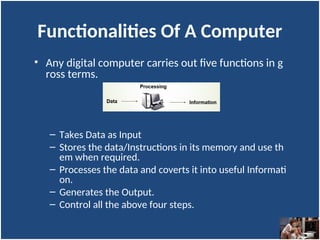
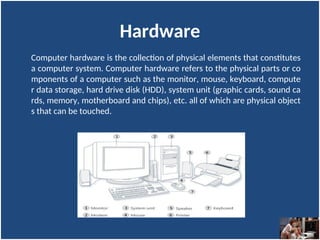
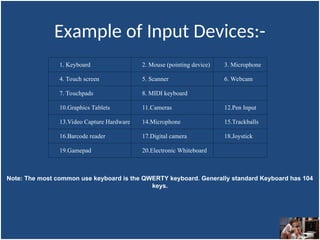
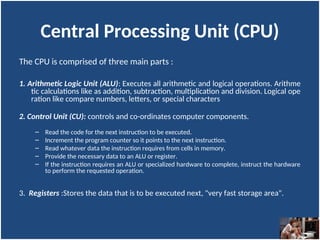
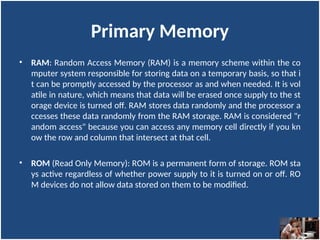
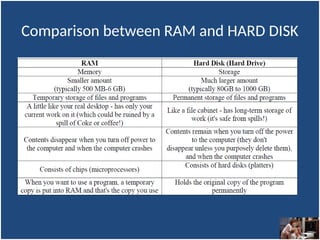
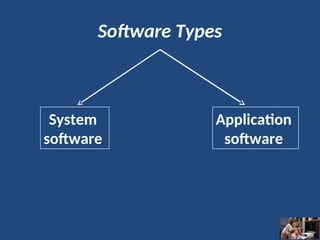
A computer is an electronic device that inputs, processes, outputs, and stores data under control of instructions stored in its memory. It consists of hardware (physical components) and software (organized collections of data and instructions), including system software for basic functions and application software for specific tasks. Key components include the CPU, RAM, ROM, and input/output devices, with storage types categorized as primary (temporary) and secondary (permanent).