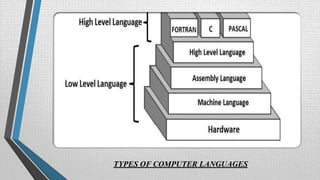
This document provides an overview of computer languages, differentiating between high-level and low-level languages, which serve as communication systems for programming computers. It describes high-level languages as easier to use and understand, offering advantages like portability, while low-level languages are closer to machine languages and offer greater speed and efficiency for hardware interactions. Additionally, it explains the functions of compilers, interpreters, assemblers, and translators in executing programming code.


















![Assembly language
• It uses mnemonic codes(short forms) for instruction and
allows the
• programmer to introduce names for blocks of memory
that hold data.
• Assembly language is designed to be easily translated
into machine language.
• Examples:-
• MOV AL,1h;load all with immediate value1 SUB
• R0,R0,#1;Decrement R0
• MUL R0,R1,R2
• STR R0,[R1,#20]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerlanguages-200824194514/85/Computer-languages-20-320.jpg)








