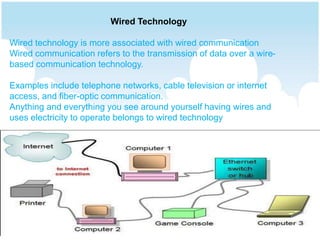
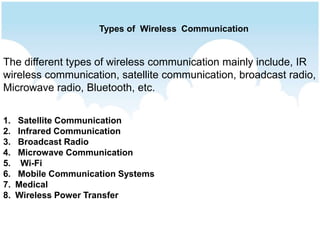
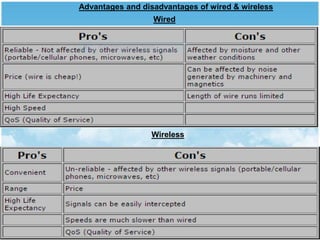
The document compares wired and wireless technologies, highlighting that wired technology relies on physical cables for data transmission, while wireless technology uses electromagnetic waves for communication. It details various types of wireless communication methods, such as satellite and infrared communication, and includes applications across different fields including telecommunications, medical systems, and mobile communication. Additionally, the document discusses the advantages and disadvantages of both wired and wireless setups.