
The document summarizes the complement system, its components, activation pathways, and functions. The complement system is a group of plasma proteins that enhance immunity. It consists of 11 main proteins that catalyze enzymatic reactions in three pathways: the classical pathway triggered by antibody-antigen complexes, the alternative pathway activated by bacterial surfaces, and the mannose-binding lectin pathway. The complement system opsonizes pathogens, releases anaphylatoxins, and forms the membrane attack complex to lyse bacteria cells. It also enhances antibody production and inflammation responses.