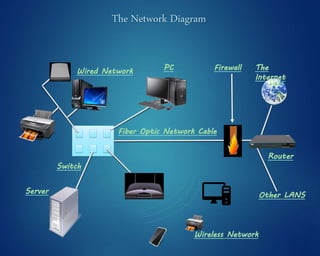
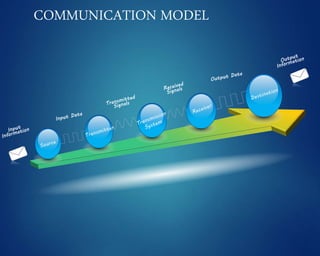
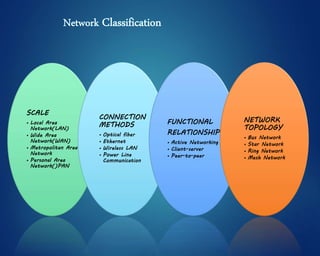
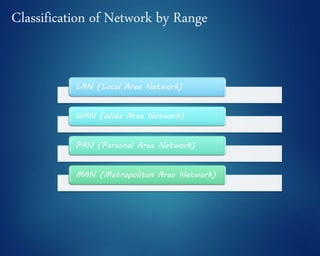
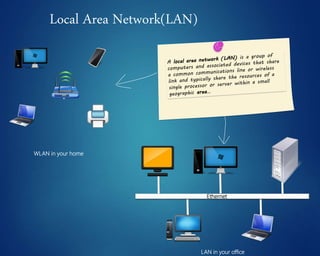
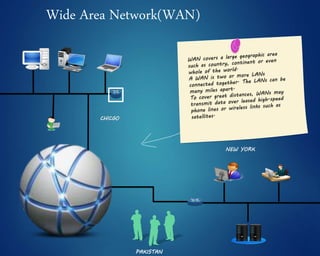
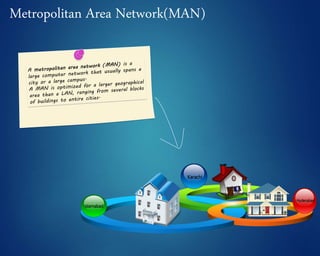
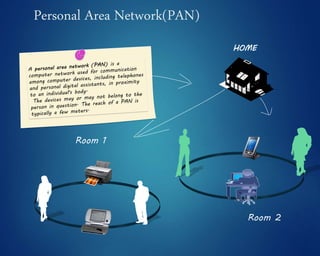
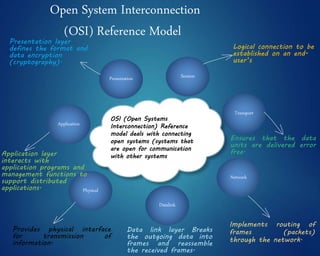
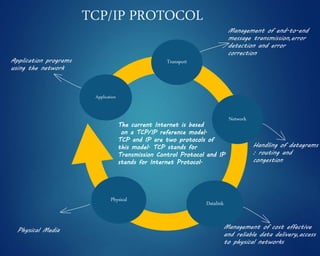
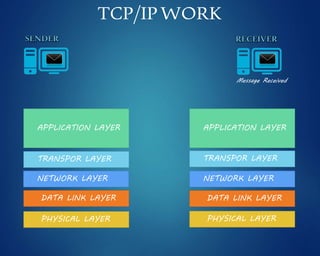
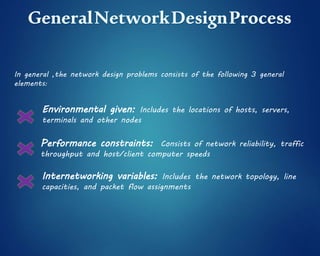
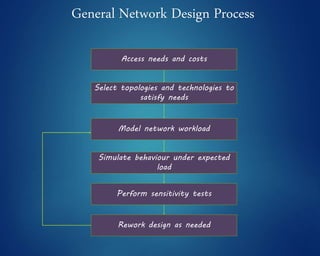
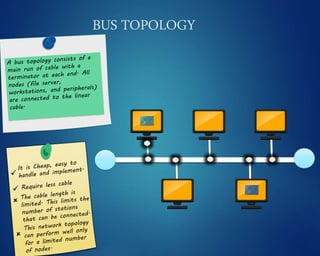
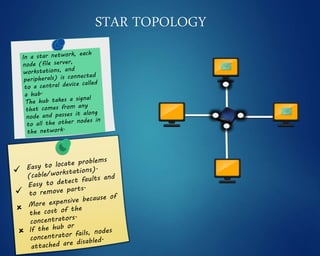
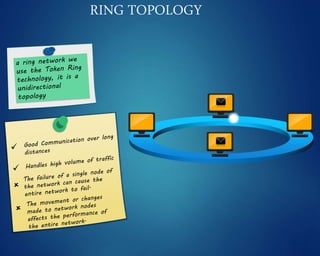
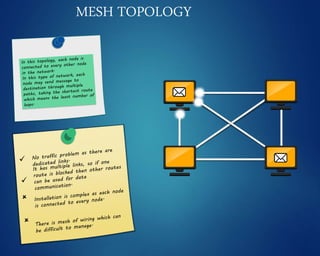
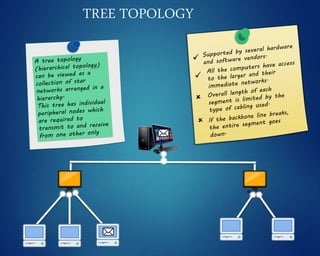
