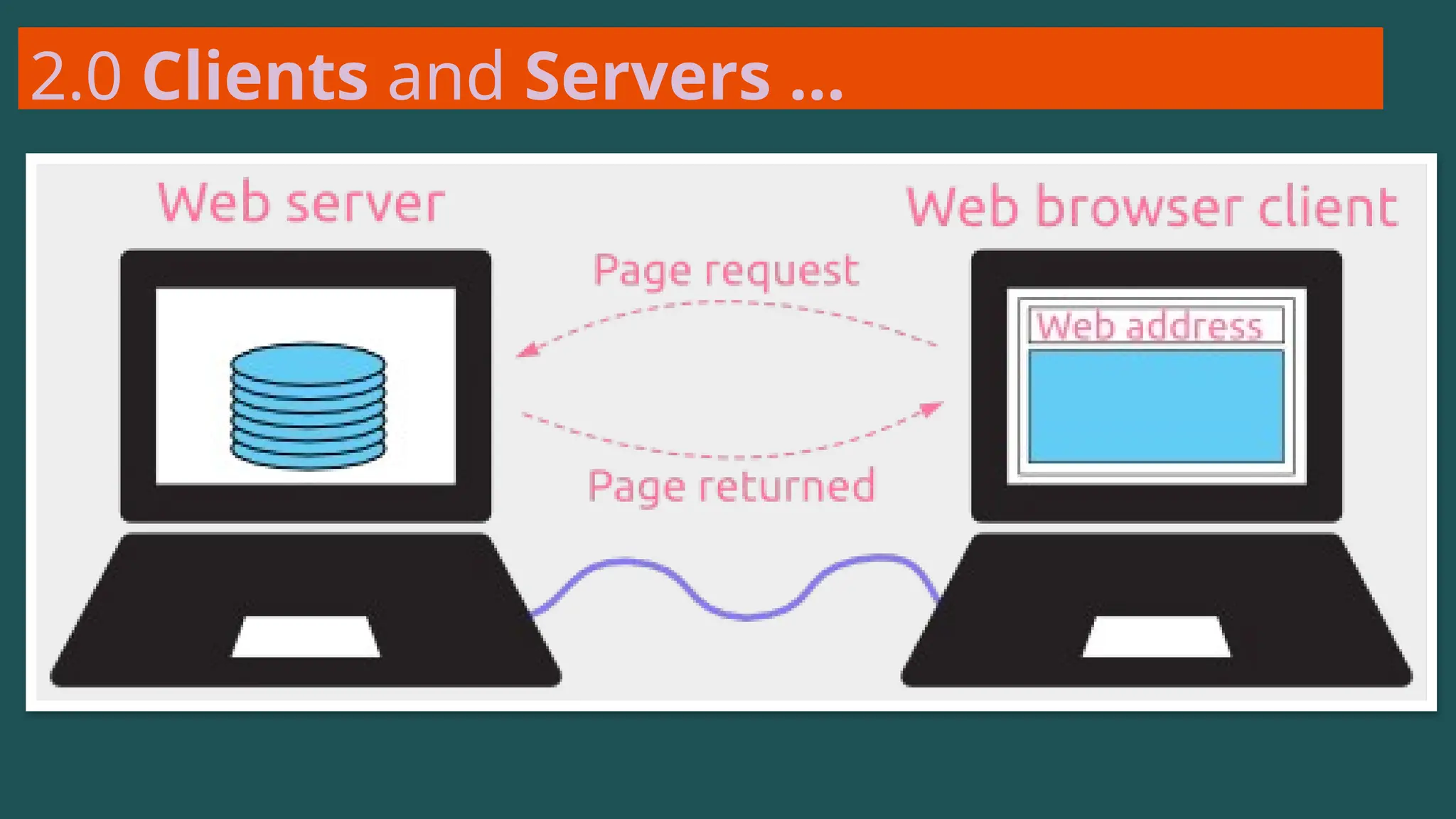
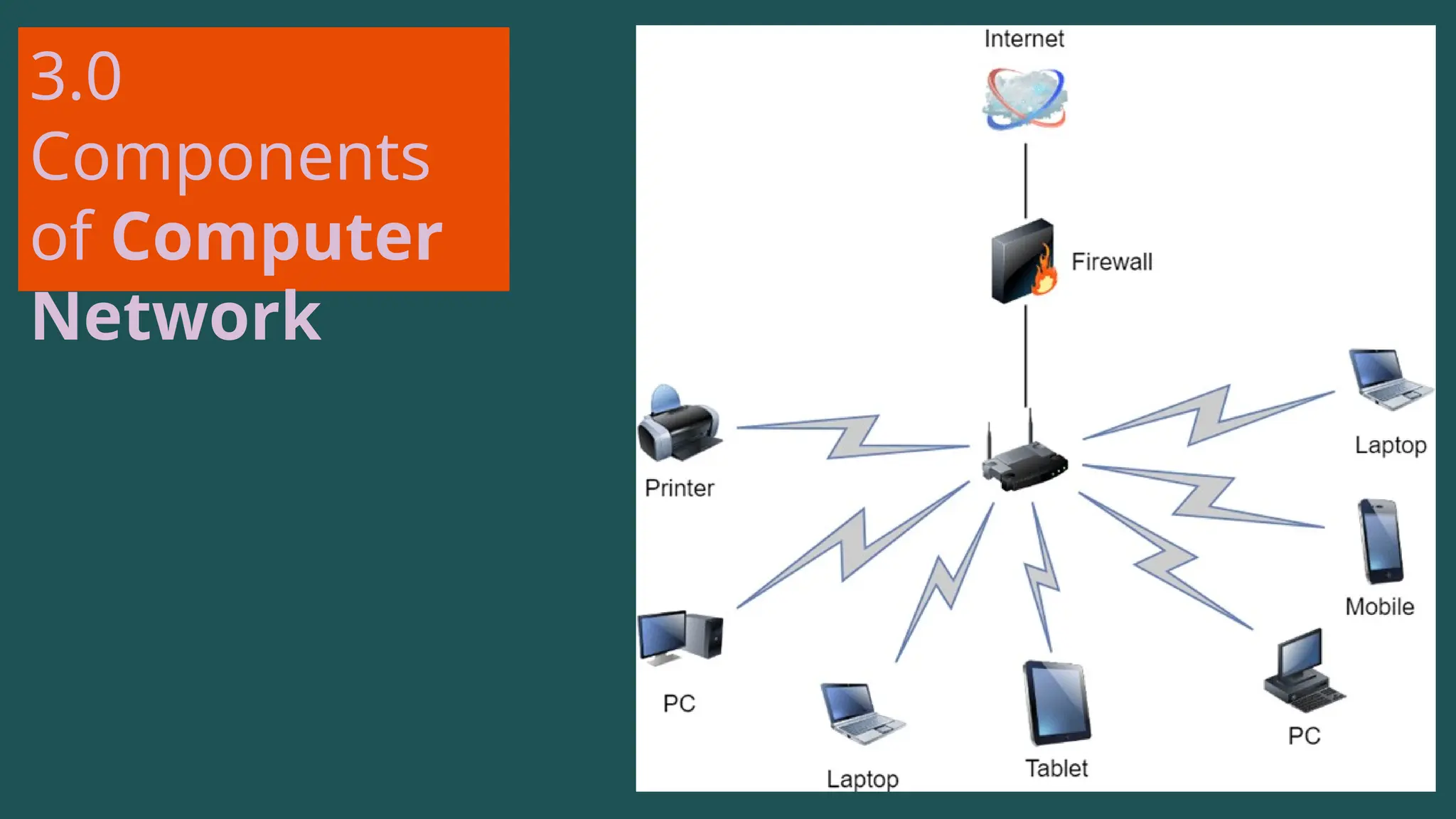
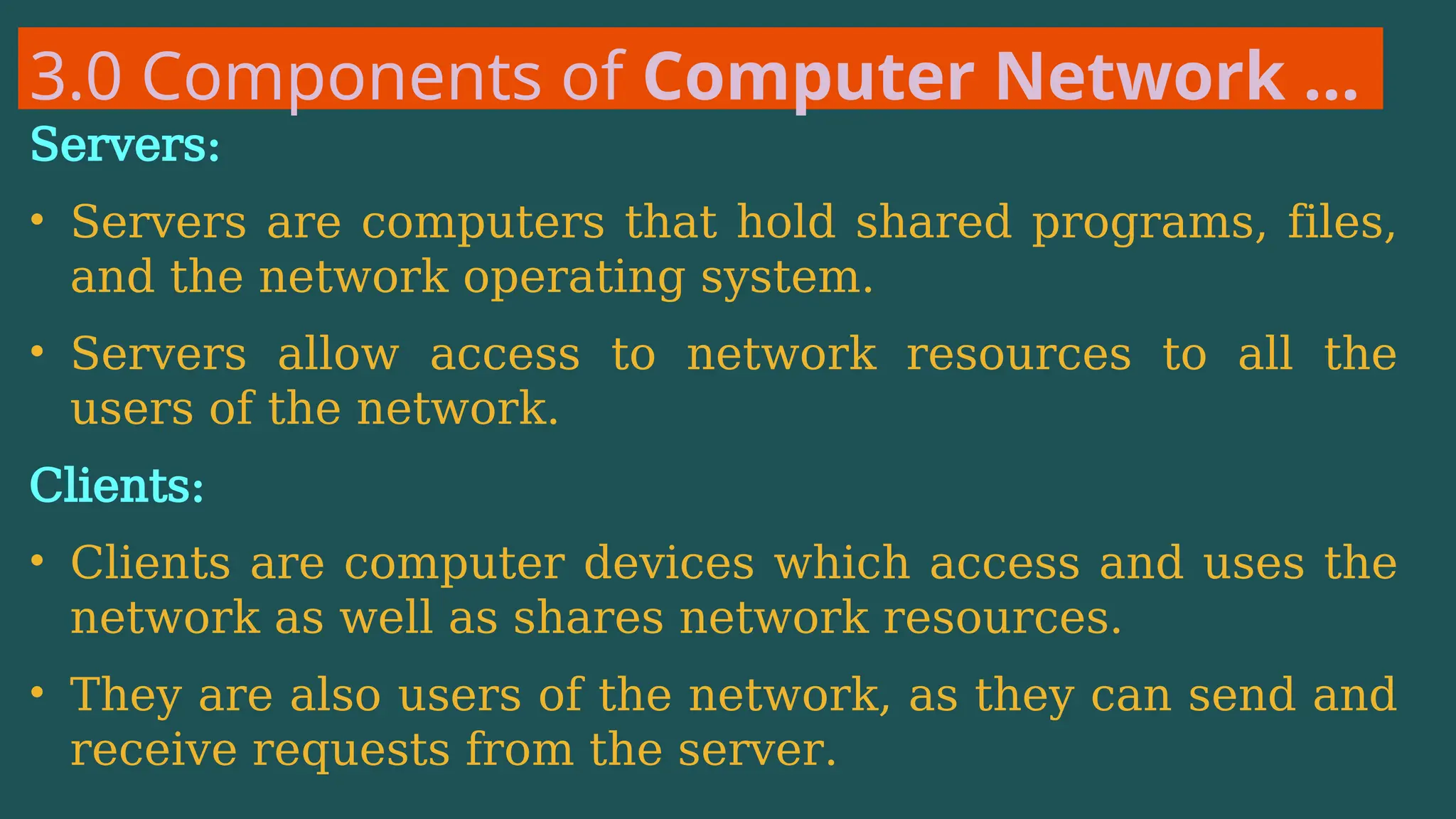
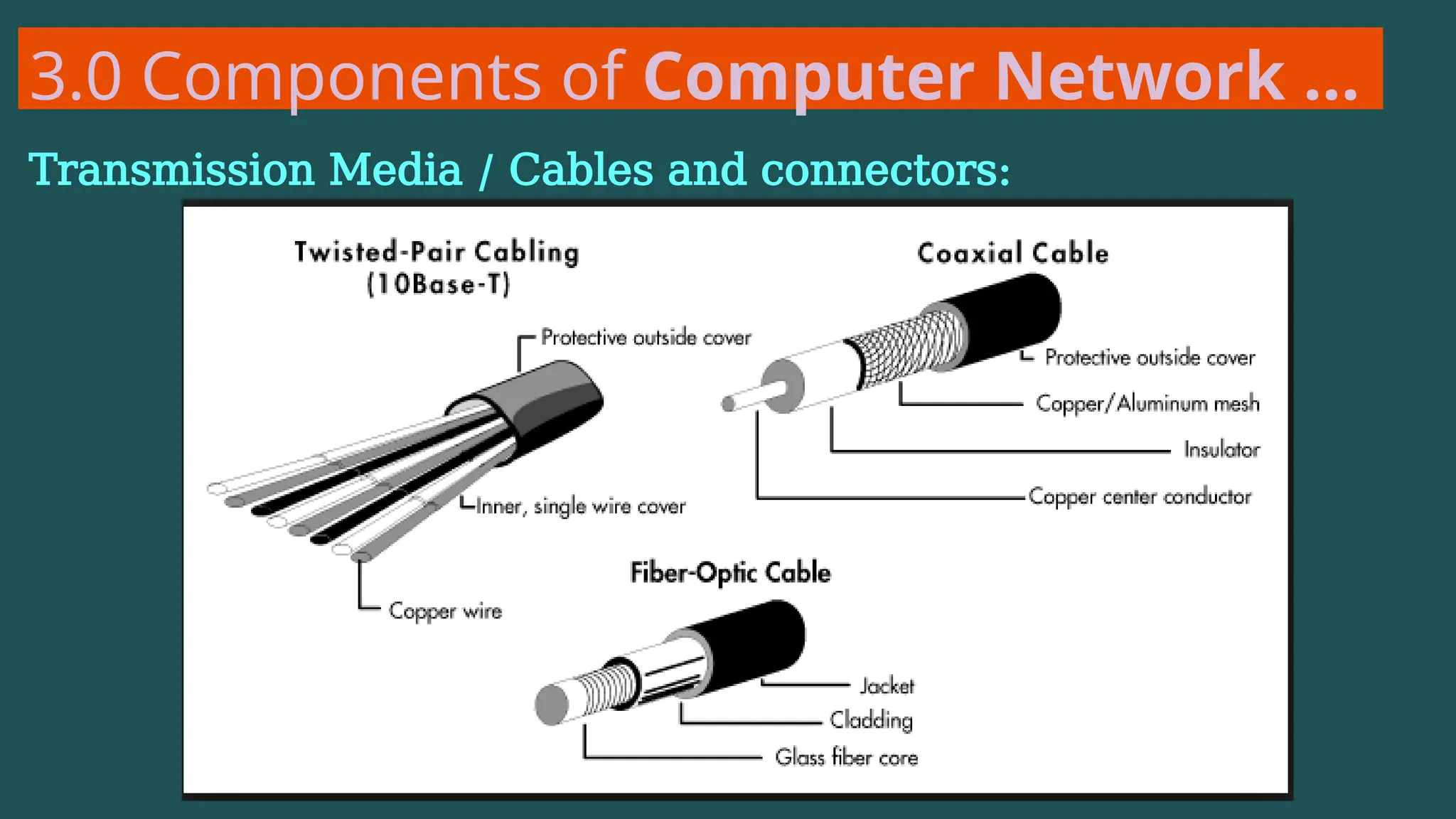
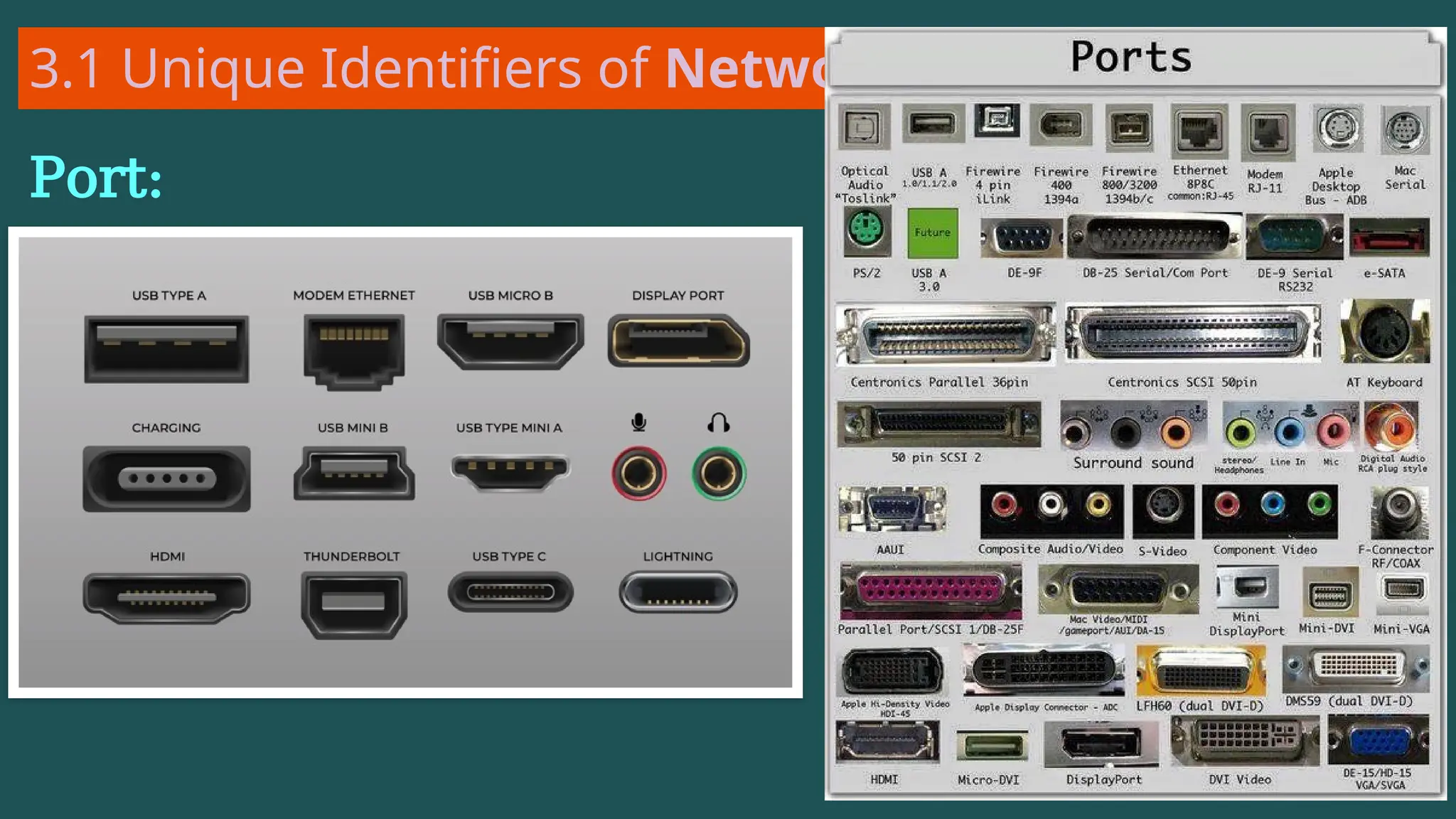
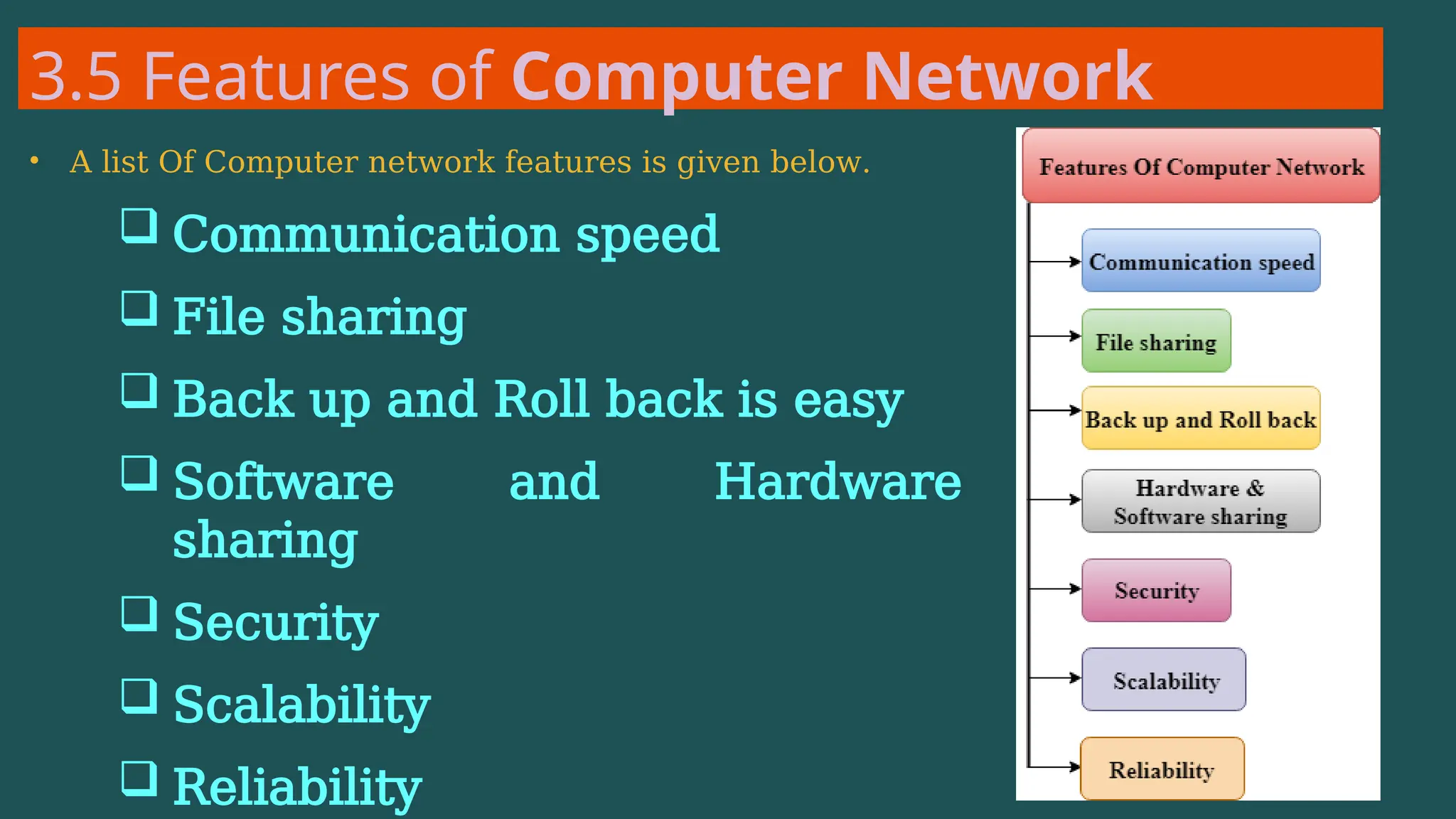
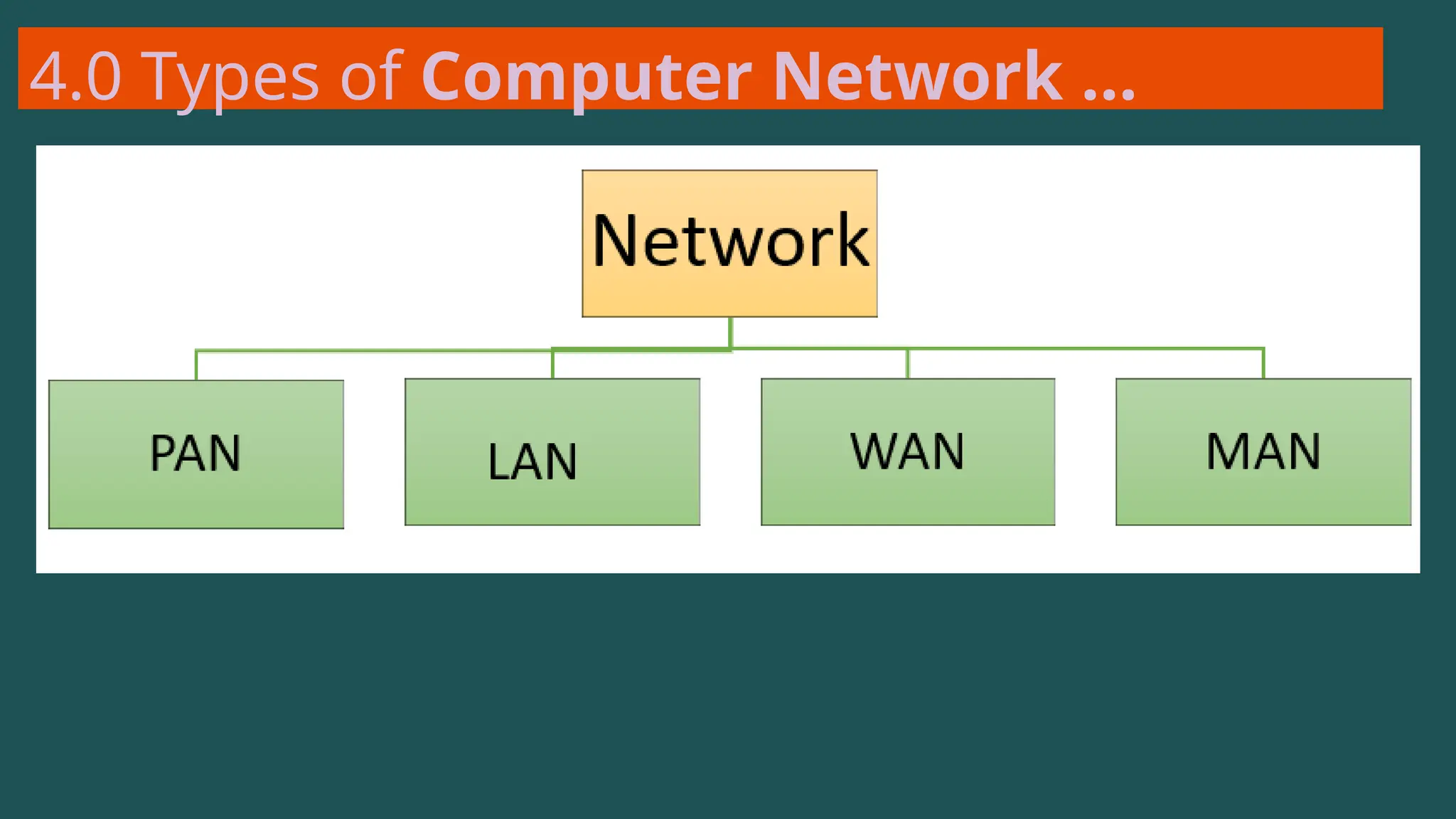
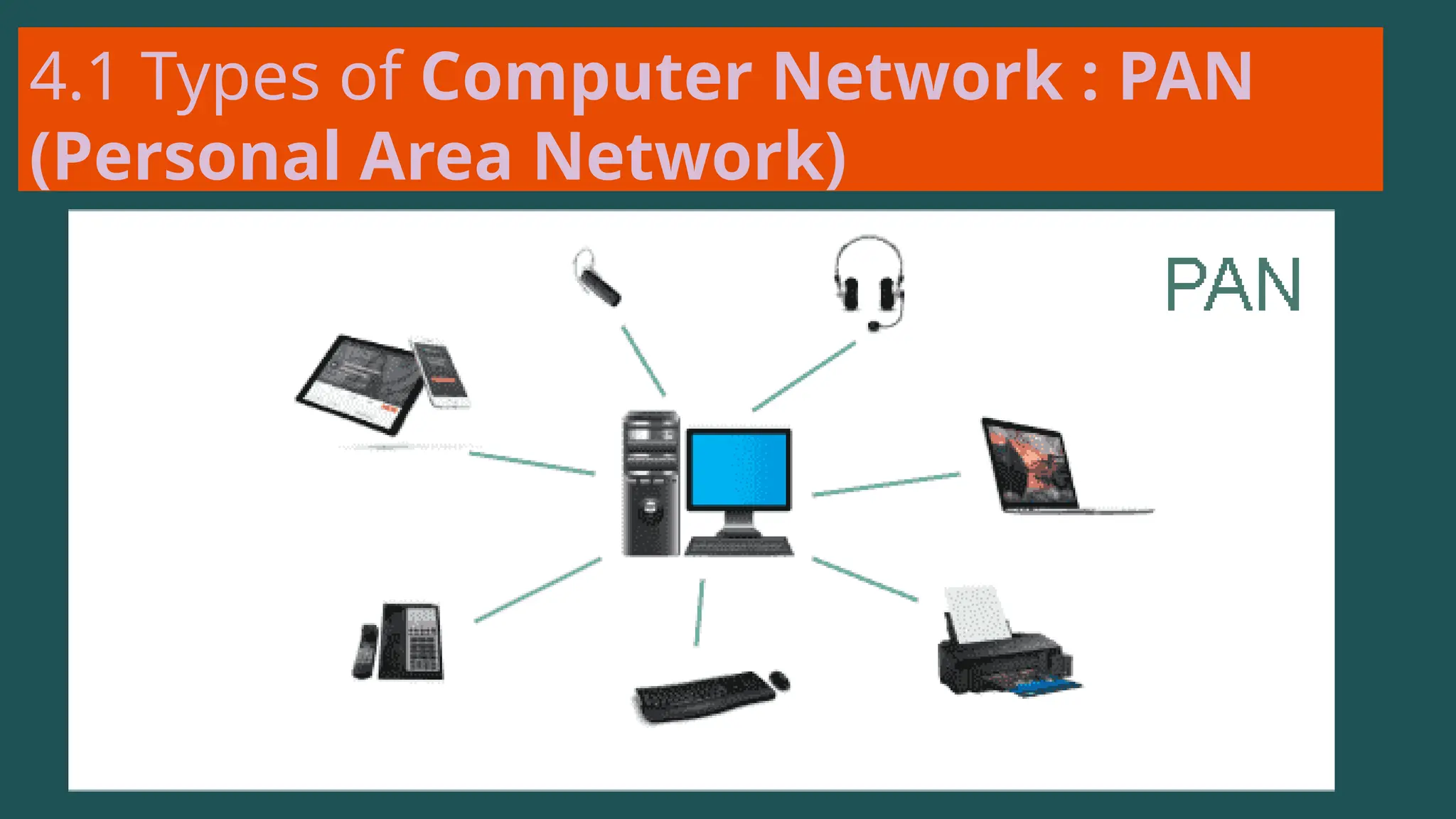
