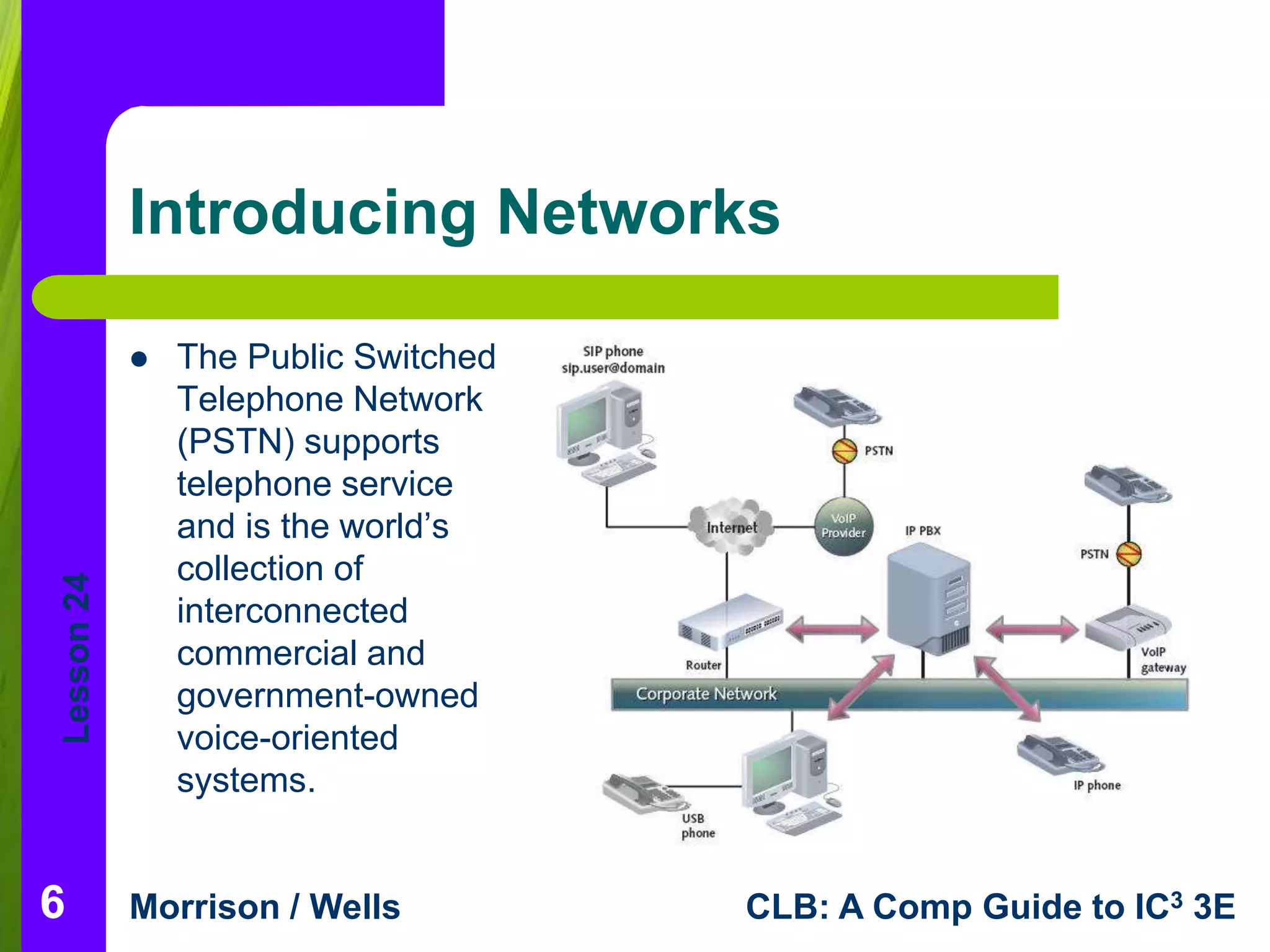
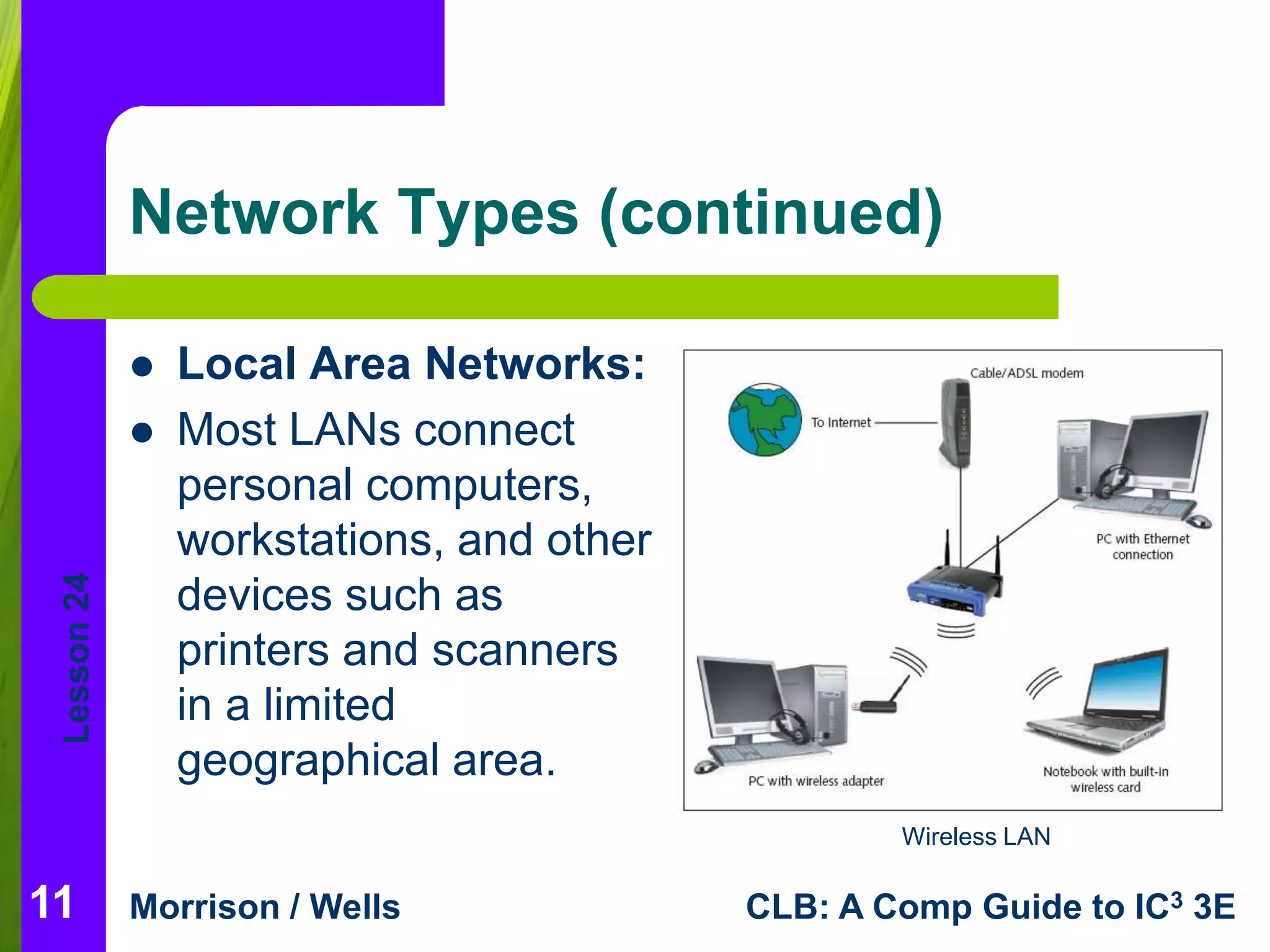
This document is a lesson on network fundamentals that describes networks, their benefits and risks. It defines key network terms and outlines different network types including local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs). The lesson discusses client/server networks and peer-to-peer networks. It also covers network communication hardware, security issues and planning for security on networks.