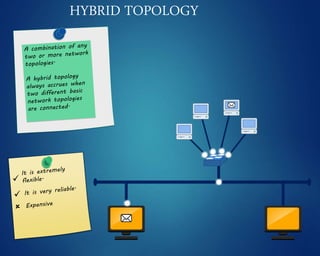
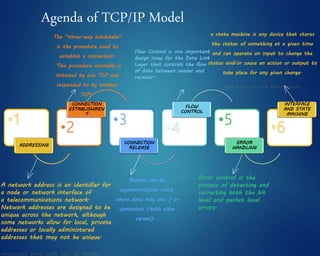
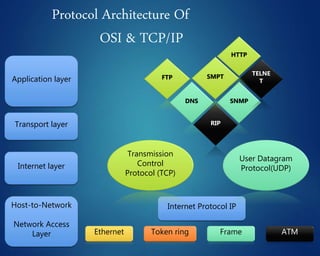
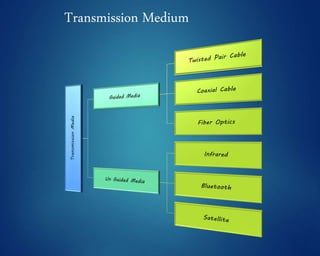
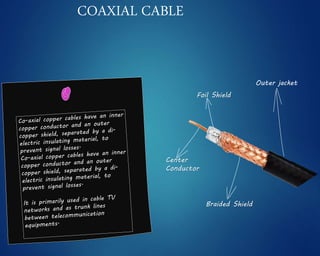
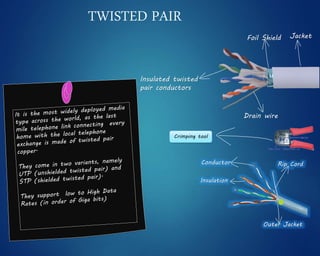
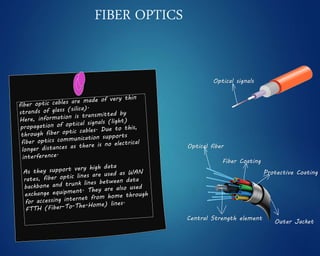
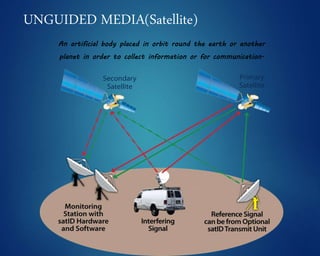
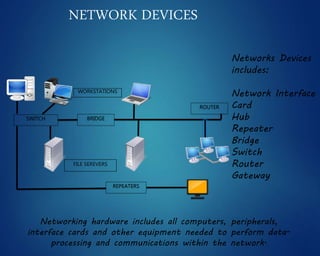
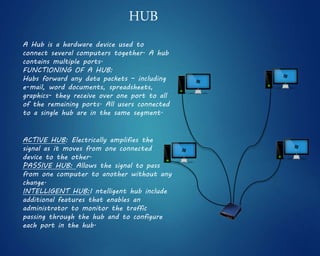
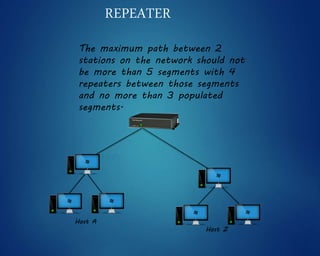
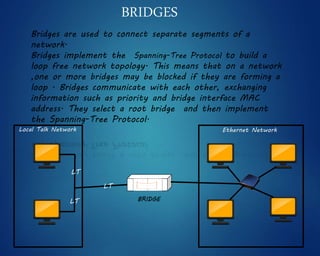
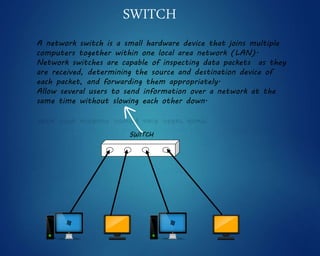
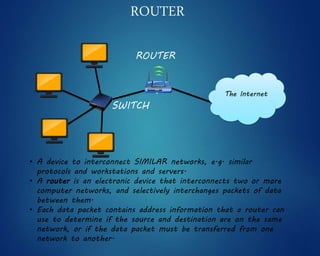
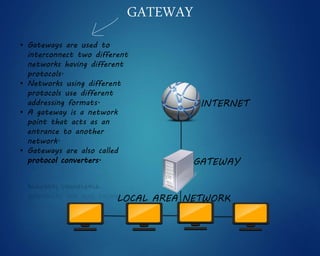
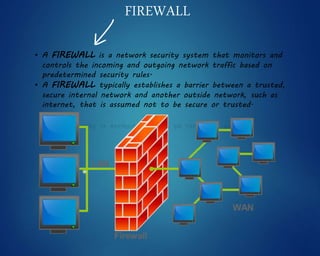
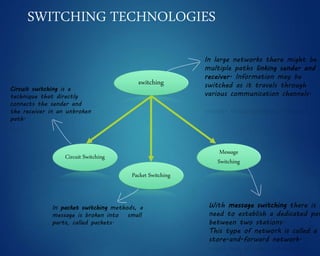
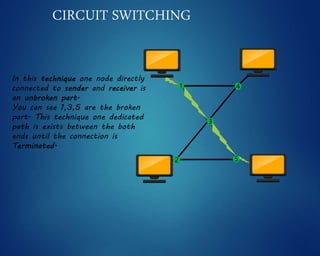