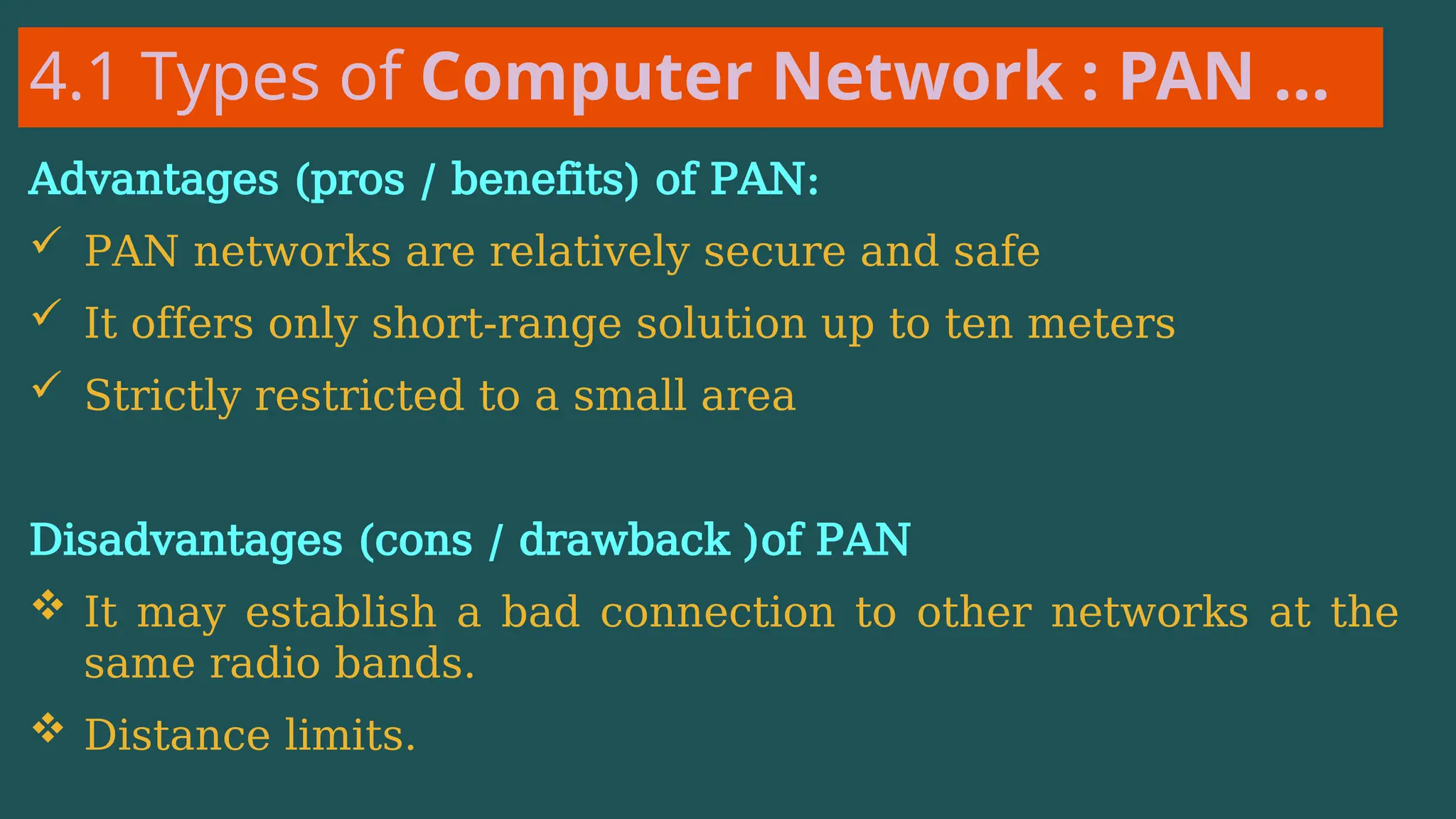
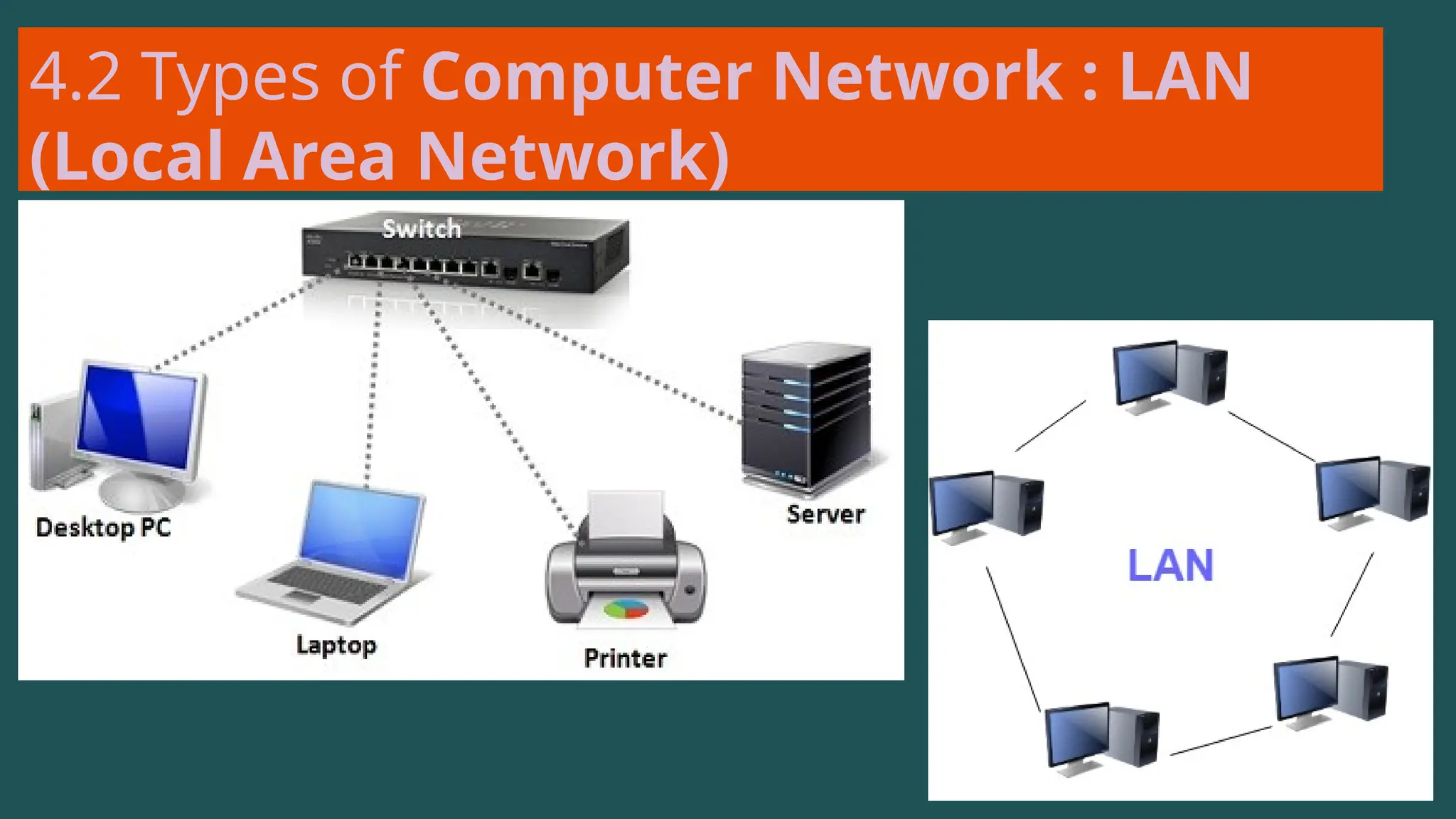
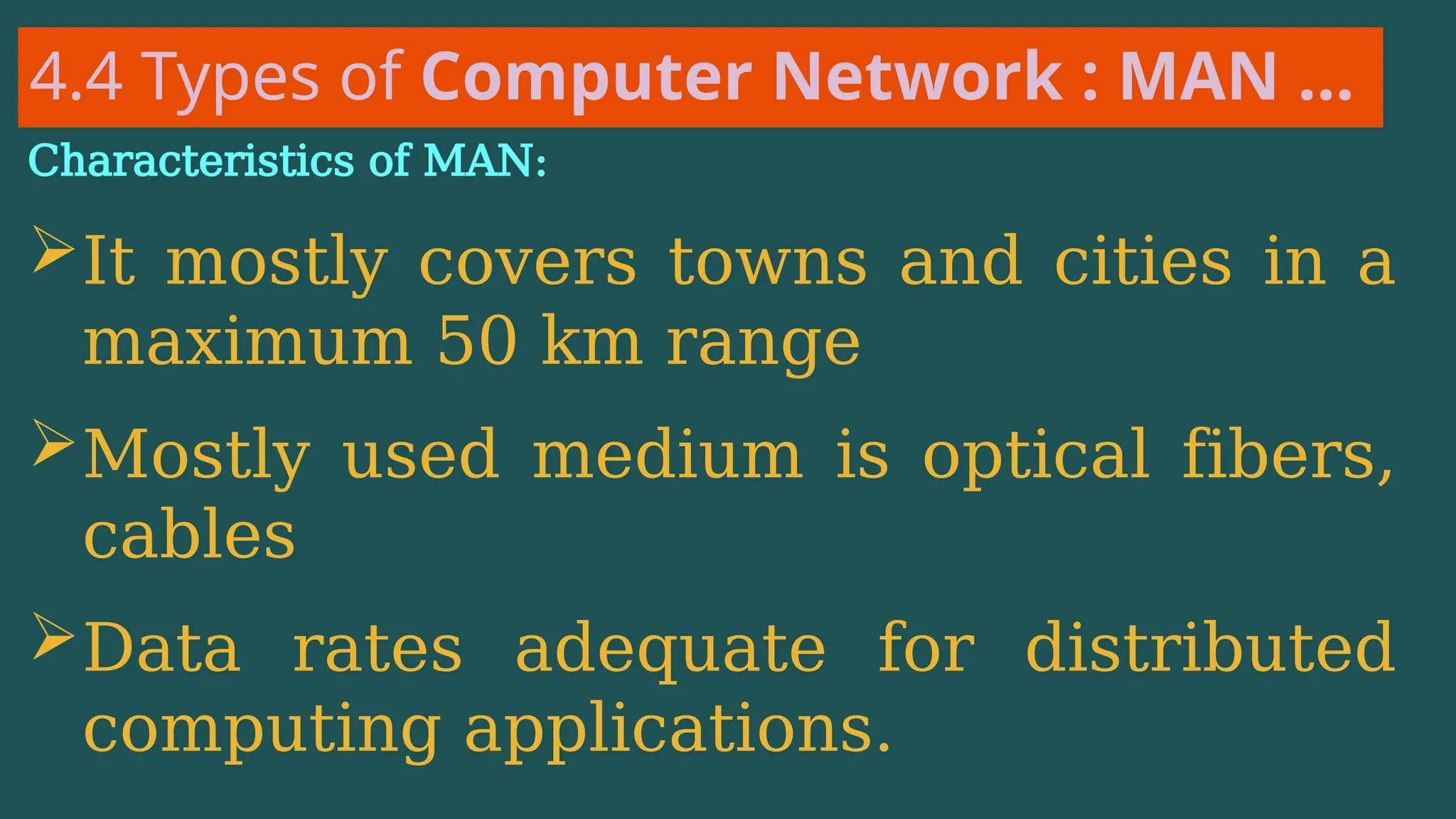
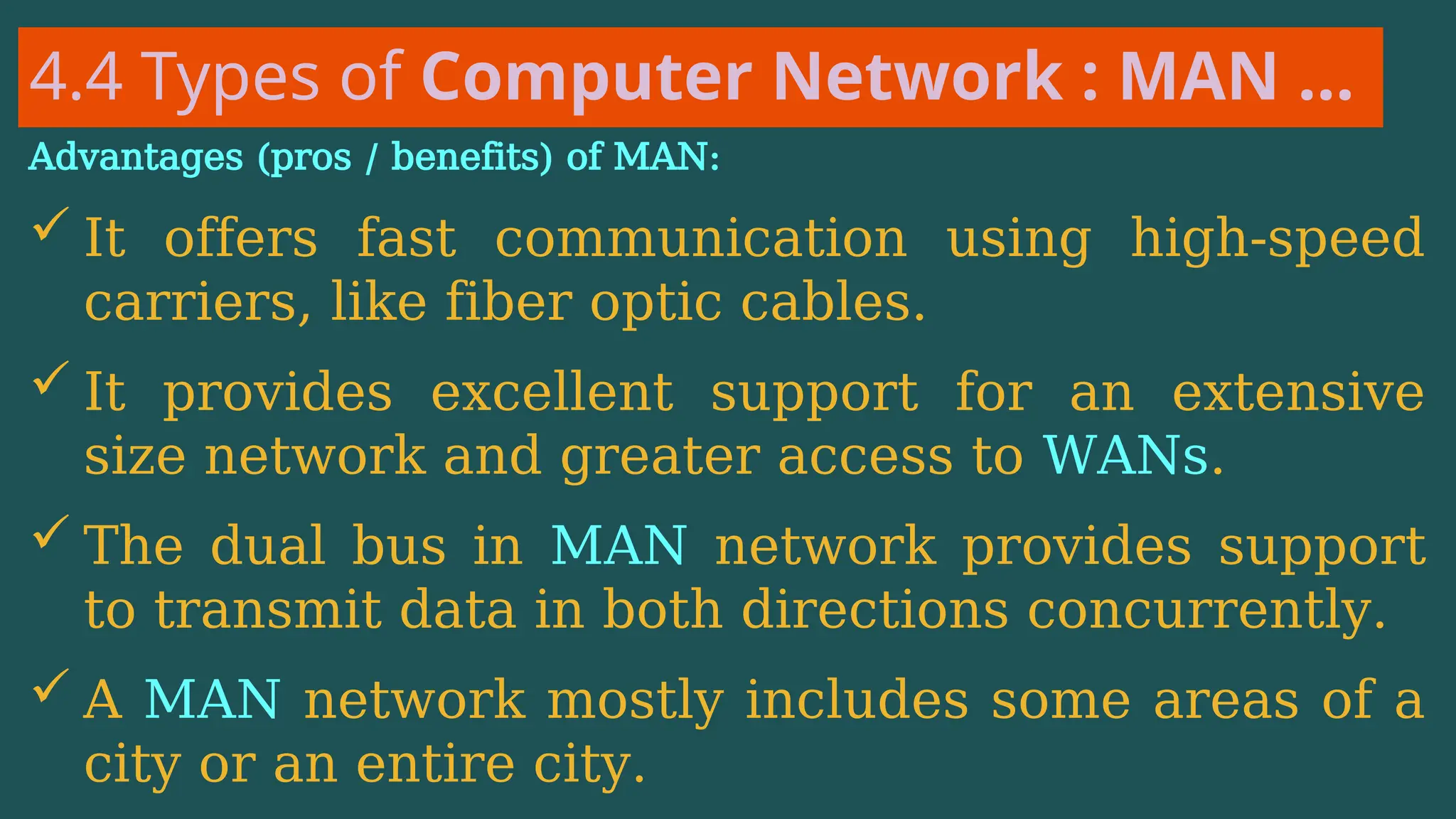
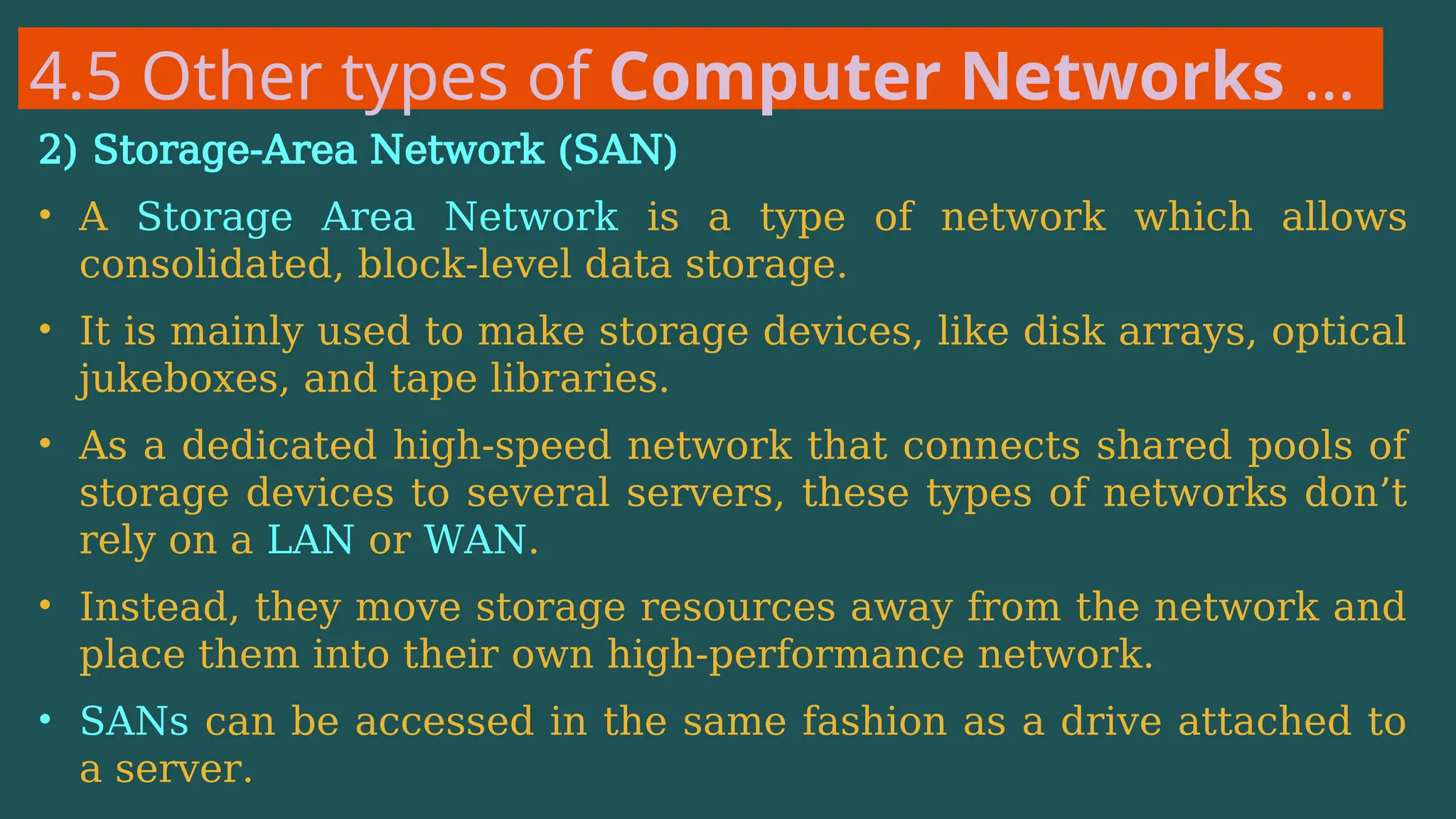
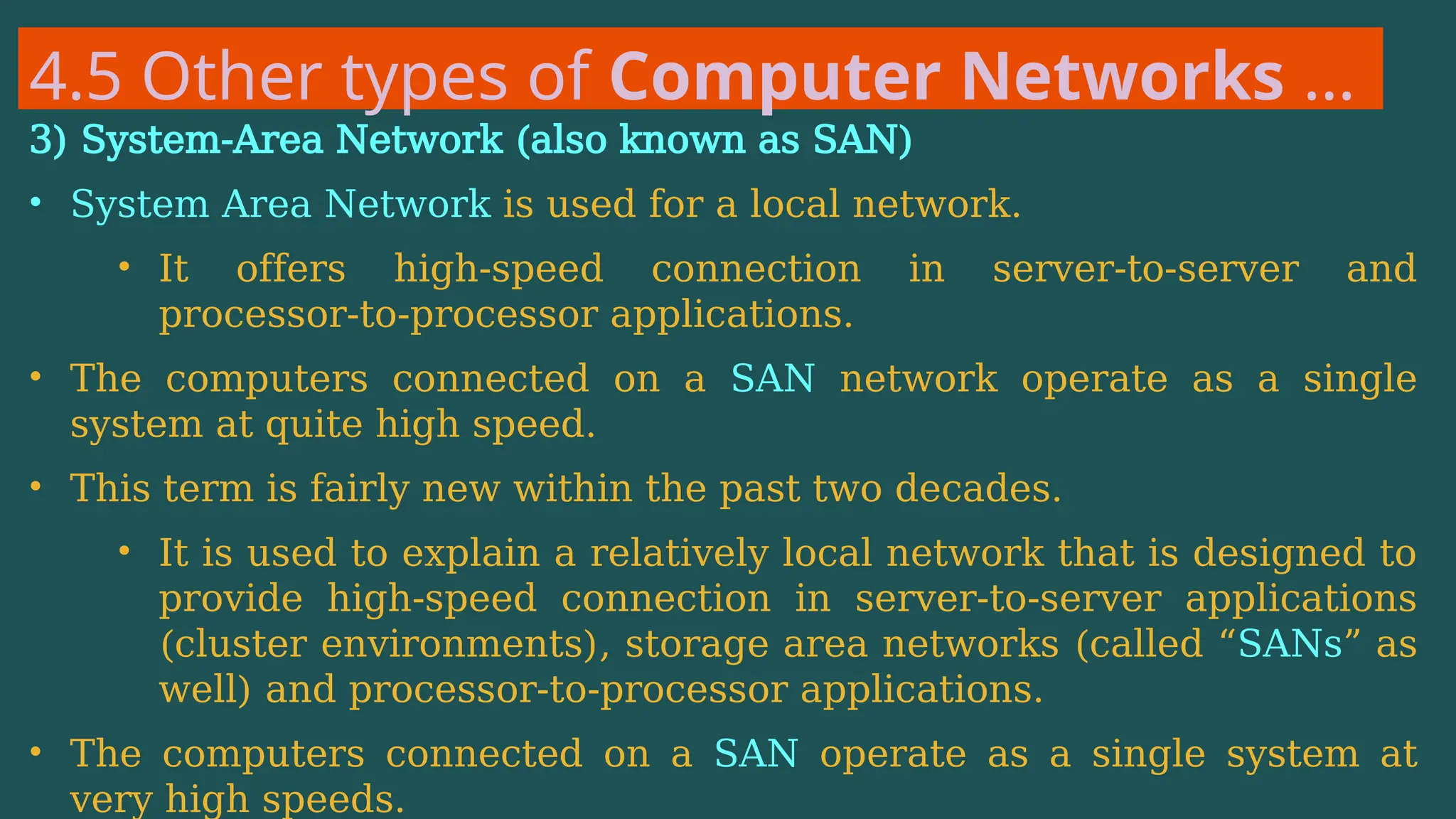
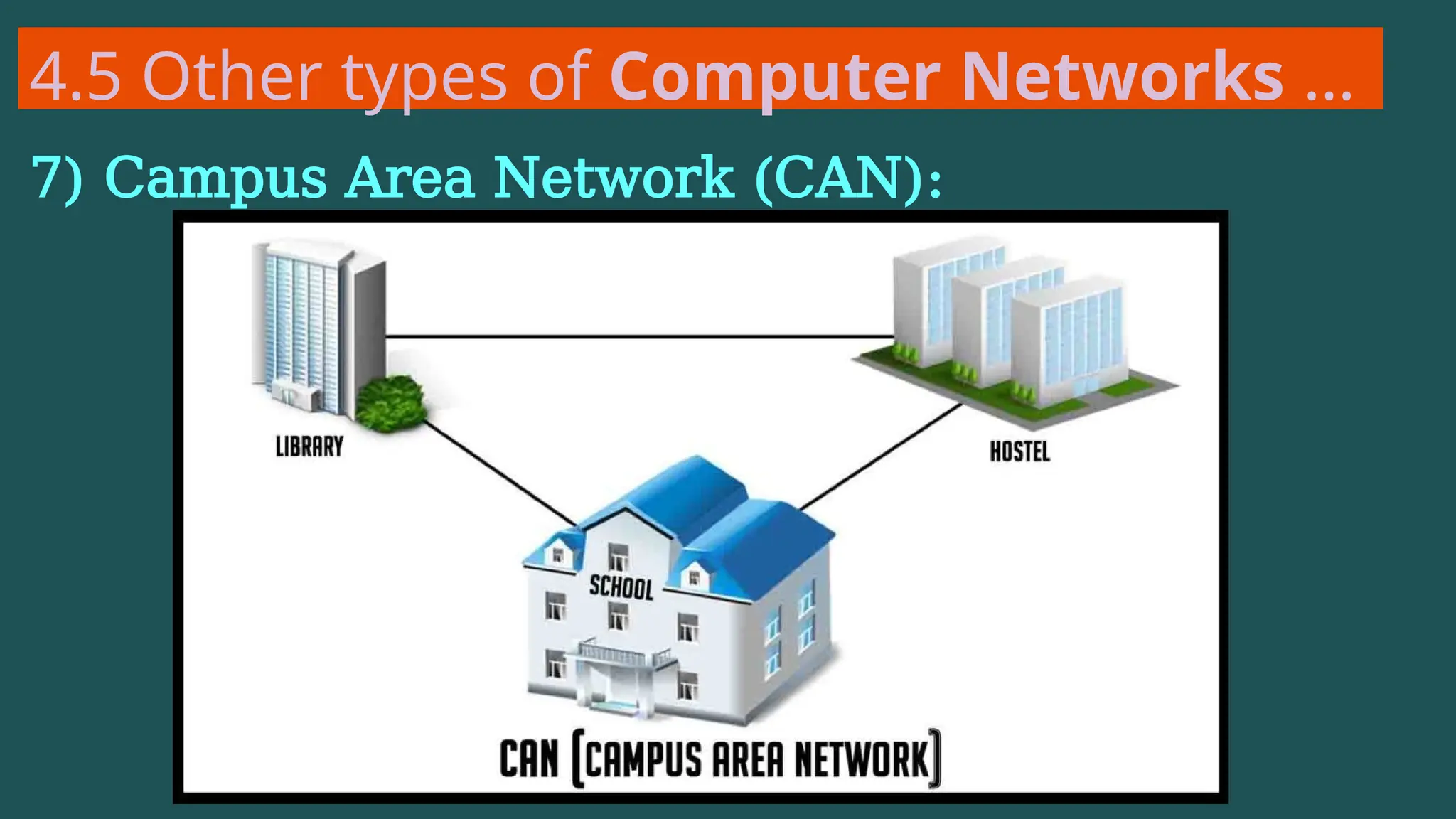
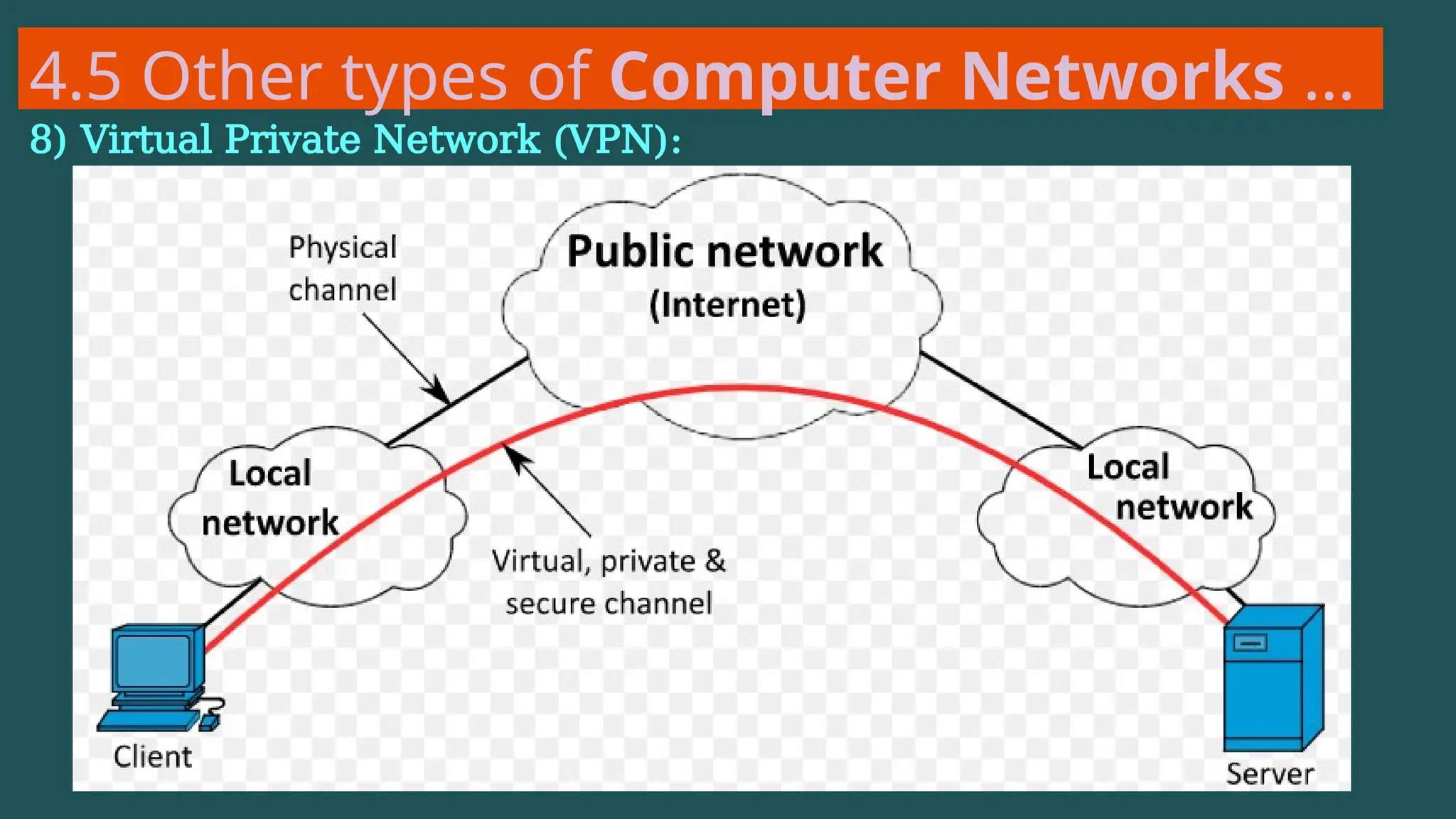
