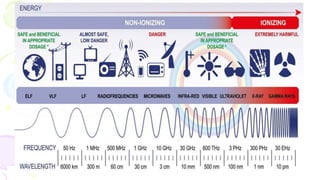
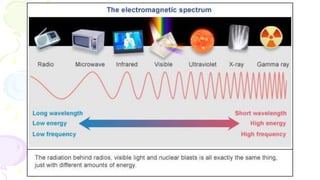
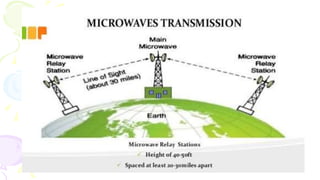
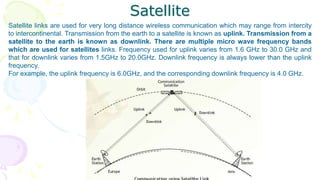
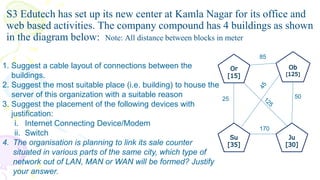
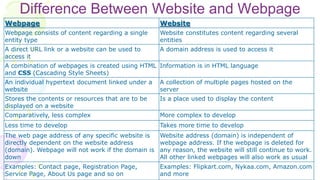
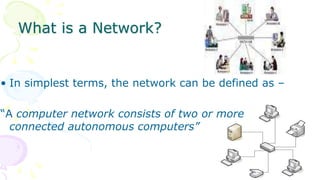
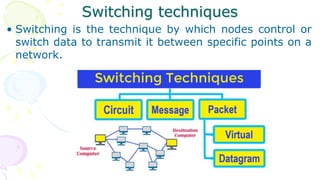
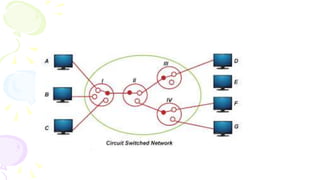
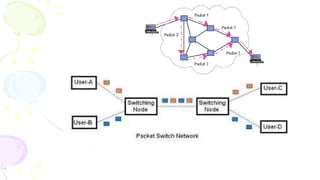
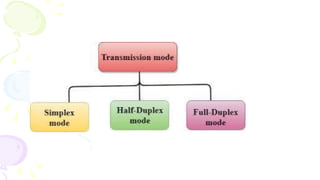
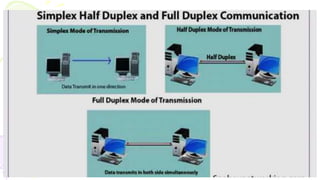
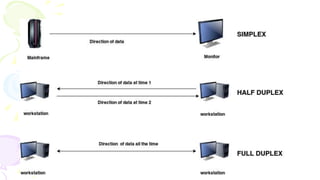
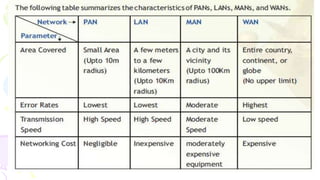
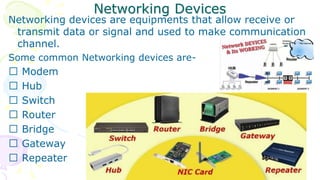
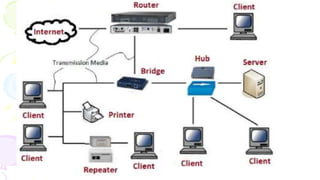
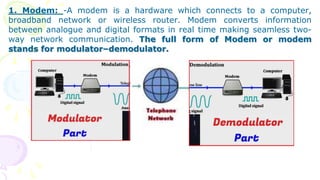
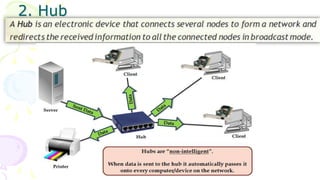
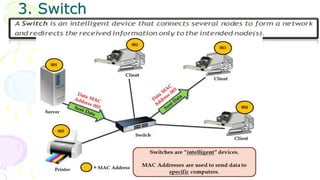
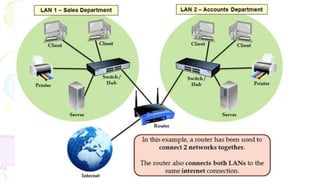
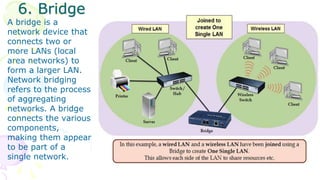
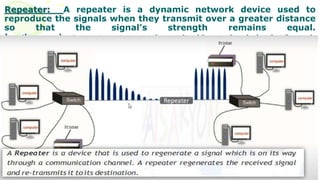
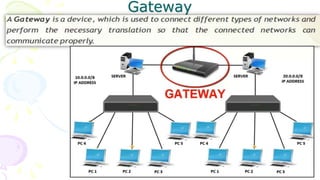
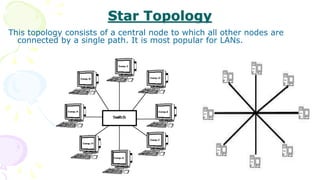
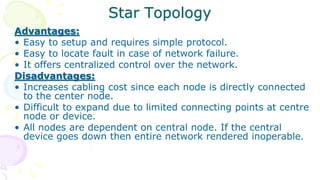
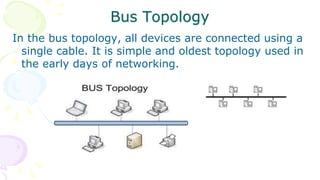
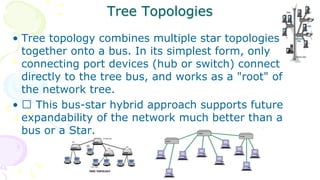
This document provides an overview of computer networks. It begins by discussing how computer networks have changed daily life through services like watching cable TV, using ATMs, emailing, and more. A network is defined as two or more connected autonomous computers. The goals of networking are sharing resources, improved communication, and reduced communication costs. Networks have senders, receivers, messages, transmission mediums, and protocols. Early networks included ARPANET and NSFNET. The internet evolved from these and allows globally connected services. Network topologies like star, bus, and types of devices like hubs, switches, and routers are also summarized.











![WLAN [Wireless LAN]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computernetworkingxiics-240125105847-e74ac19c/85/Computer-Networking_XII_CS_CBSE_OFKVS-ppt-25-320.jpg)




![Transmission Media
[Communication Channel ]
• All the computers or connecting devices in the network
must be connected to each other by a Transmission Media
or channel.
• A communication channel is either a physical transmission
medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a
multiplexed medium such as a radio channel in
telecommunications and computer networking.
• The selection of Media depends on the cost, data transfer
speed, bandwidth and distance.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computernetworkingxiics-240125105847-e74ac19c/85/Computer-Networking_XII_CS_CBSE_OFKVS-ppt-38-320.jpg)