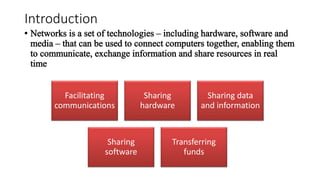
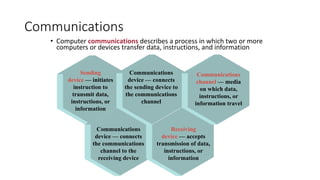
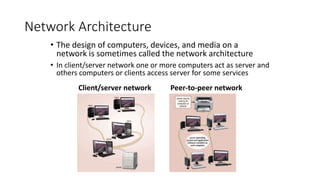
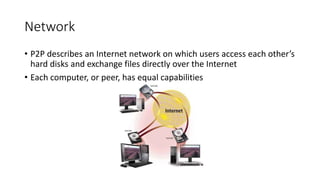
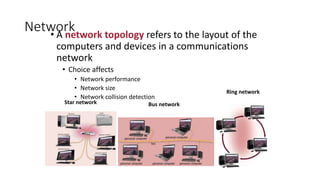
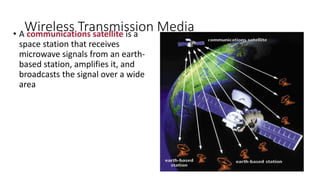
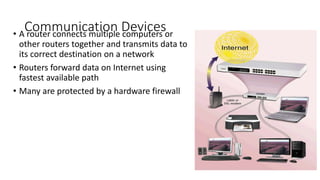
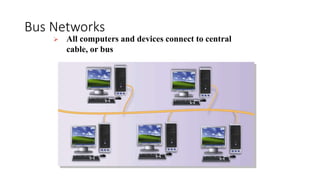
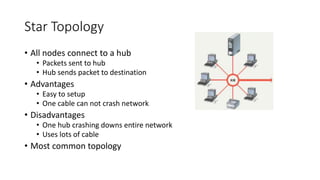
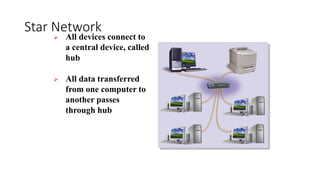
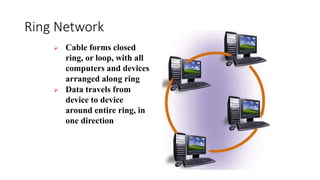
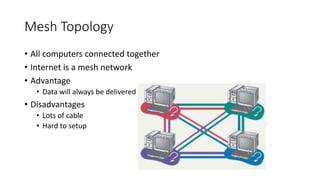
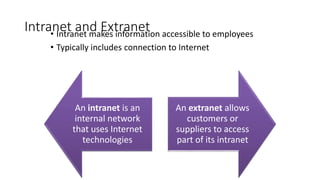
This document discusses computer networks and networking concepts. It defines what a network is and describes different types of networks including local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), home area networks (HANs), and personal area networks (PANs). It also covers networking devices, protocols, transmission media, and standards used for communication on networks.