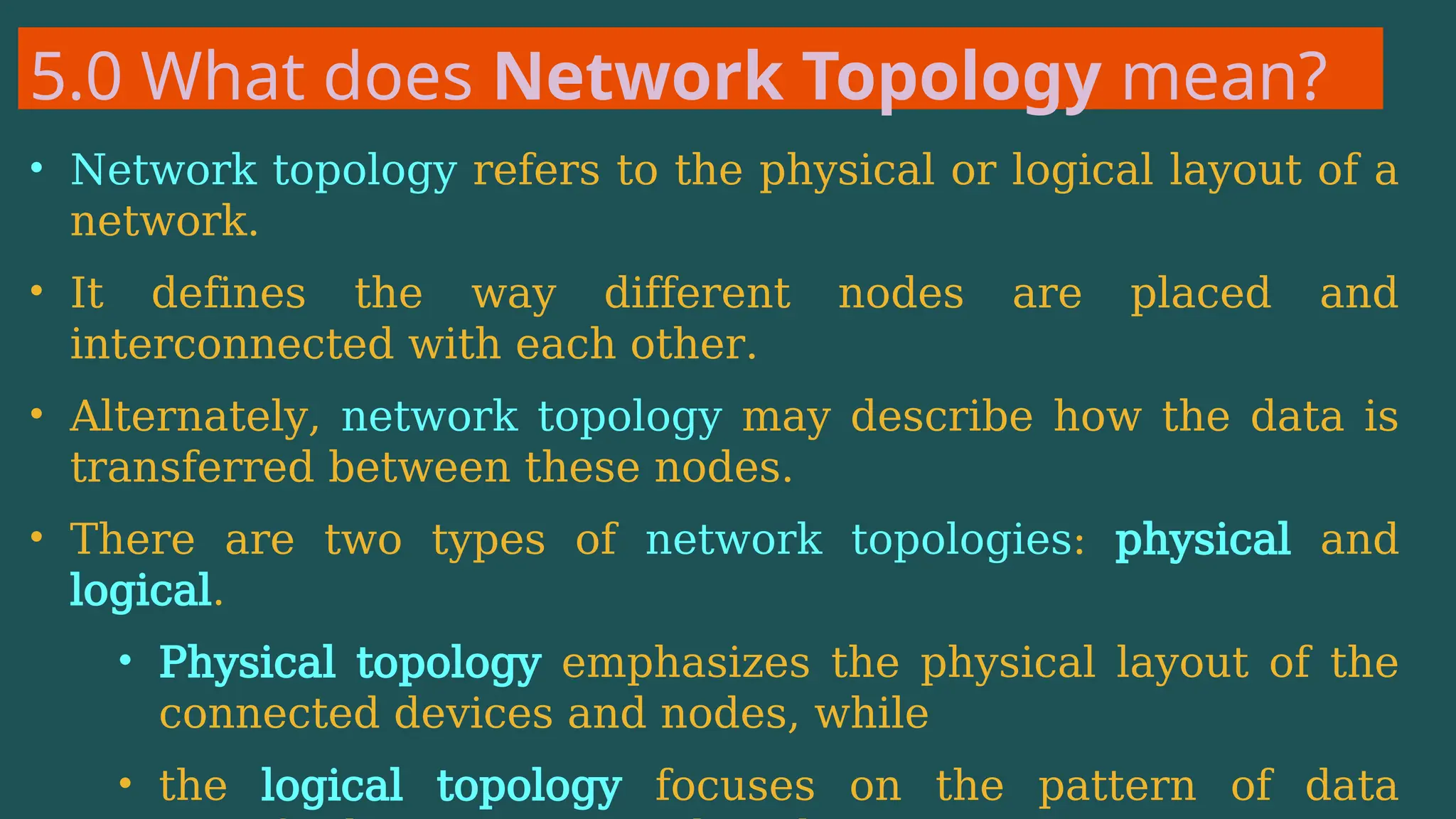
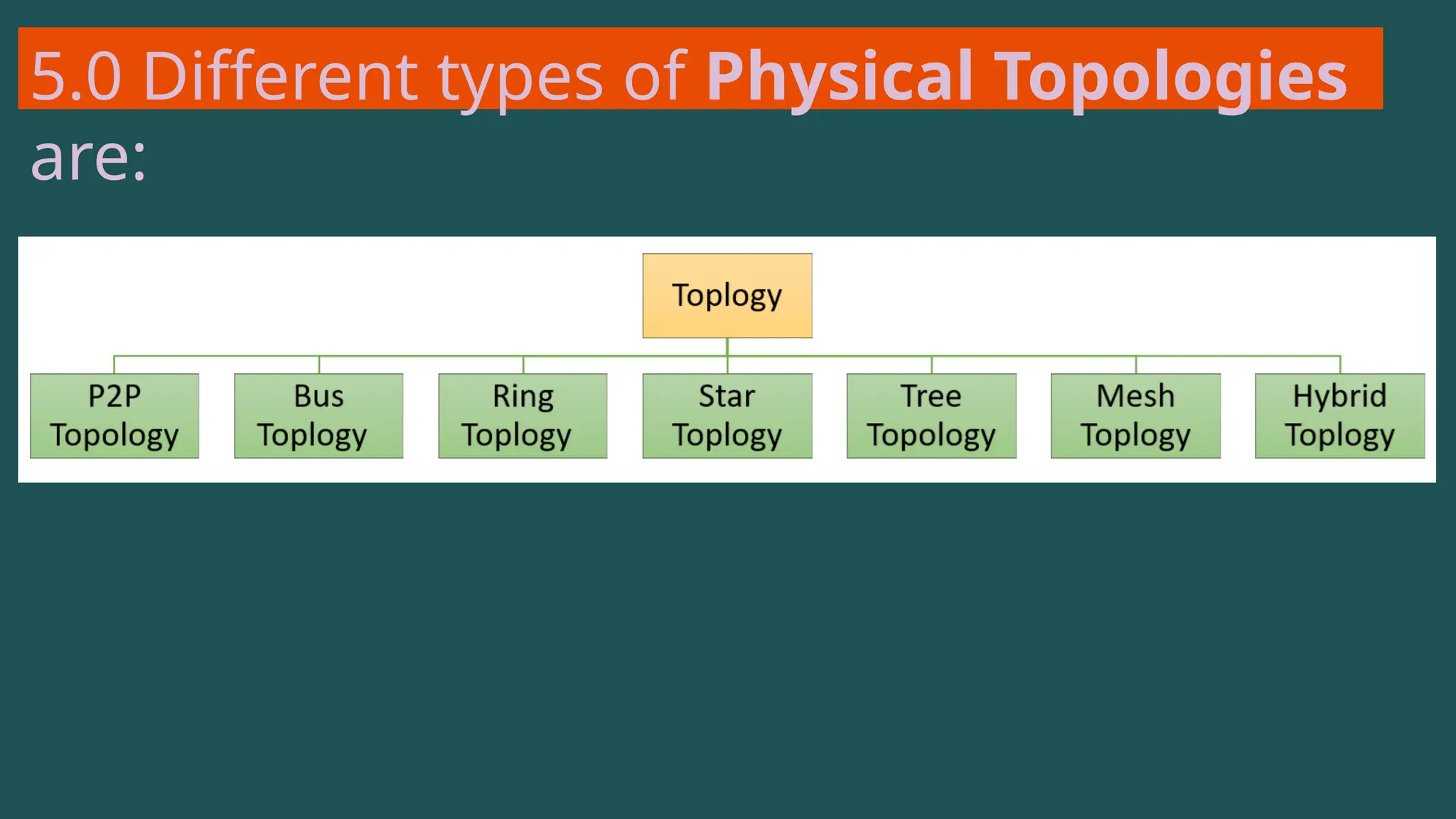
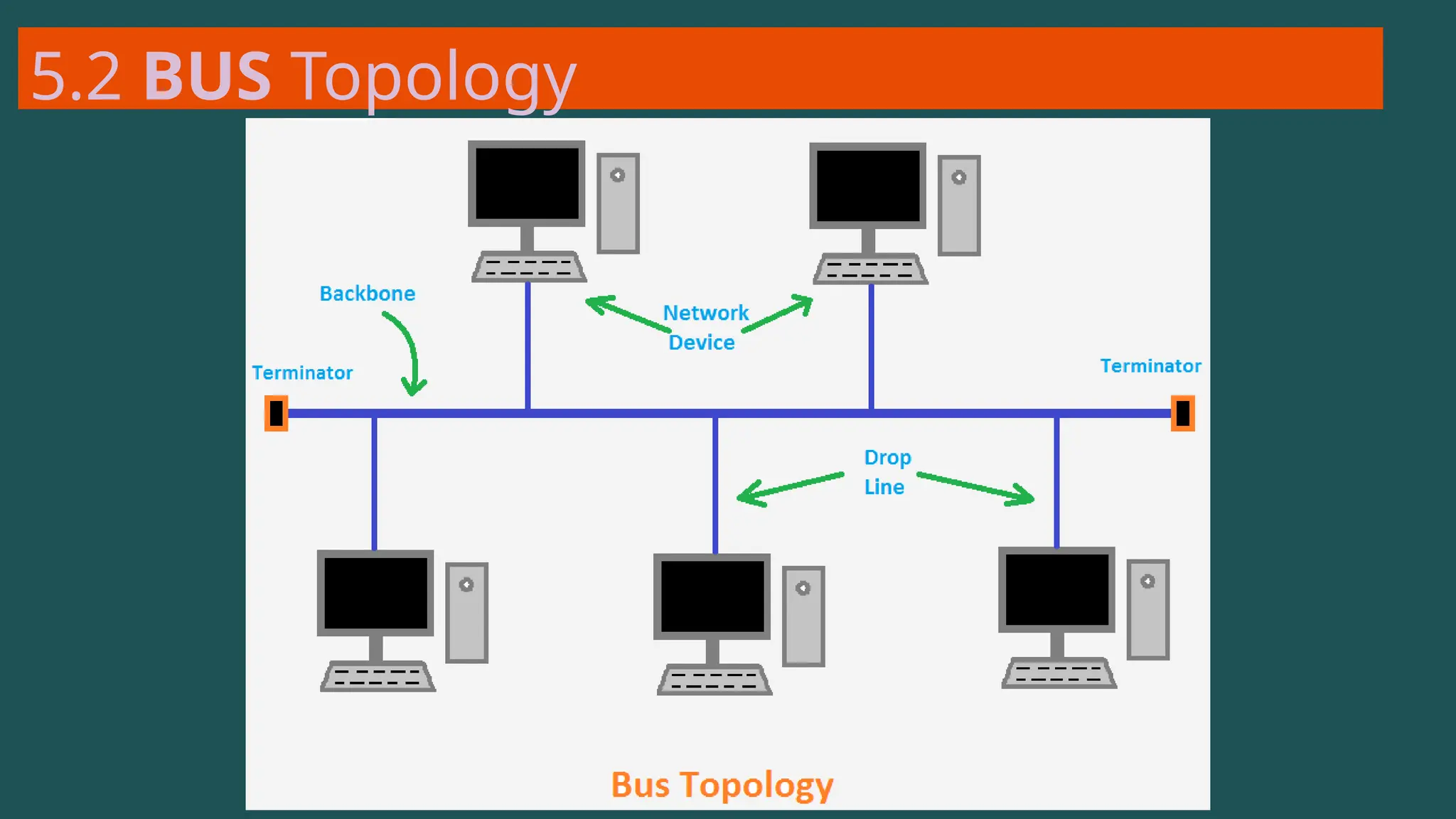
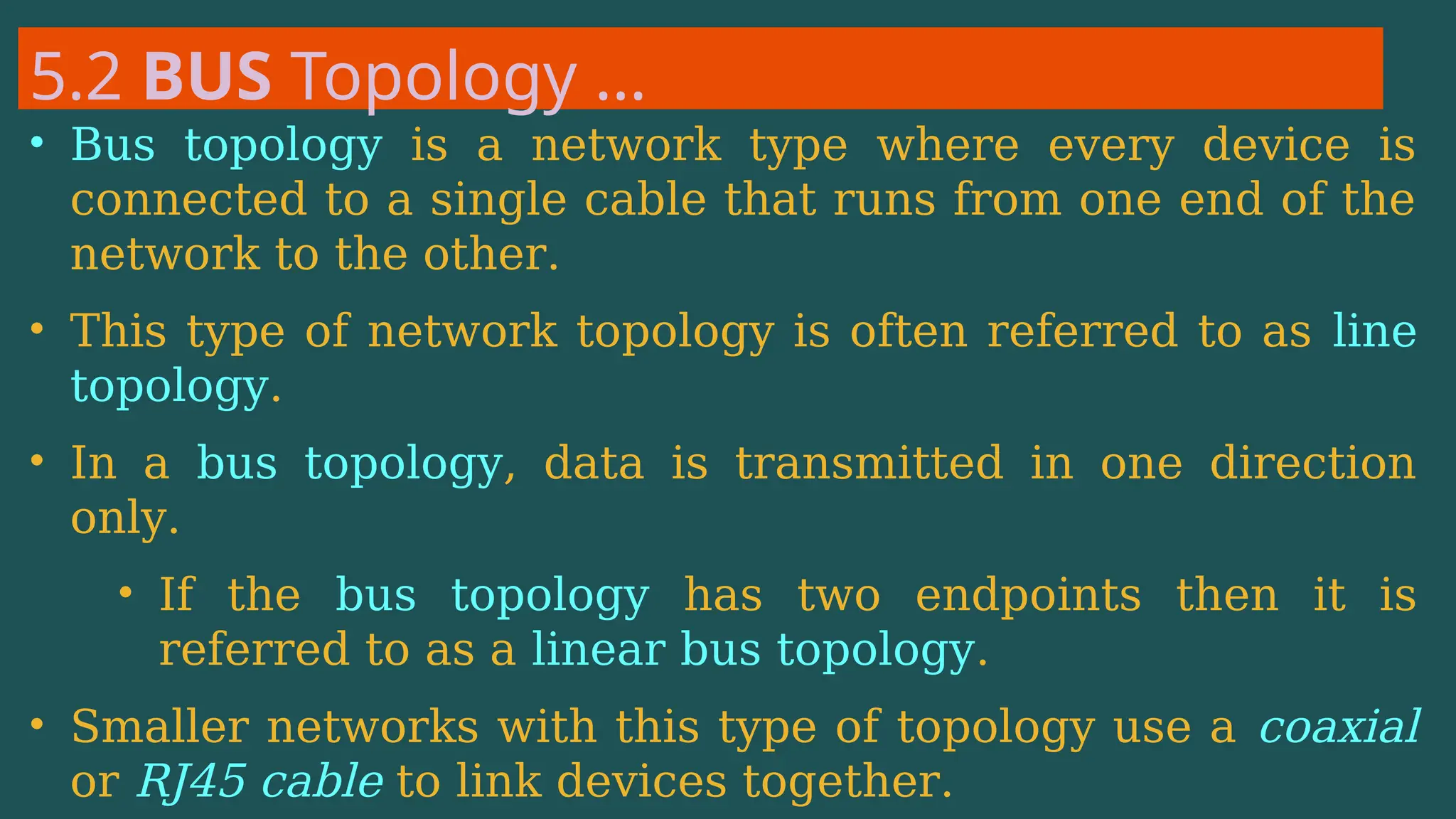
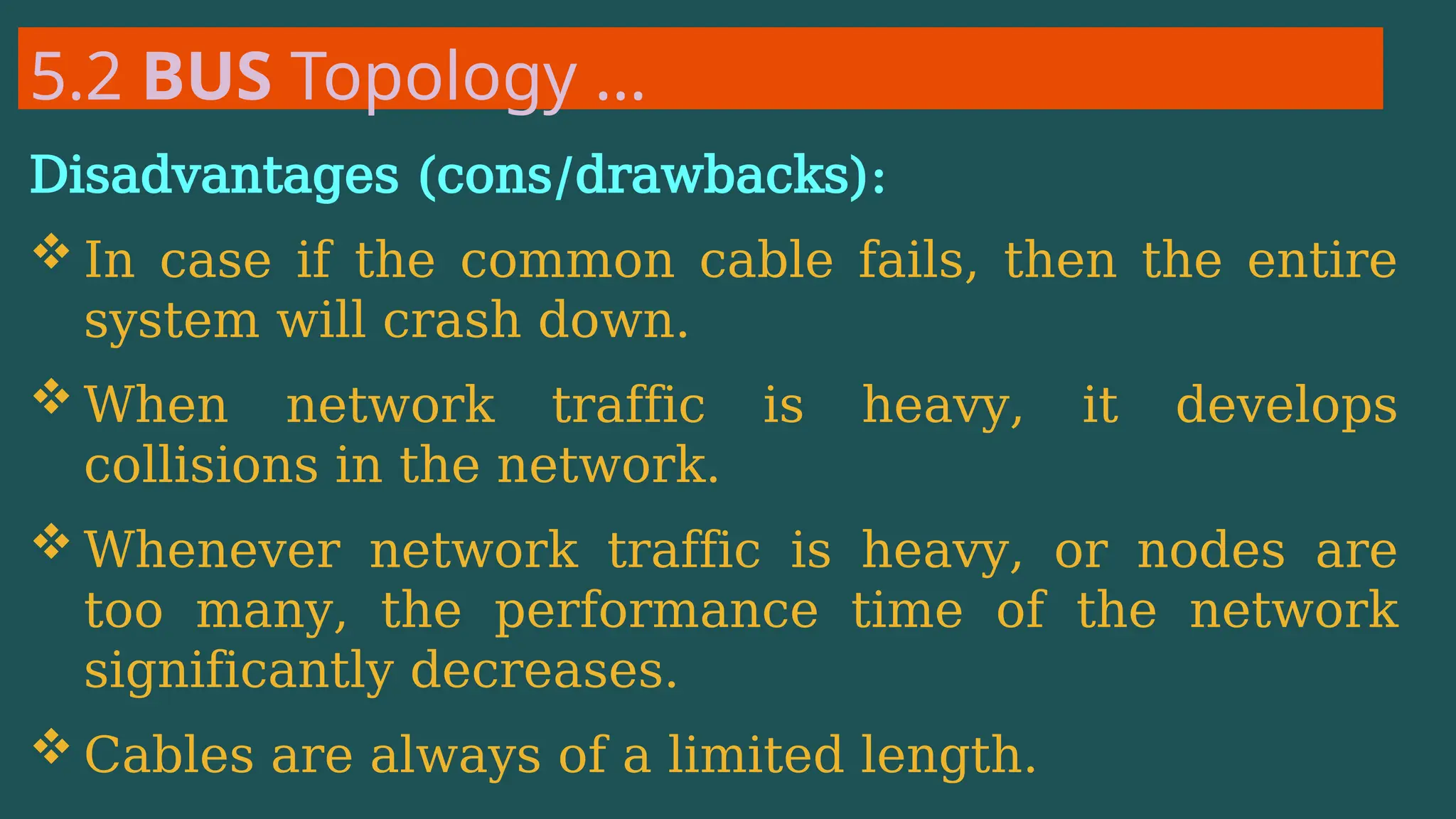
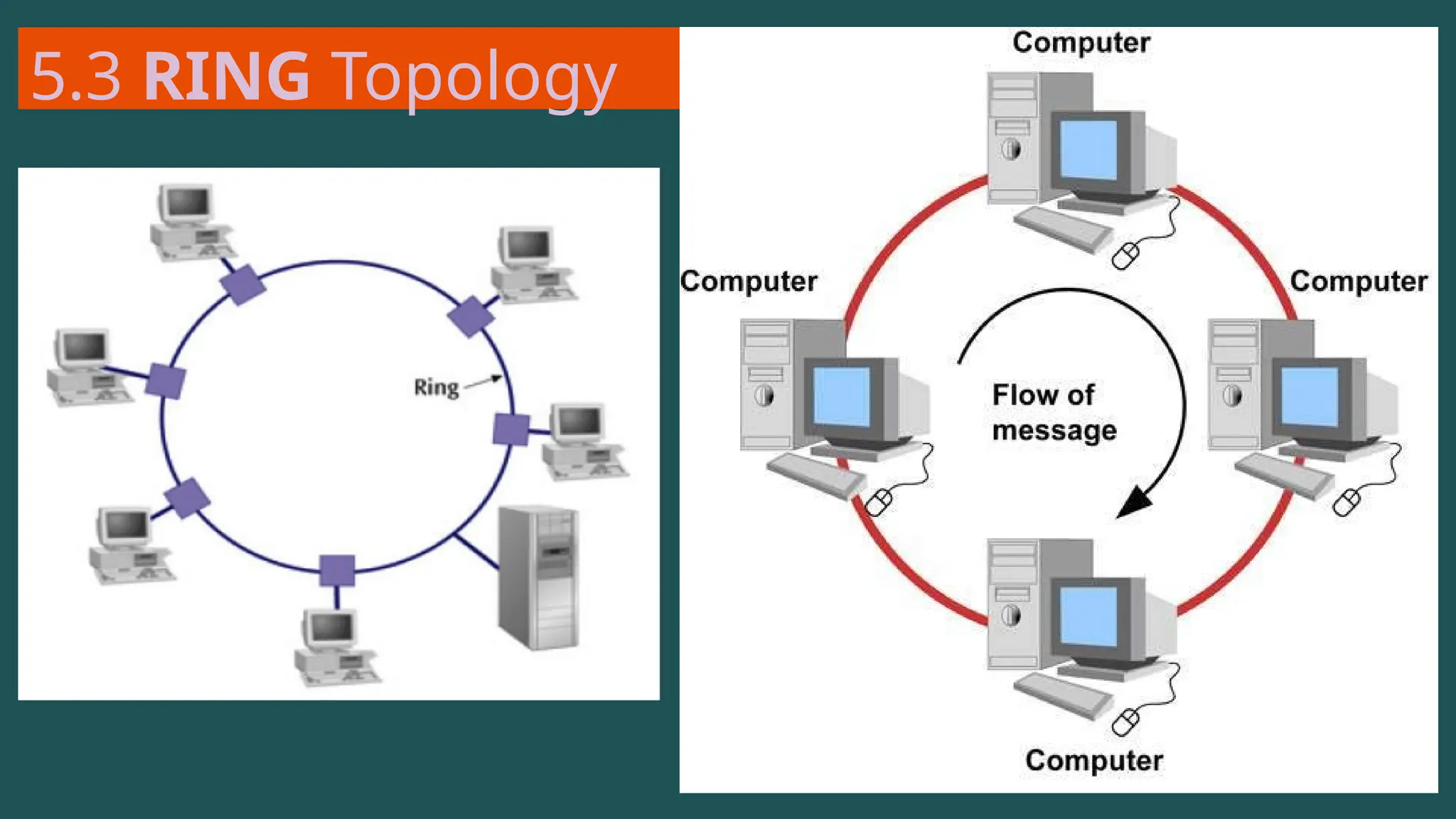
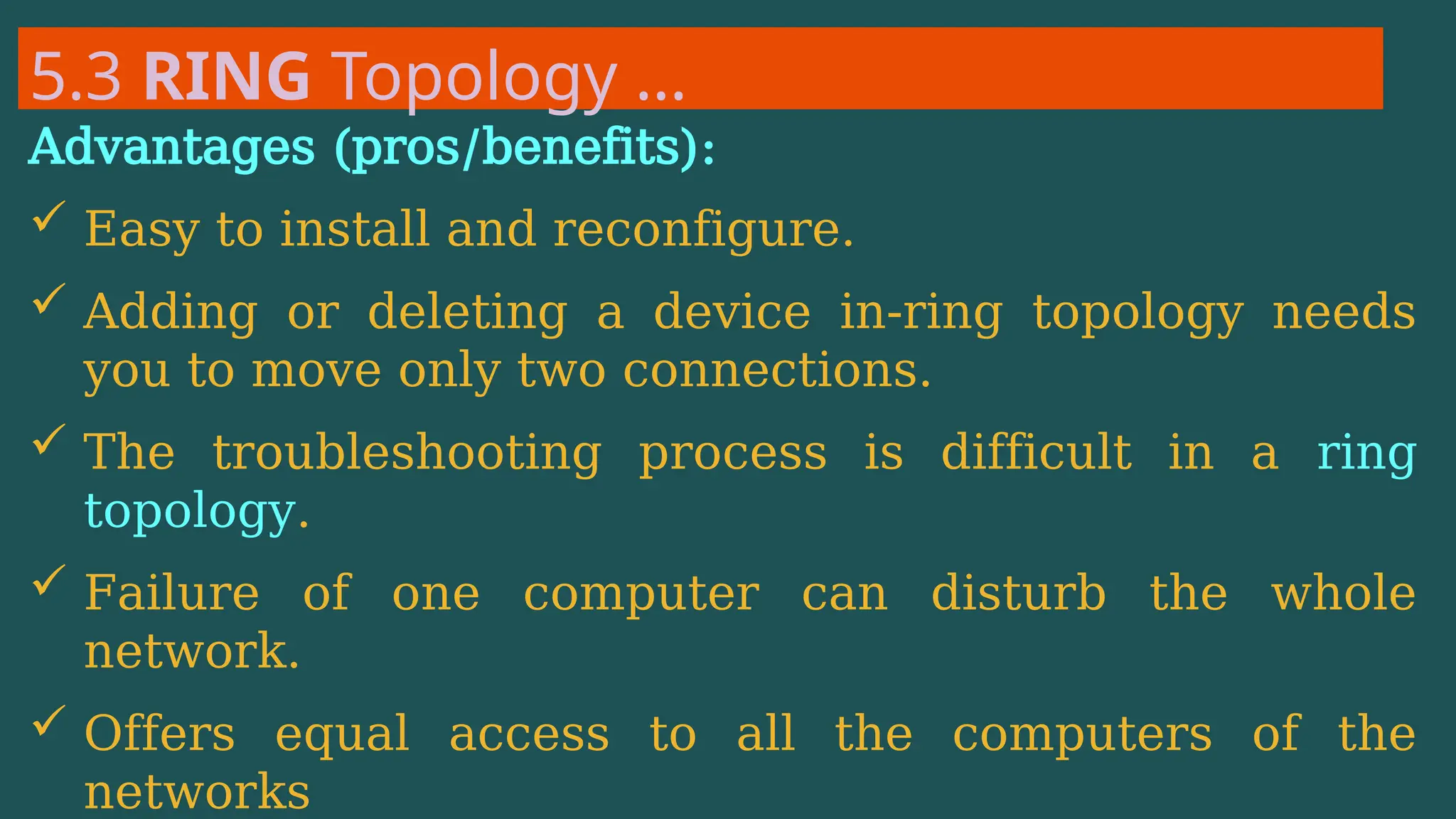
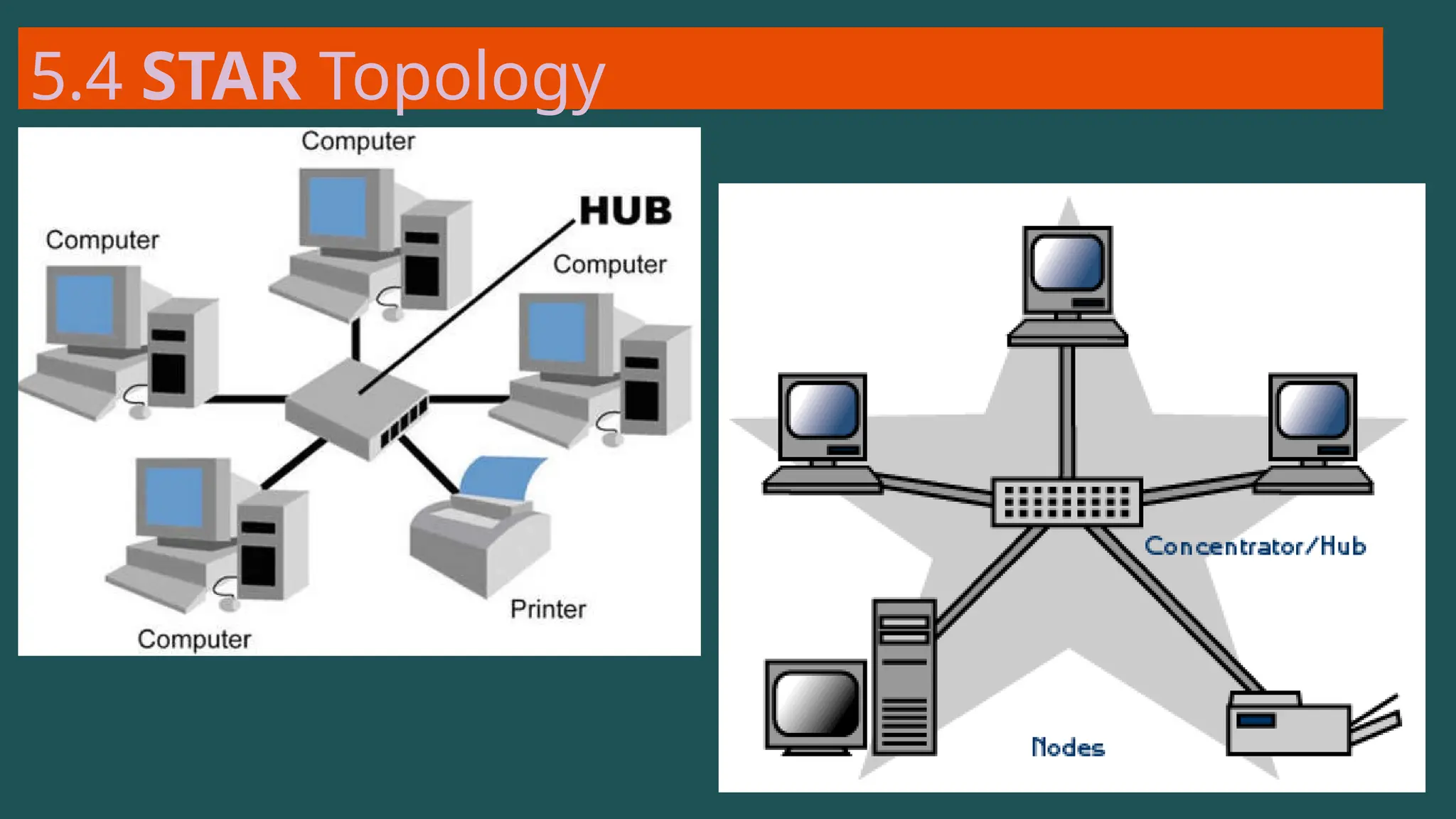