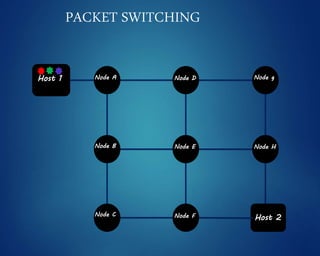
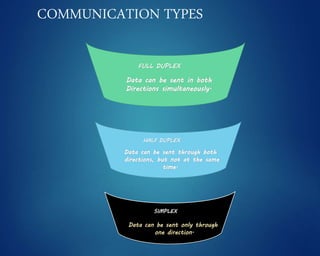
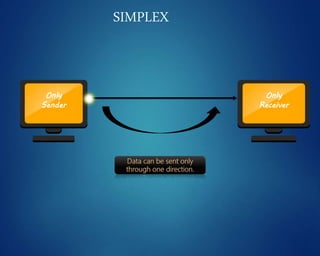
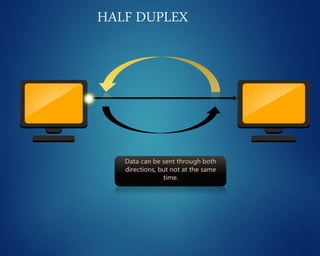
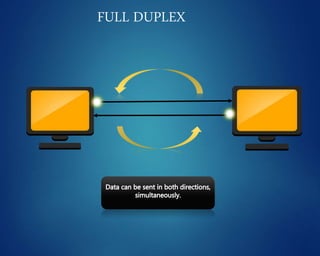
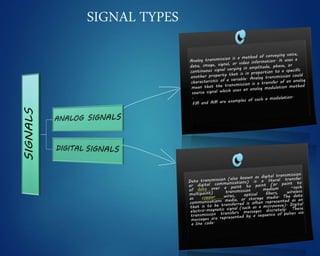
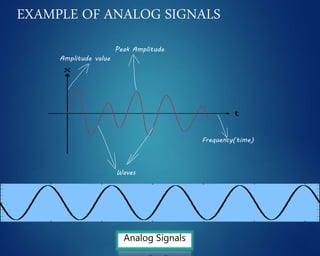
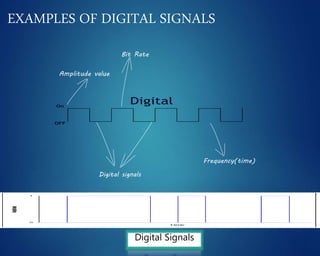
This document provides an overview of computer networks. It discusses network diagrams, classifications of networks by range including LAN, WAN, PAN and MAN. Common network topologies such as bus, star, ring and mesh are described. The OSI and TCP/IP models are explained. Common network devices, switching technologies, and transmission media are defined. Signal types including analog and digital are also summarized.