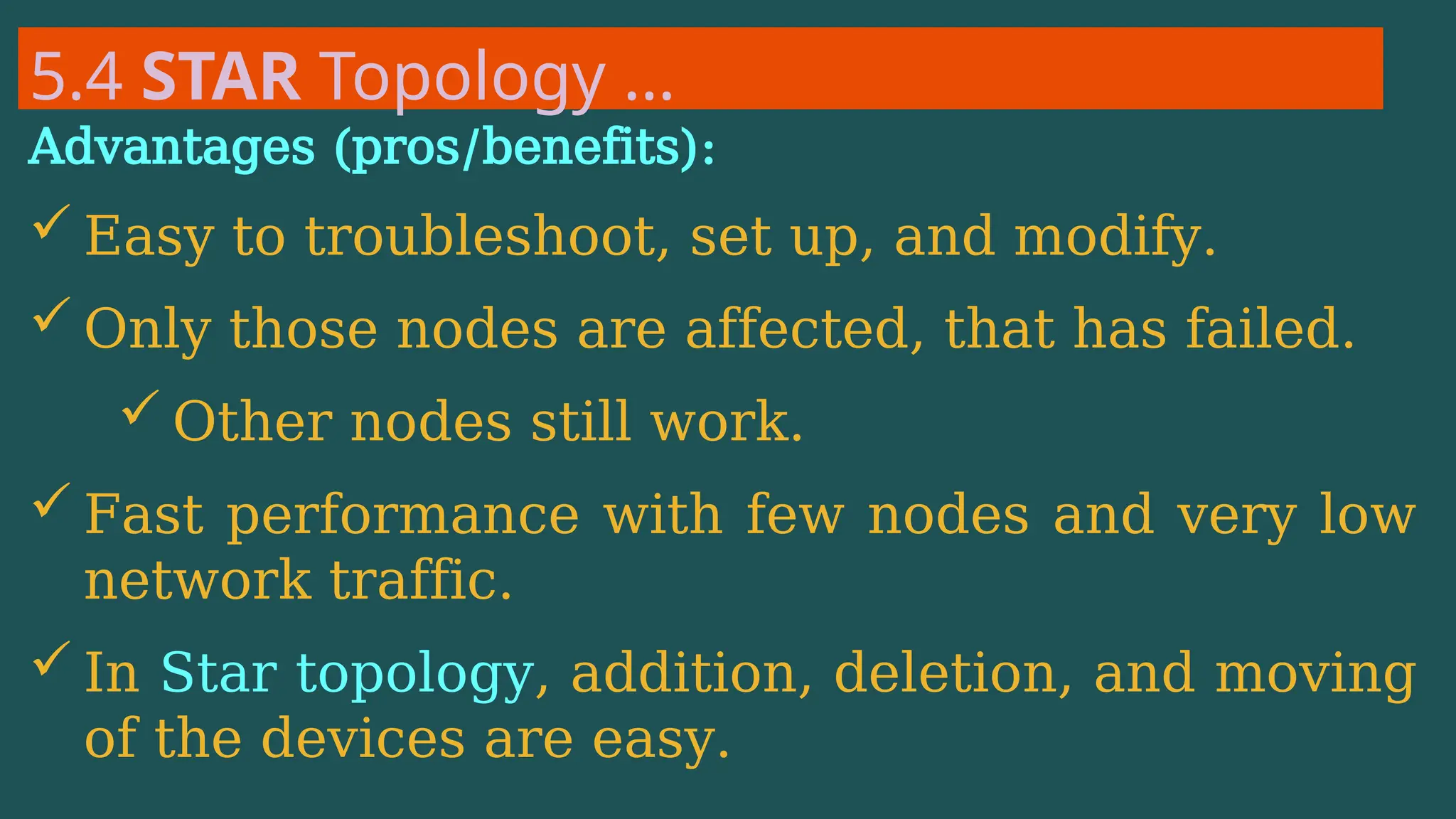
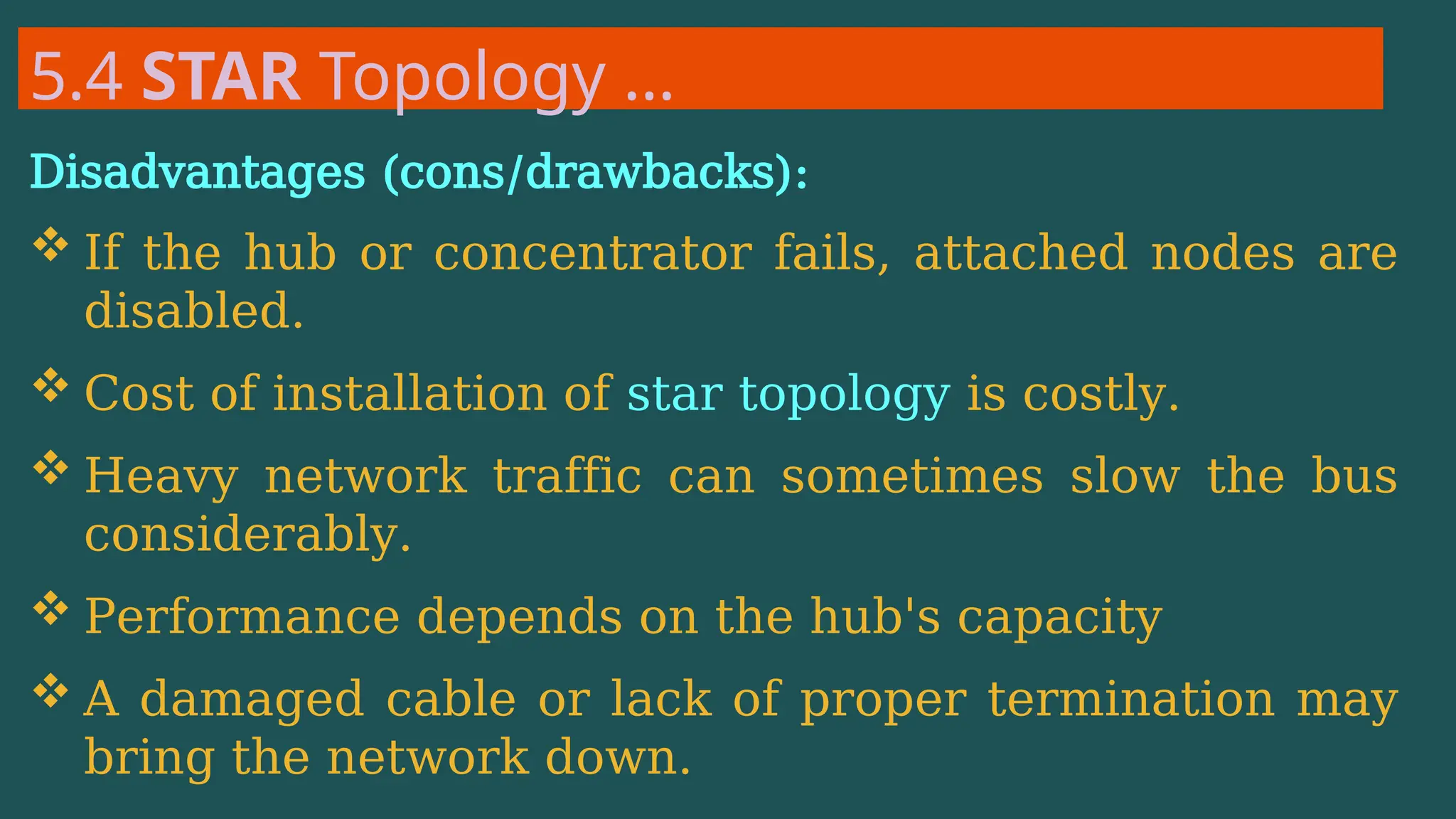
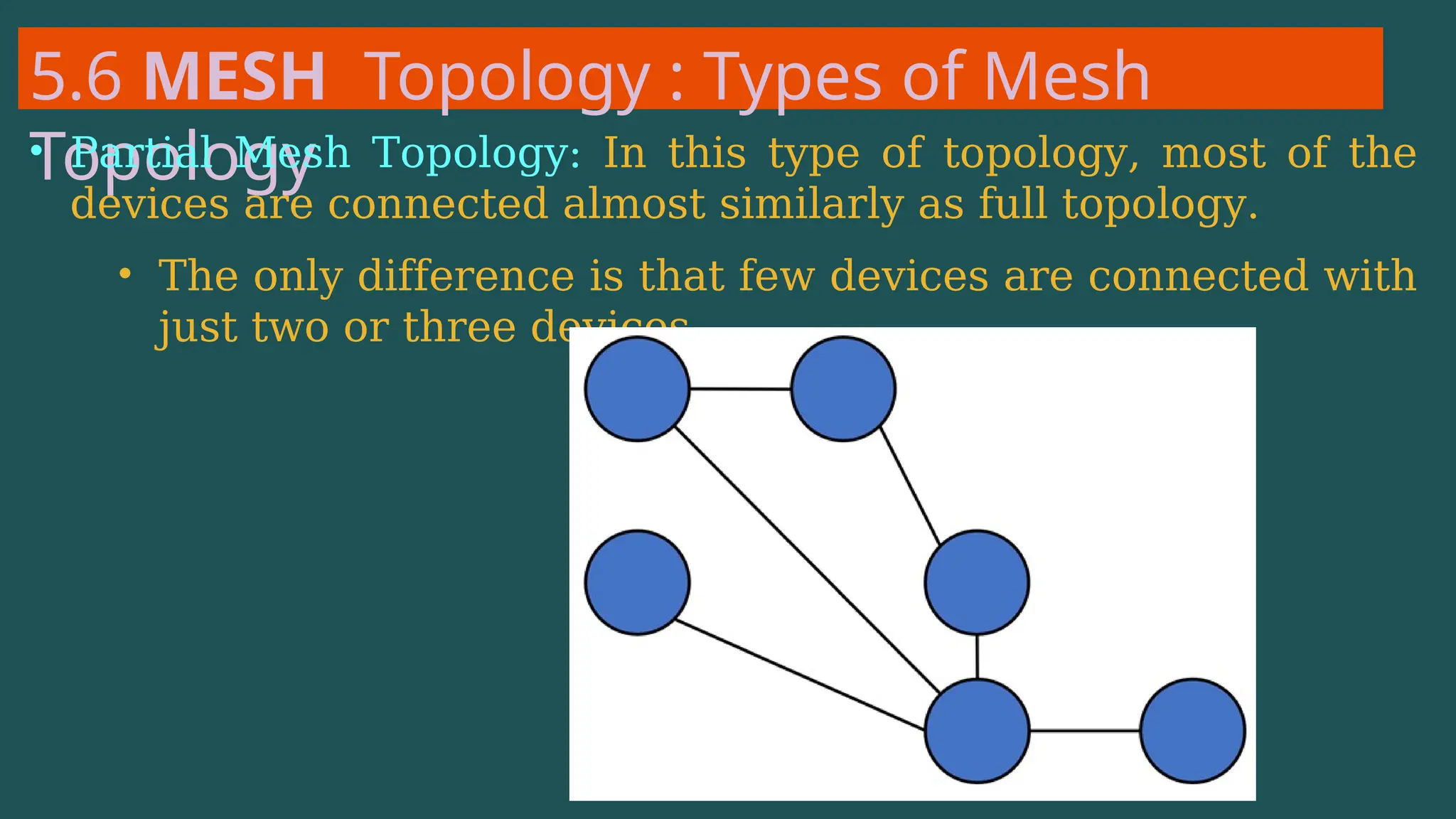
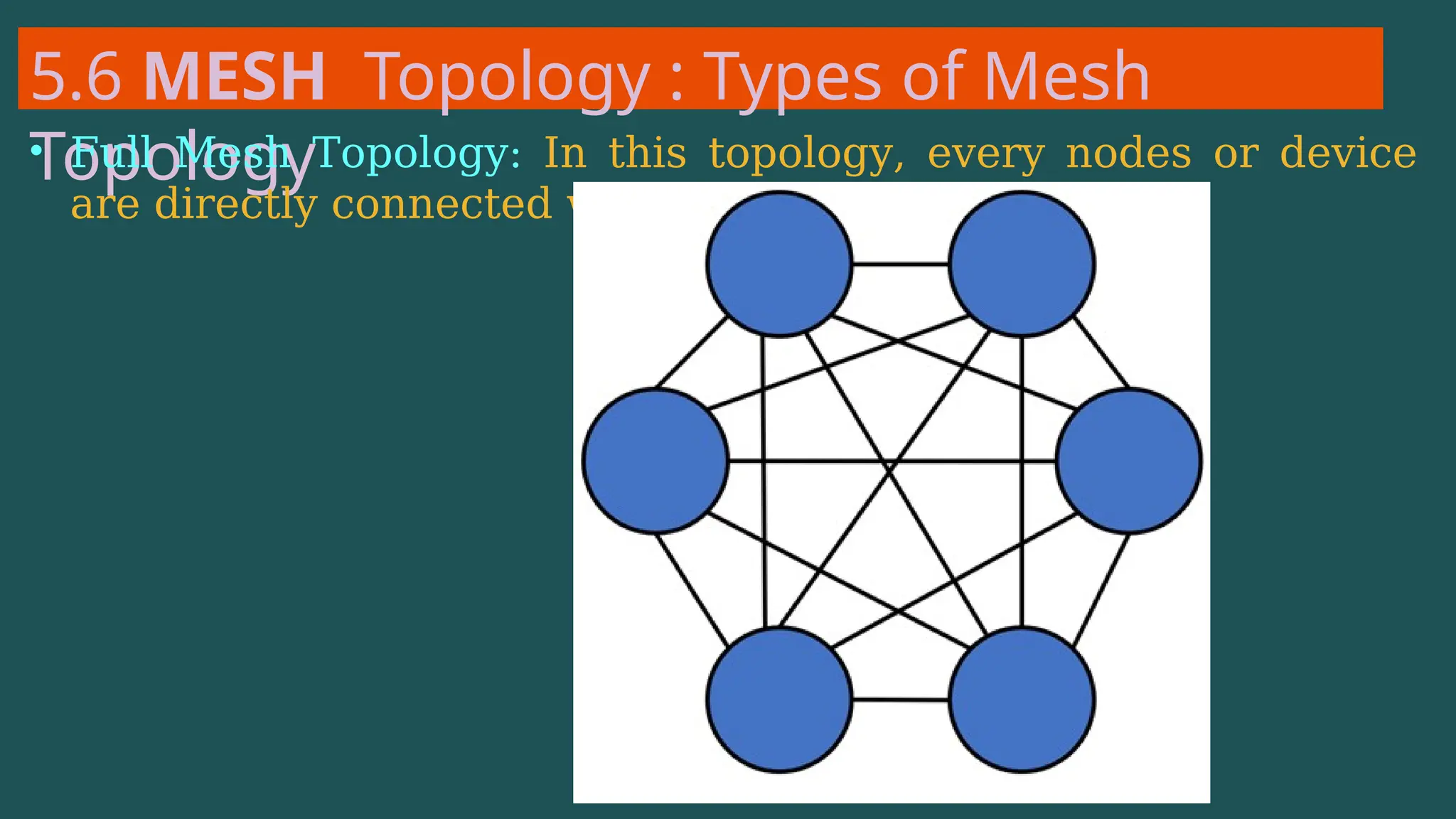
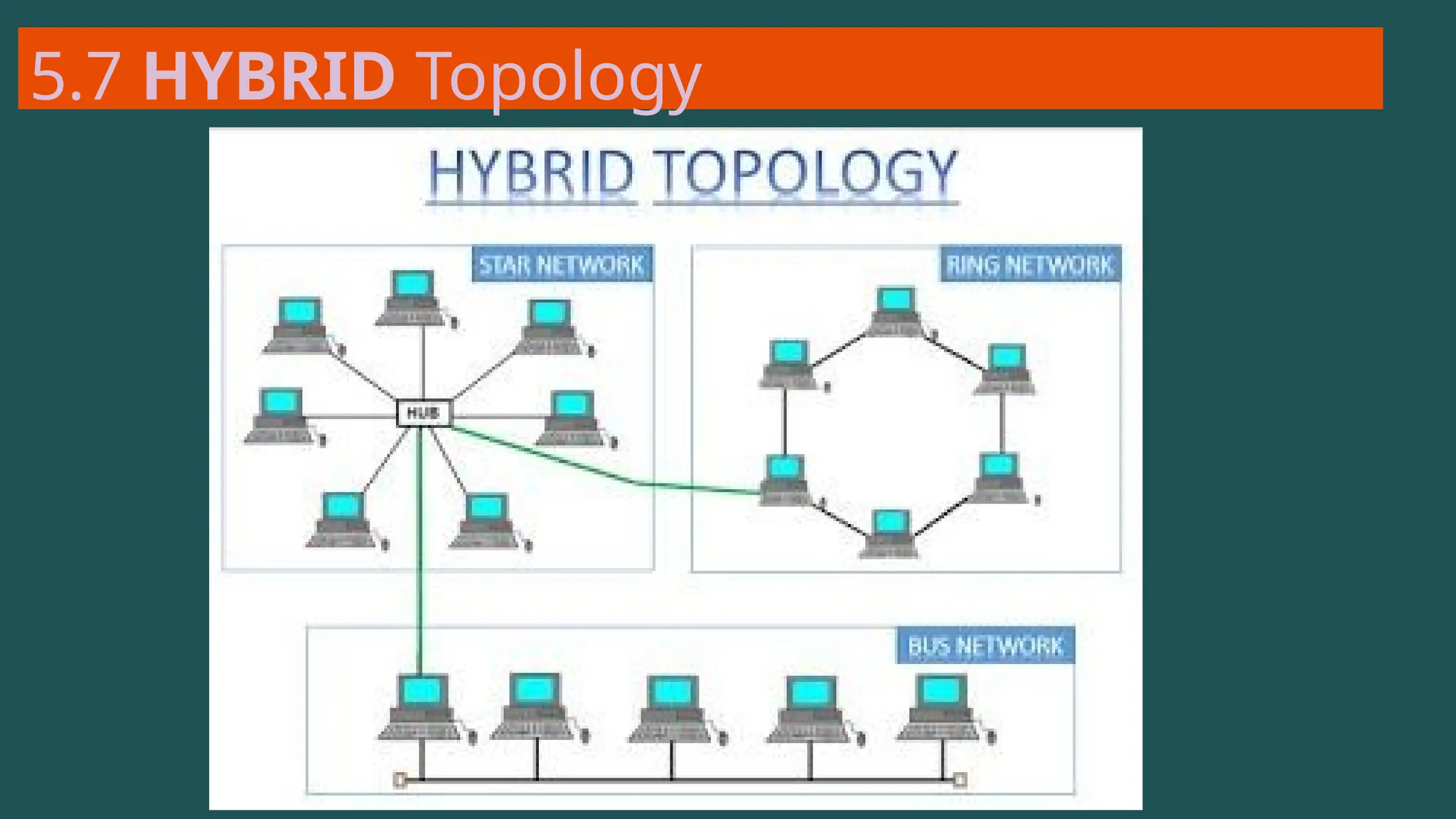
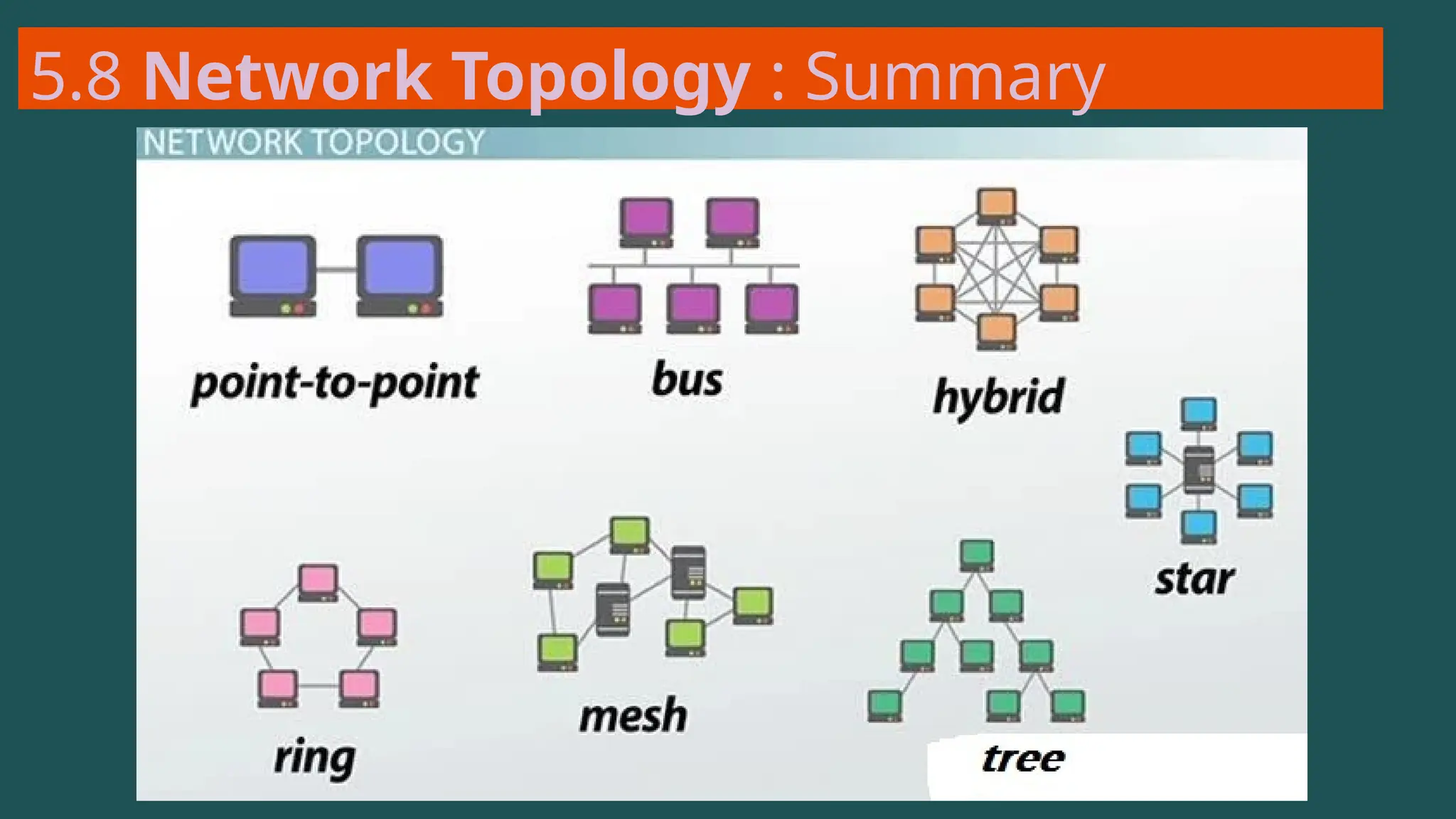
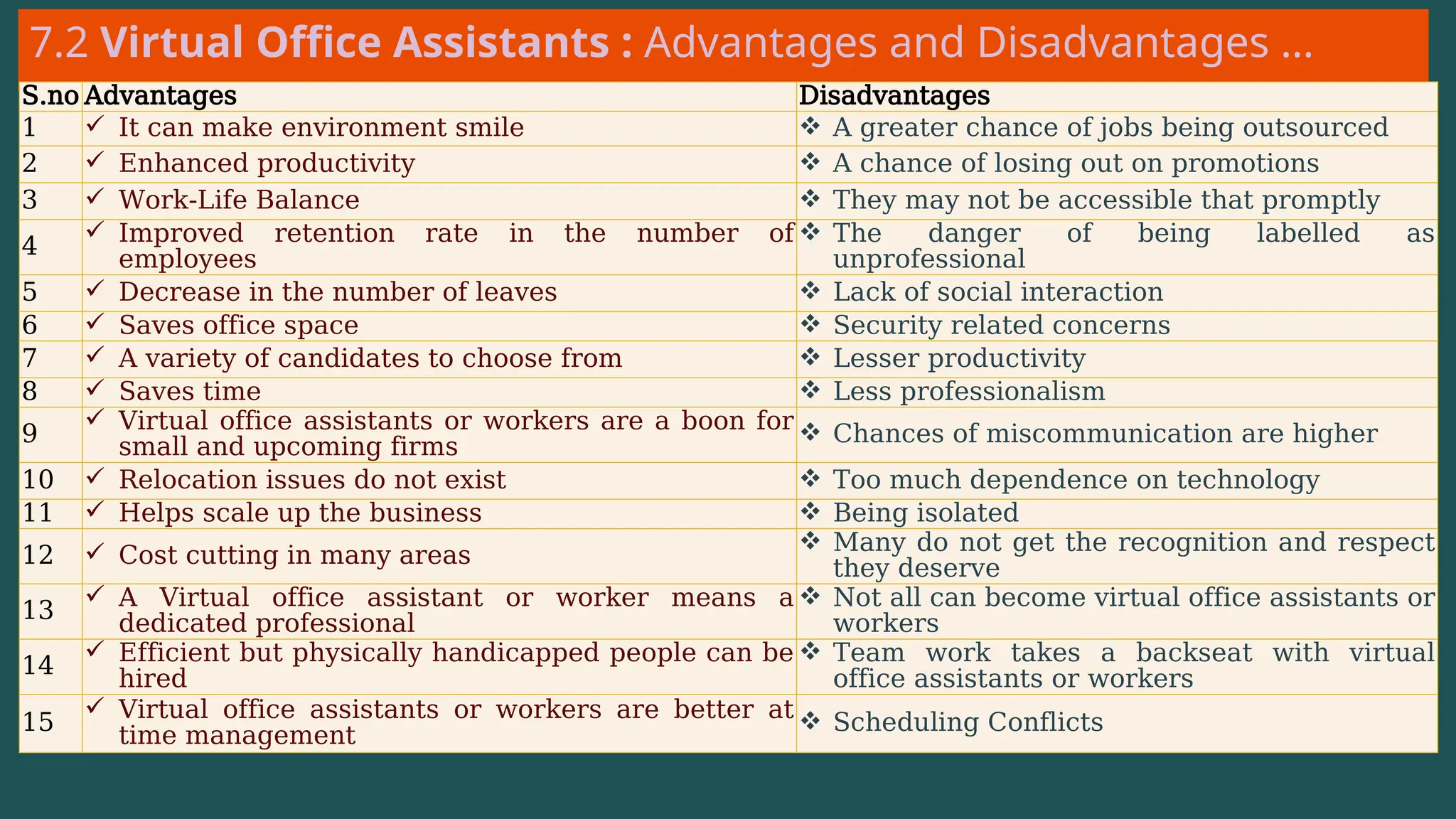
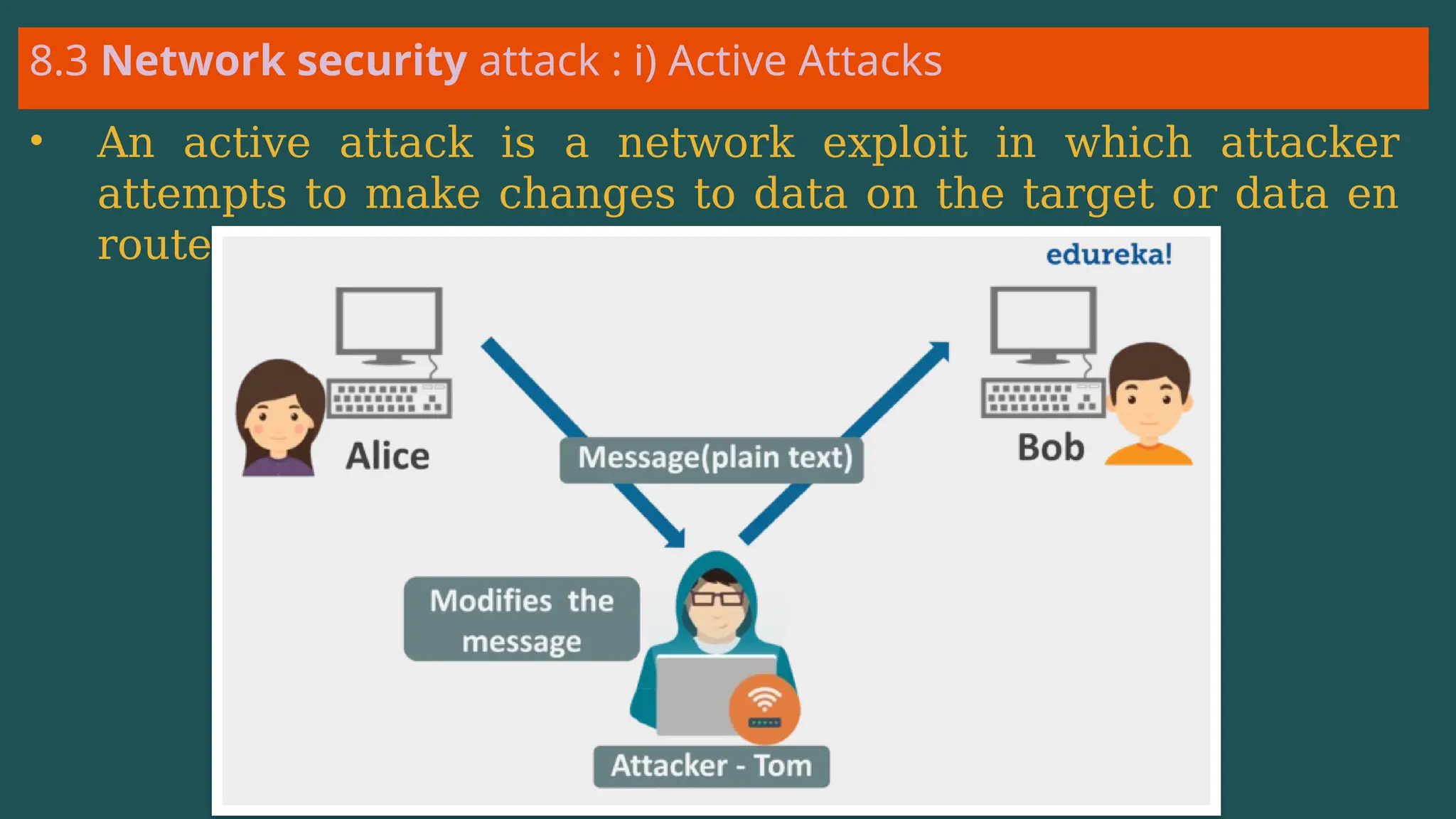
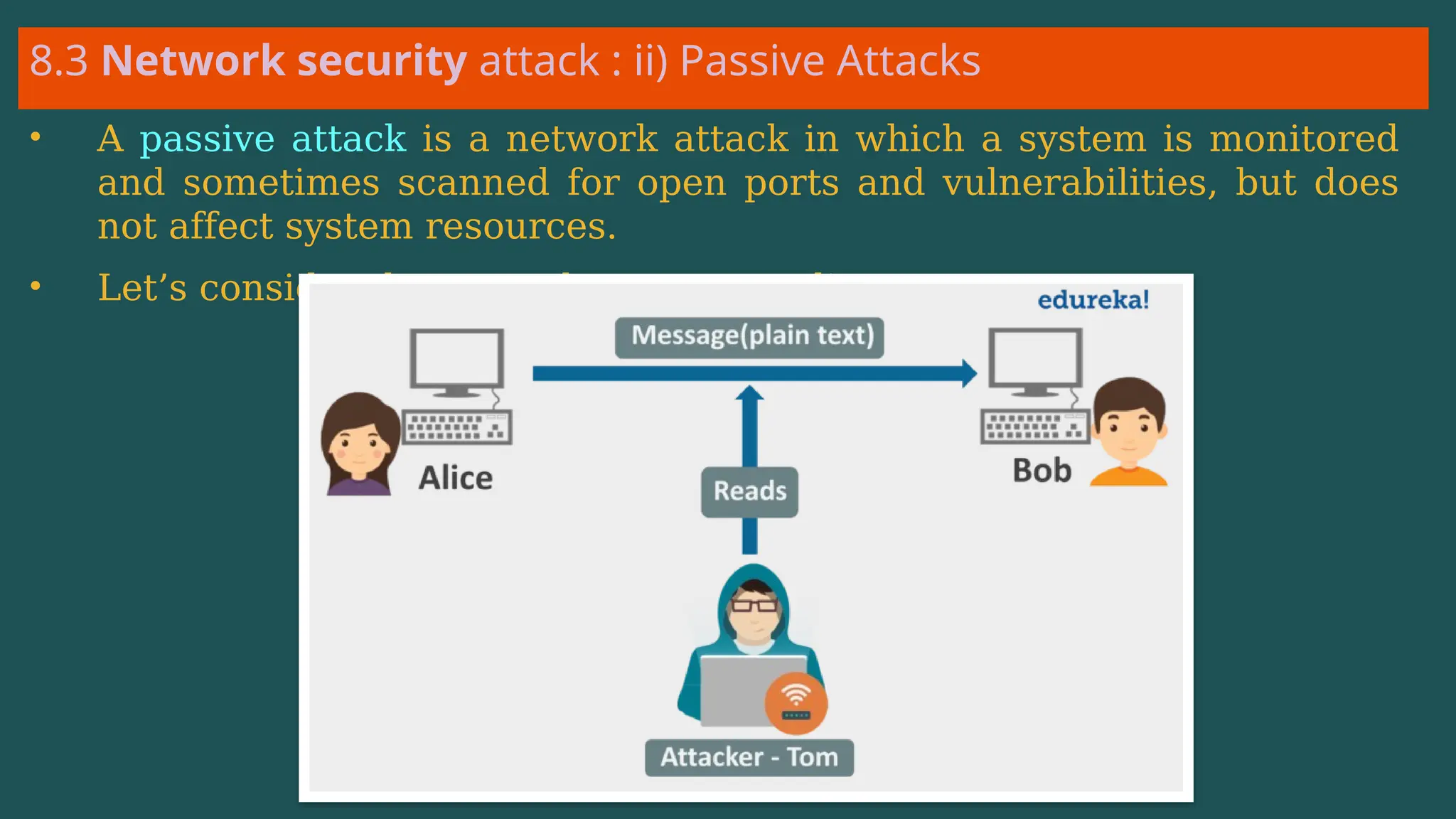
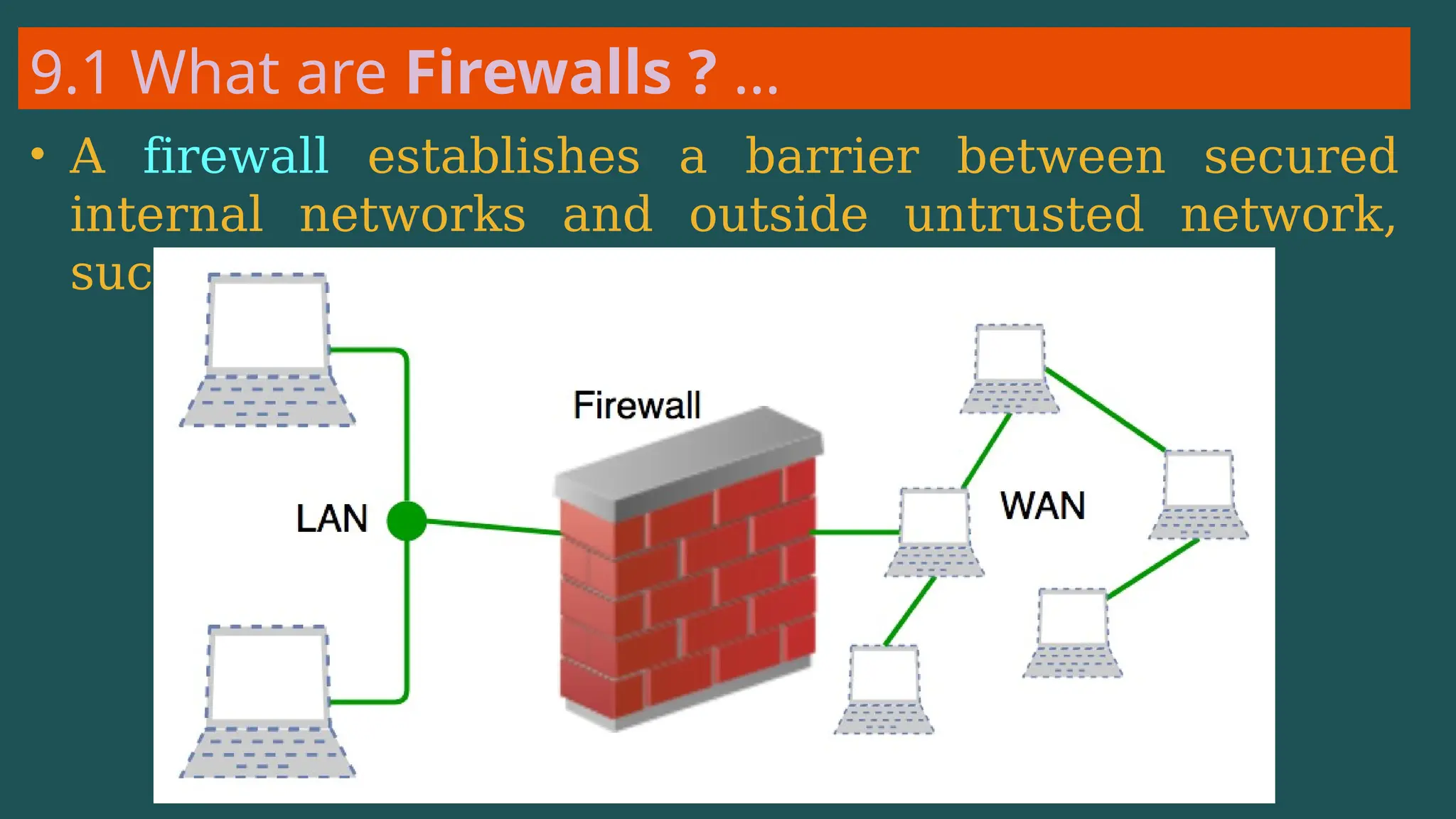
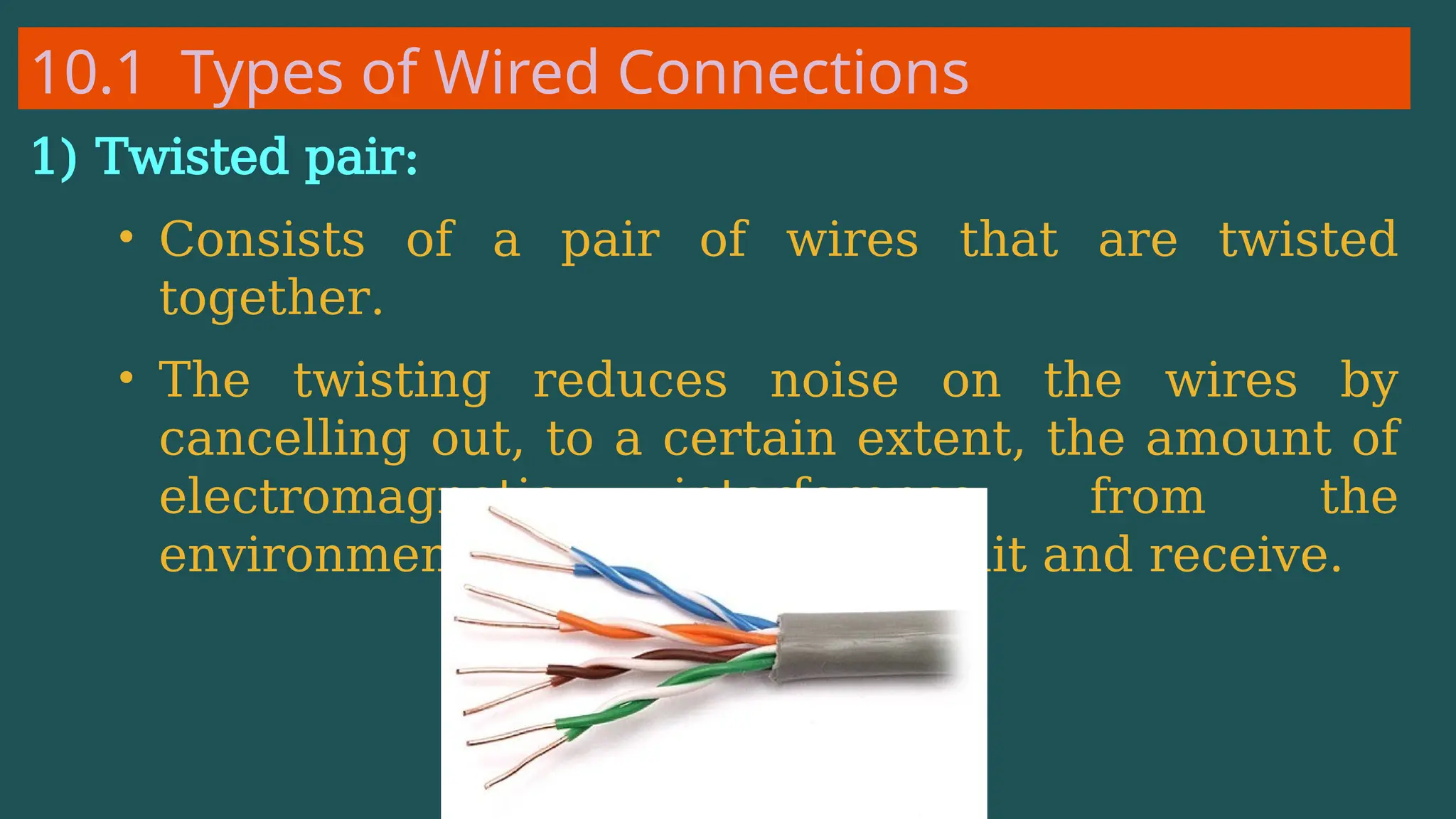
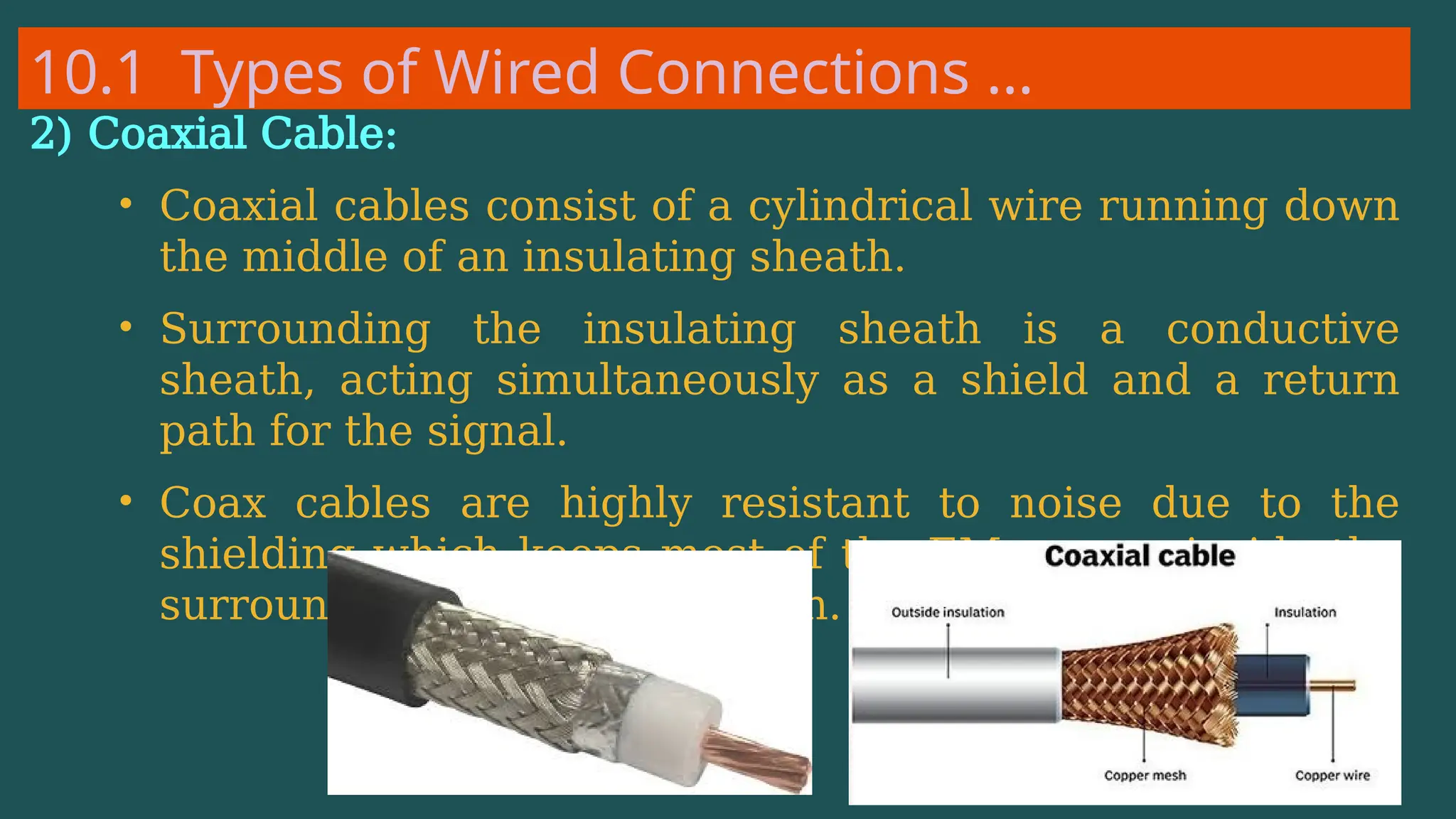
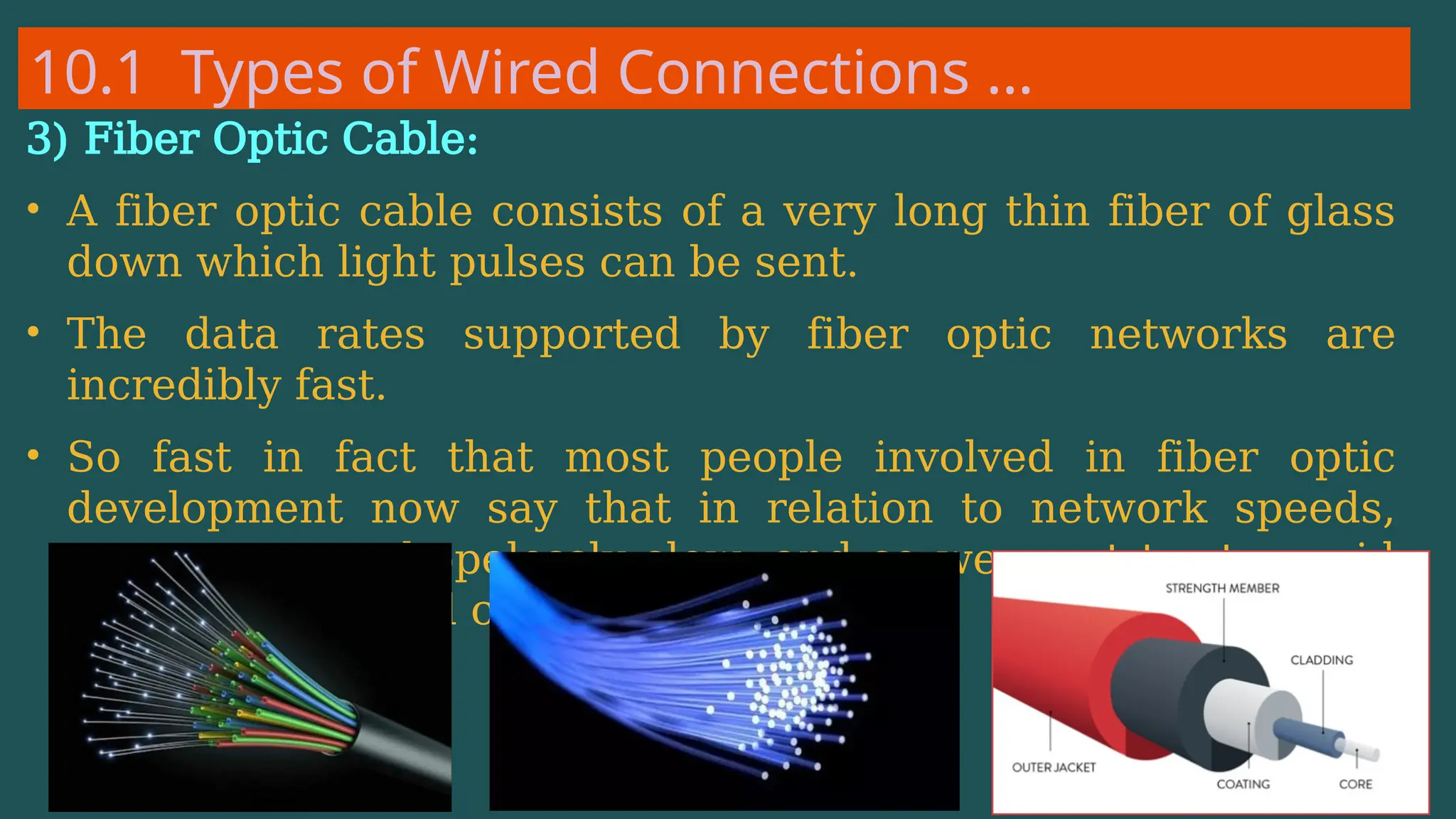
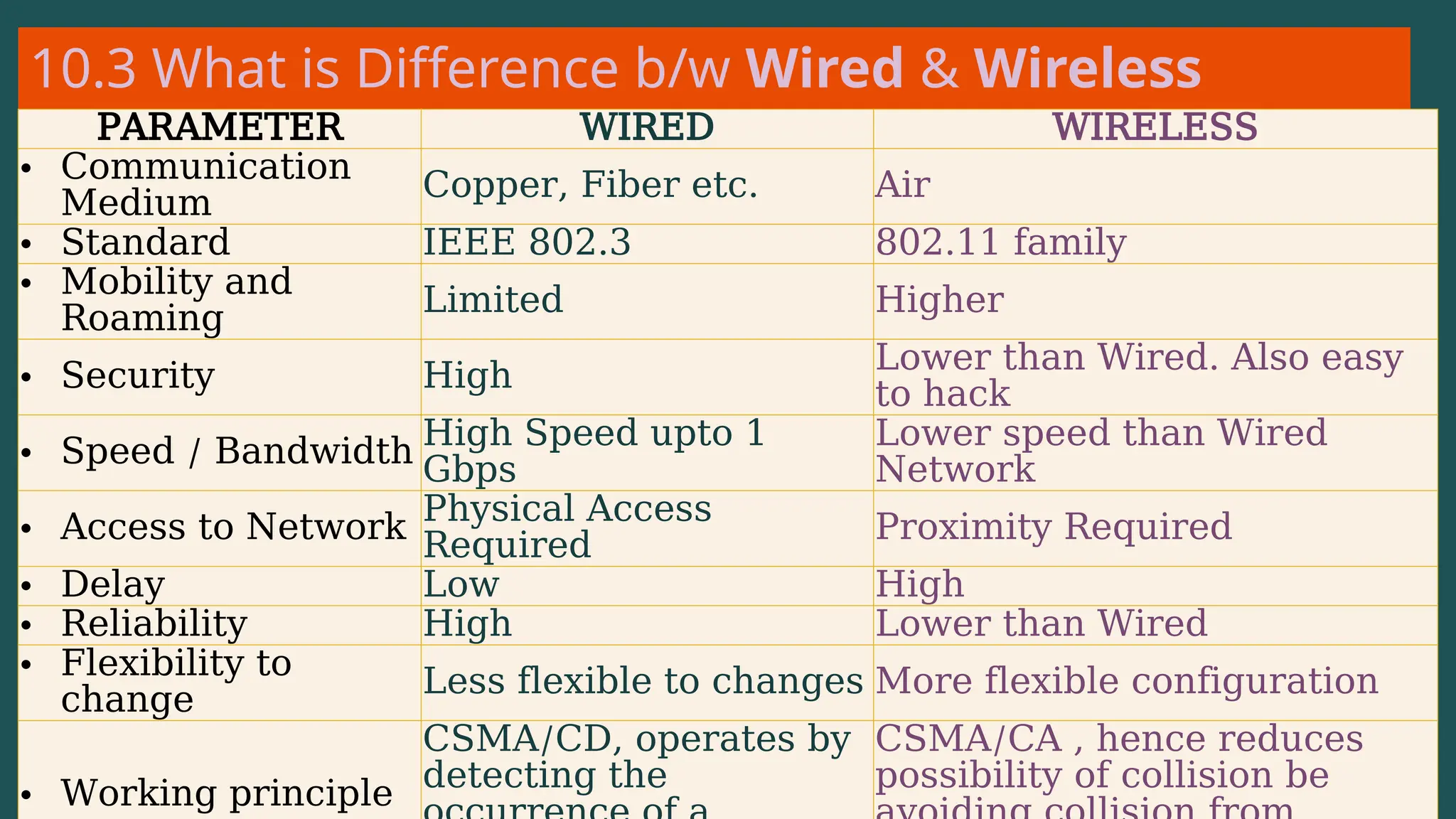
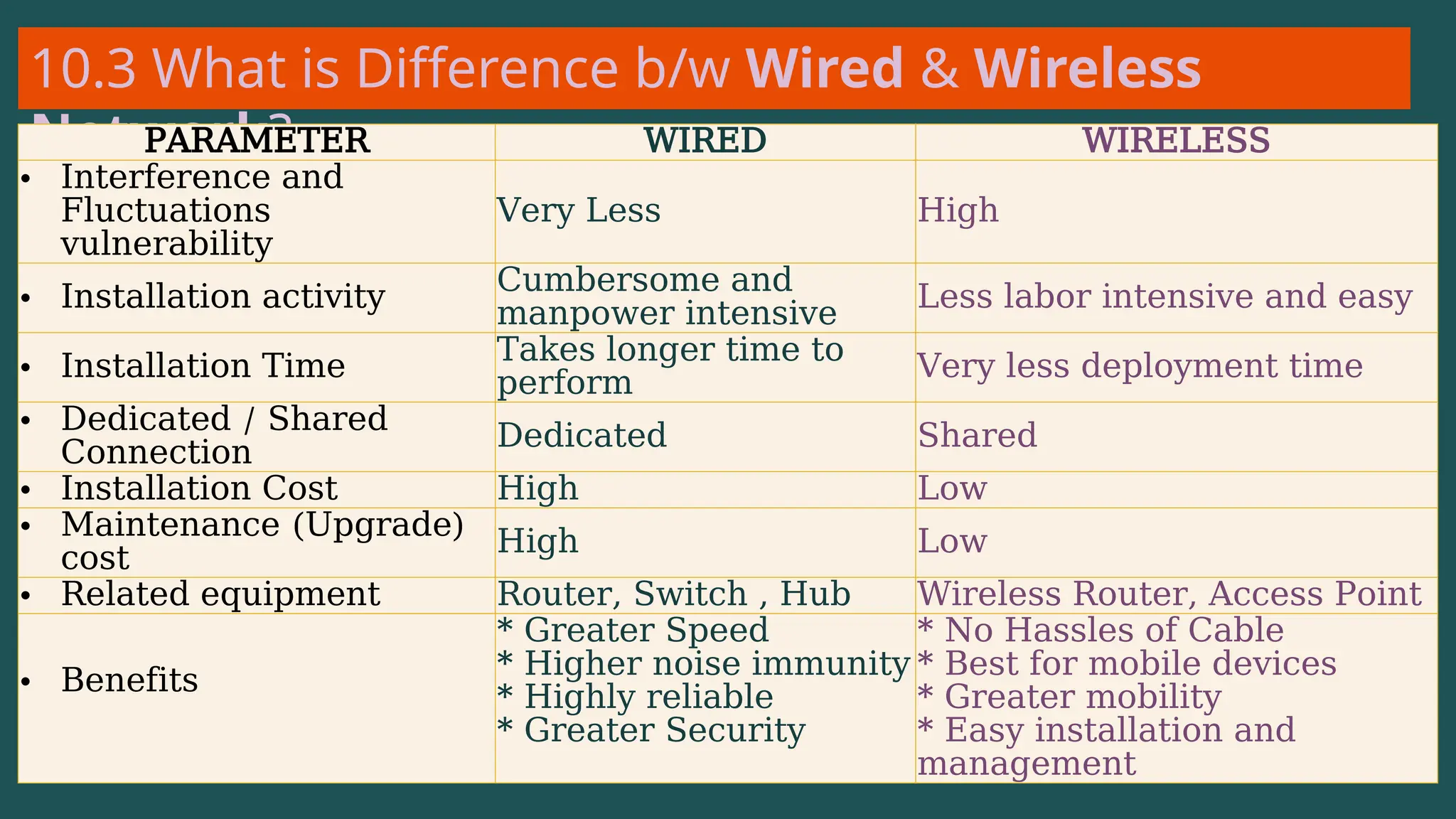
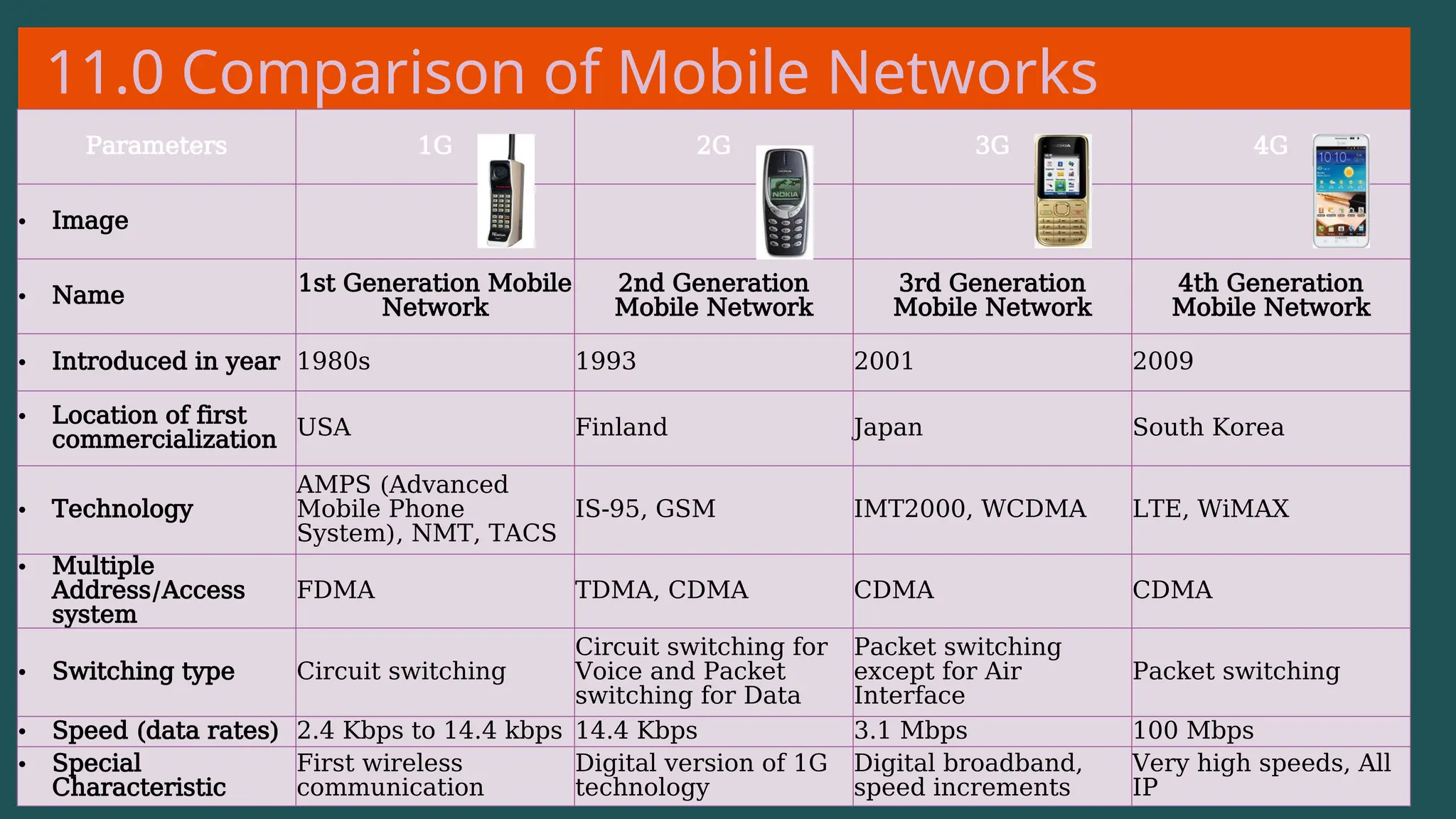
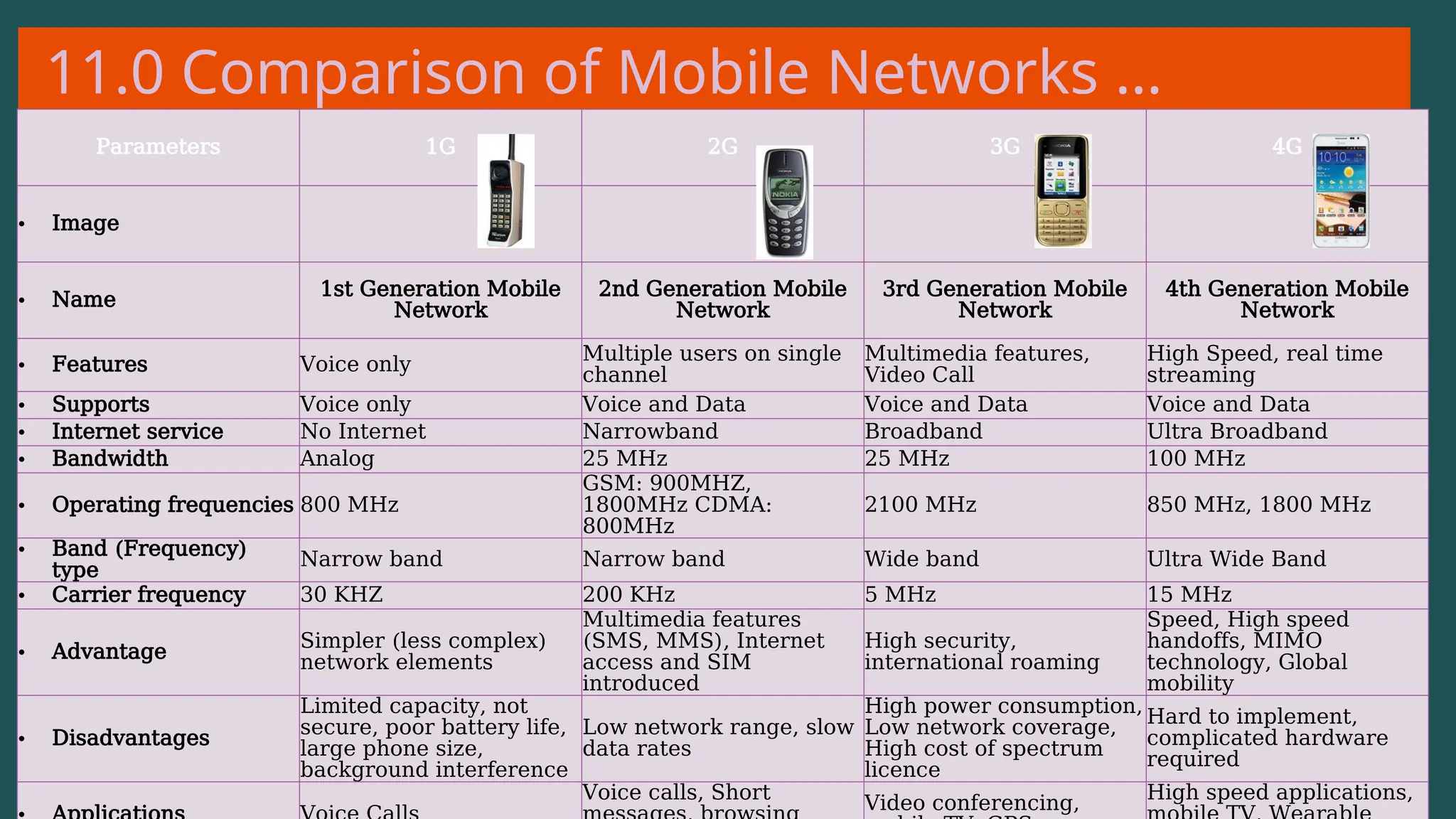
The document provides an overview of computer networking, defining it as a system of interconnected devices used for communication and resource sharing. It discusses types of networks including Personal Area Networks (PAN), Local Area Networks (LAN), Wide Area Networks (WAN), and Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN), as well as their advantages and disadvantages. Key components of computer networks, such as clients, servers, transmission media, and various protocols, are also explained.


![1.1 What is a Computer Network ?
• net·work: [net-wurk] – noun, a
system containing any combination
of computers, computer terminals,
printers, audio or visual display
devices, or telephones
interconnected by
telecommunication equipment or](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02thebasicsofcomputernetworking-240925103243-e525a37a/75/The-Basics-and-Understanding-of-Computer-Networking-pptx-3-2048.jpg)